Figure 1. Zebrafish nocturnin-a and nocturnin-b are similar to frog and mammalian nocturnin genes. A: An unrooted phylogenetic tree of nocturnin proteins suggests zebrafish nocturnin-b is more similar to frog nocturnin than nocturnin-a. The scale bar represents 5% estimated sequence divergence. B: An alignment of the amino acid sequences of the nocturnin homologs of human, mouse, Xenopus laevis, and zebrafish revealed high conservation: Identical amino acid residues between different nocturnin homologs are highlighted
in gray. The deadenylation catalytic domain is boxed. C: An reverse transcription (RT)-PCR analysis with two primer pairs for each zebrafish nocturnin gene showed that nocturnin-b was expressed in 5-dpf and adult zebrafish eyes, as well as in 5-dpf whole larval fish, whereas nocturnin-a expression was not detectable in the eyes, although it was detectable in the 5-dpf whole larval fish. D: RT–PCR analysis of nocturnin-a and nocturnin-b expression in adult eyes at 8 AM, 12 PM, 4 PM, 8 PM, 12 AM, and 4 AM, noting prominent nocturnin-b expression but undetectable nocturnin-a expression. E: Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) revealed the rhythmic changes in nocturnin-b expression in zebrafish adult eyes at the 8 AM, 12 PM, 4 PM, 8 PM, 12 AM, and 4 AM y-axis, fold differences between nocturnin-b and elf2a, normalizing against the level at 8 AM. Error bars (standard deviations) are based on three experiments.
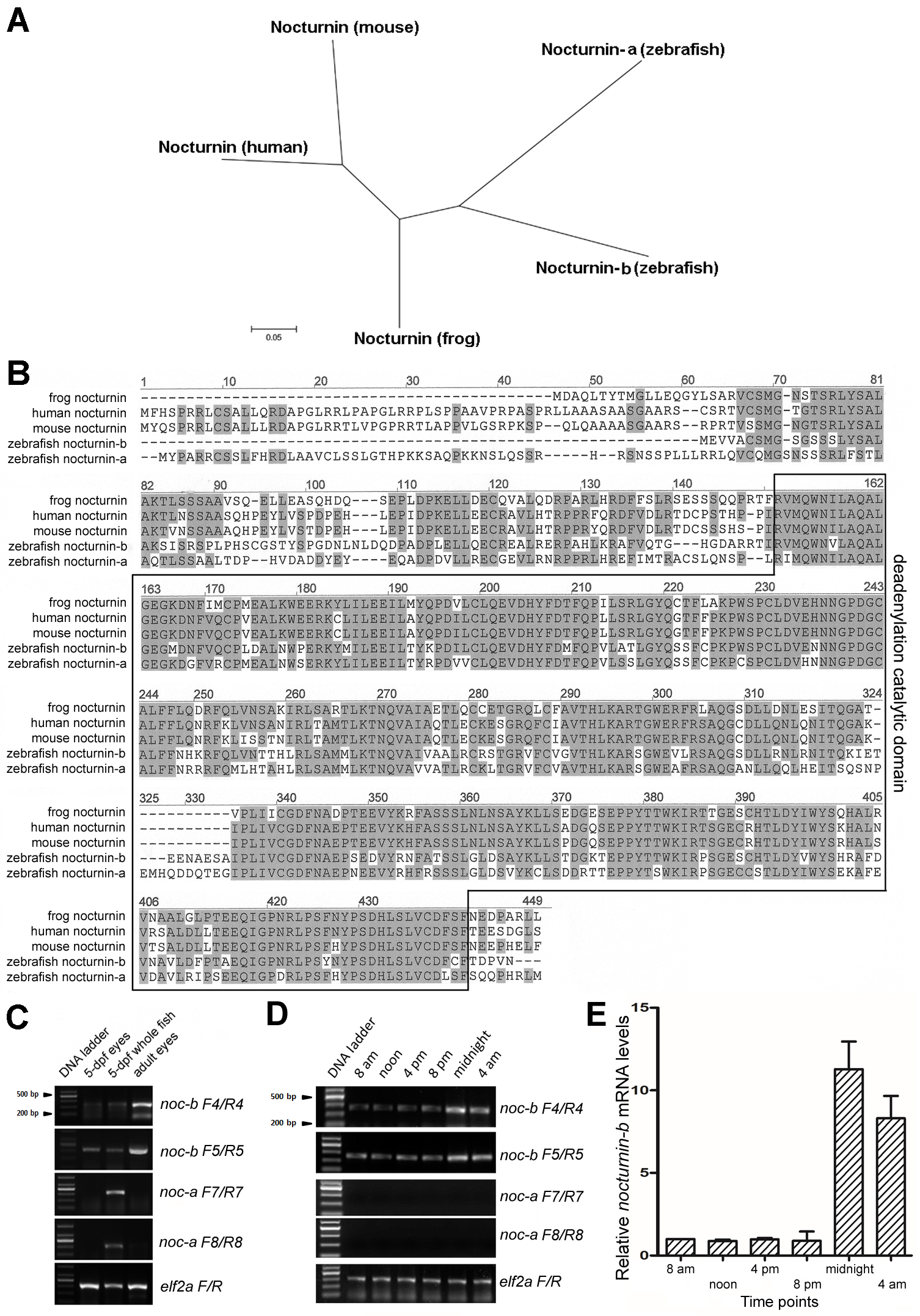
 Figure 1 of
Yang, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1039-1047.
Figure 1 of
Yang, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1039-1047.  Figure 1 of
Yang, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1039-1047.
Figure 1 of
Yang, Mol Vis 2017; 23:1039-1047. 