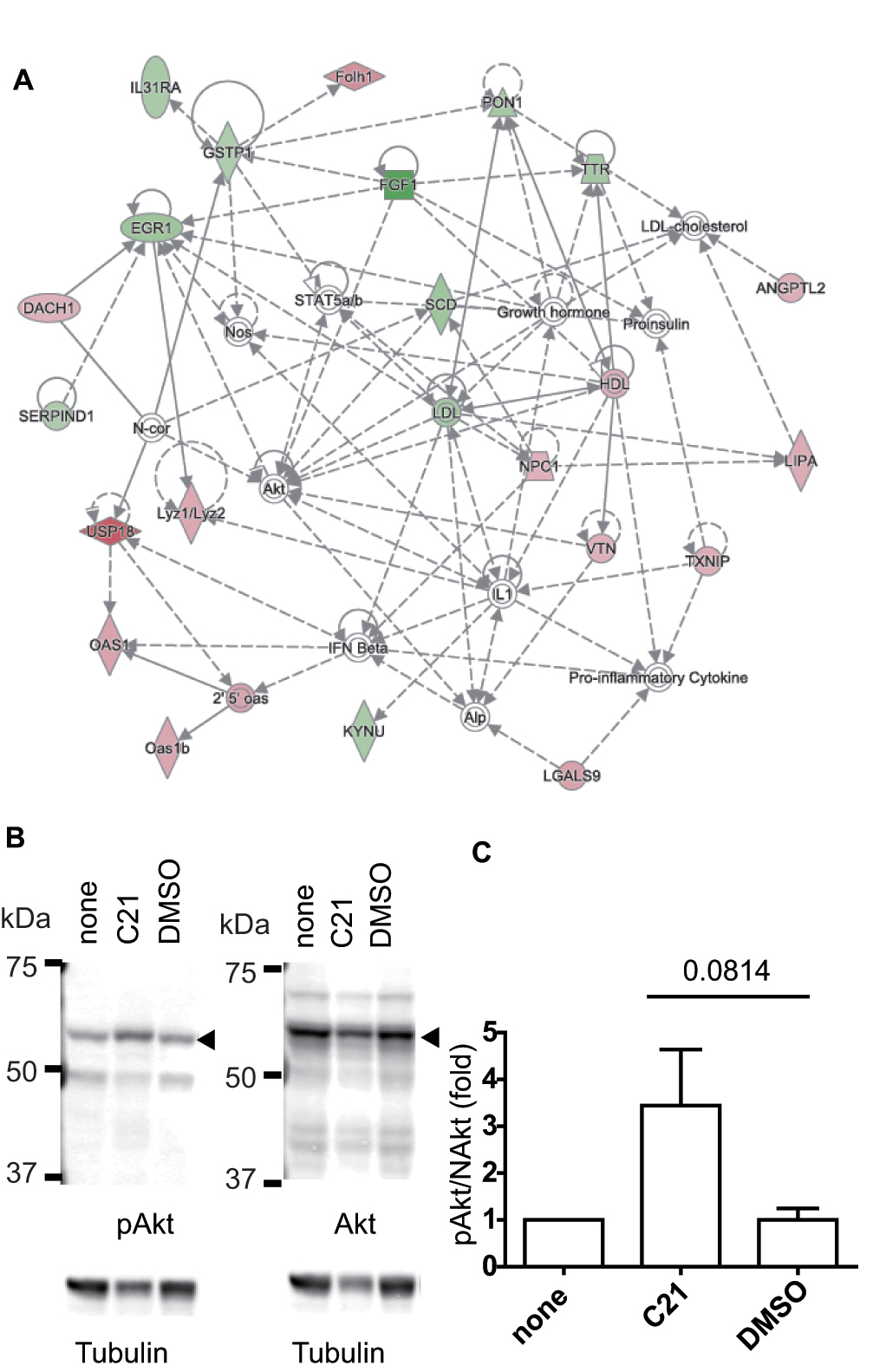
Figure 3. Network analysis and Akt phosphorylation upon Dock5 inhibition.
A: A network analysis of the affected gene expression in the lens epithelial cells (LECs) of rupture of lens cataract (RLC)
mice was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) software. In the second highest scored network in the LECs from
the RLC mice, “Lipid Metabolism, Molecular Transport, Small Molecule Biochemistry,” the protein–protein associations are shown
(for details, see
Figure 2A).
B: Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells were cultured on a plastic dish and treated with or without N-(3,5-dichlorophenyl)
benzenesulfonamide (C21) and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) for 48 h. The cells were washed and subjected to SDS–PAGE and western
blotting with the antibodies indicated at the bottom.
C: The intensity of the corresponding bands was quantified and the value of phosphorylated (cellular homolog of murine thymoma
virus akt8 oncogene, also called protein kinase B) Akt/total Akt was normalized by the value of the cells without drug treatment
(denoted as “none”). The graph shows the averages from five independent experiments with the standard error of the mean (SEM),
and the
p value (0.0814) was calculated using the
t test. The average ± SEM values were 3.44 ± 1.20 for C21 and 1.00 ± 0.25 for DMSO.
 Figure 3 of
Xu, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1081-1092.
Figure 3 of
Xu, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1081-1092.  Figure 3 of
Xu, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1081-1092.
Figure 3 of
Xu, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1081-1092.