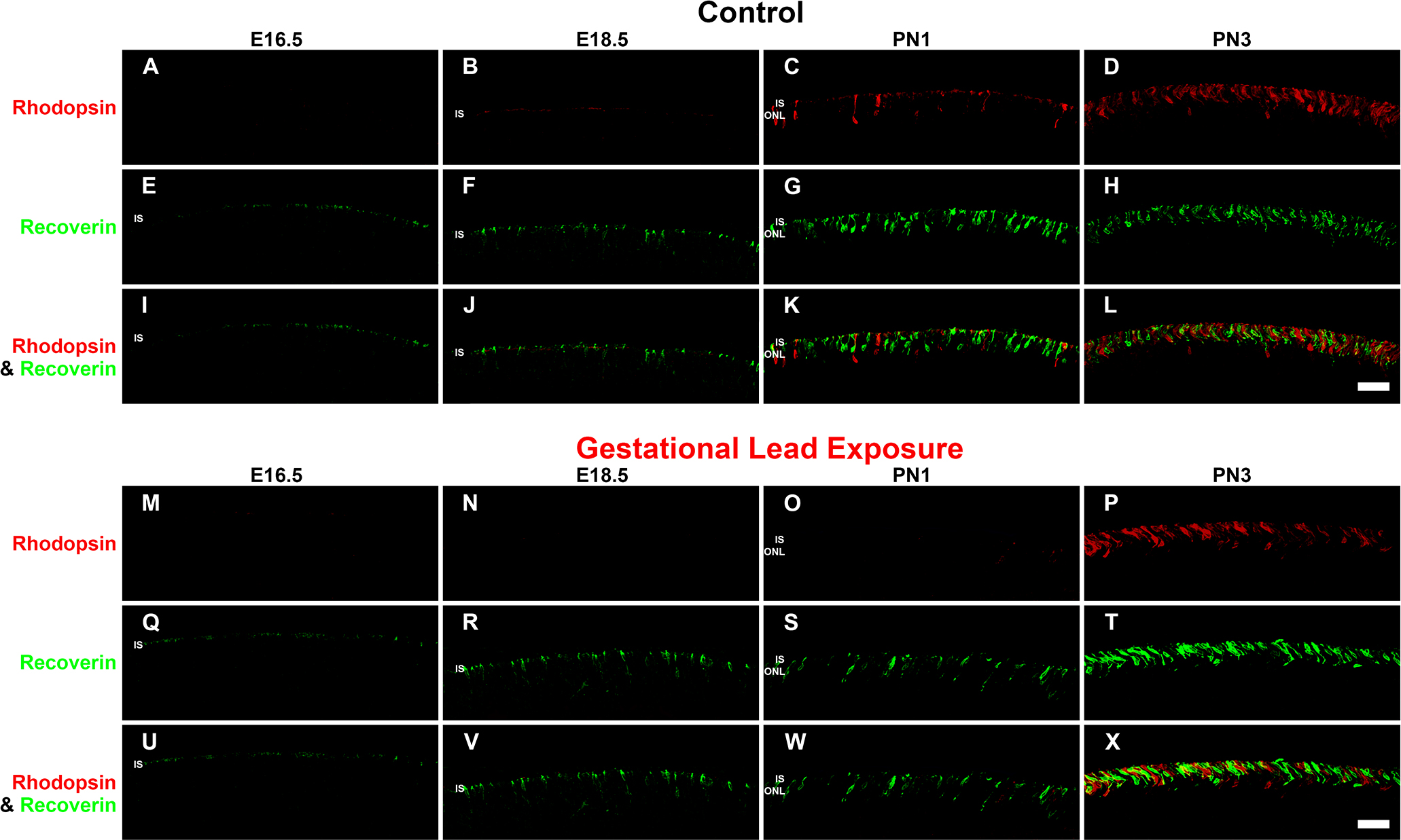
Figure 2. GLE delayed rhodopsin-IR, but not recoverin-IR, in developing retinas (E16.5-PN3). The developing retinas (E16.5-PN3) from
(
A–L) the control and (
M–X) GLE mice were double labeled with antibodies against rhodopsin (red:
A–D and
M–P) and recoverin (green:
E–H and
Q–T), and colabeling was examined in the merged images (yellow:
I–L and
U–X).
A–D: In the control retinas, a faint amount of rhodopsin-IR was first observed in the ISs at E18.5. At PN1 and PN3, rhodopsin-IR
increased in the ISs and in the ONL.
E–H: In the control retinas, recoverin-IR was first observed in cone ISs at E16.5. From E18.5 to PN3, recoverin-IR increased in
the ISs and ONL.
I–L: The colabeling of recoverin and rhodopsin-IR was first detected at PN1.
M–P: In the GLE retinas, a few faint rhodopsin-IR rod ISs were detected at E18.5. At PN1 and PN3, rhodopsin-IR increased in the
rod ISs and ONL. Thus, there was a two-day delay in the appearance of rhodopsin-IR in GLE retinas (
Table 3).
Q–T: In the GLE retinas, like the control retinas, recoverin-IR was first seen at E16.5. From E18.5 to PN3, recoverin-IR increased
in the ISs and ONL.
U–X: In the GLE retinas, the colabeling of recoverin and rhodopsin was first detected at PN3 as opposed to at PN1 in the control
retinas. Scale bar = 40 μm. GLE = Gestational lead exposure; IR = immunoreactivity; E = embryonic; PN = postnatal; IS = inner
segment; ONL = outer nuclear layer.
 Figure 2 of
Chaney, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1468-1489.
Figure 2 of
Chaney, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1468-1489.  Figure 2 of
Chaney, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1468-1489.
Figure 2 of
Chaney, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1468-1489.