Figure 1. Intracellular signaling involved in mediating the osmotic expression of the NFAT5 gene in RPE cells. The level of NFAT5 mRNA was determined with real-time reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR analysis in cells cultured 6 h in iso- (control) and hyperosmotic
(+100 mM NaCl) media. A: Involvement of intracellular signal transduction pathways. The following blocking agents were tested: the inhibitor of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation, SB203580 (10 µM); the inhibitor of extracellular signal–regulated kinases
1 and 2 (ERK1/2) activation, PD98059 (20 µM); the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), inhibitor SP600125 (10 µM); and the inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)-related kinases,
LY294002 (5 µM). Vehicle controls were made with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; 0.1%) and NaOH (1 M; 1:150). B: Involvement of protein kinase activities and calcium signaling. The following blocking agents were tested: the inhibitor
of protein kinase C α/β (PKCα/β), Gö6976 (1 µM); the protein kinase A (PKA) inhibitor, H-89 (1 µM); the inhibitor of Src tyrosine
kinases, PP2 (100 nM); the calpain inhibitor, PD150606 (100 µM); the serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK) inhibitor
GSK650394 (GSK; 1 µM); the cell-permeable calcium chelator, BAPTA/AM (5 µM); the phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ) inhibitor, U73122
(4 µM); and the inositol triphosphate (IP3) receptor inhibitor, 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB; 100 µM). Means ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 3–7 independent
experiments using cell lines from different donors. Significant difference versus unstimulated control: *p<0.05. Significant difference versus NaCl control: ●p<0.05.
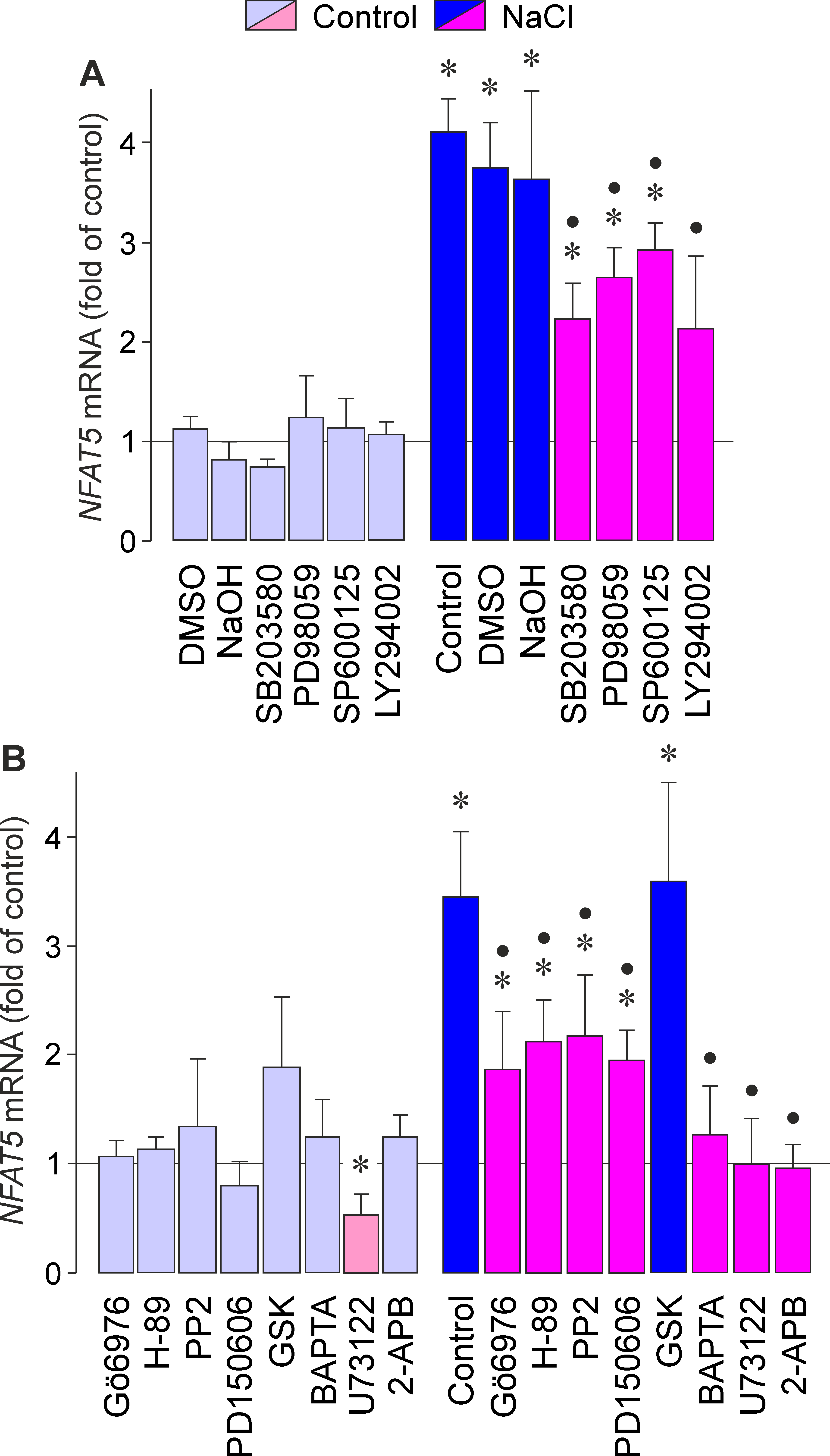
 Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2017; 23:116-130.
Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2017; 23:116-130.  Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2017; 23:116-130.
Figure 1 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2017; 23:116-130. 