Figure 3. Src activation mediates SCF-induced retinal vascular hyperpermeability and internalization of VE-cadherin. A–B: Src inhibitor blocks stem cell factor (SCF)-induced increase in retinal vascular permeability. In A, paracellular permeability was determined using human retinal microvascular endothelial cell (HRMEC) monolayers that were
pretreated with SU6656 (1 μM) for 30 min before the stimulation with rh SCF (50 ng/ml) or PBS (*p<0.05, #p>0.05 versus PBS, n = 4). In B, in vivo retinal vascular leakage was determined as described above. PP2 (1.5 mg/kg) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) was intraperitoneally
injected into mice at 1 h before the intravitreal injection of rm SCF (50 ng in 1 μl of PBS) or an equivalent volume of PBS
into each eye (*p<0.05, ns = not significant, n = 5). C–D: Src inhibitor blocks SCF-induced internalization of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin. In C, HRMECs were pretreated with SU6656 (1 μM) or imatinib mesylate (10 μM) for 30 min before the stimulation with rh SCF (50
ng/ml) or PBS. The arrows indicate the disappearance of VE-cadherin (green) at the cell junctions. The arrowheads indicate
colocalization of internalized VE-cadherin with endosome antigen 1 (EEA1; red). In D, imatinib mesylate (20 mg/kg), PP2 (2 mg/kg), or PBS was intraperitoneally injected into mice at 1 h before the intravitreal
injection of rm SCF (50 ng in 1 μl of PBS) or an equivalent volume of PBS in each eye. Retinal whole mounts were stained with
anti-VE-cadherin immunoglobulin G (IgG; green) and Alexa Fluor® 594-conjugated isolectin GS-IB4 (red). The arrowheads indicate the focal loss of VE-cadherin in the retinal vascular junctions.
Scale bars in (C) and (D) = 25 μm and 100 μm, respectively.
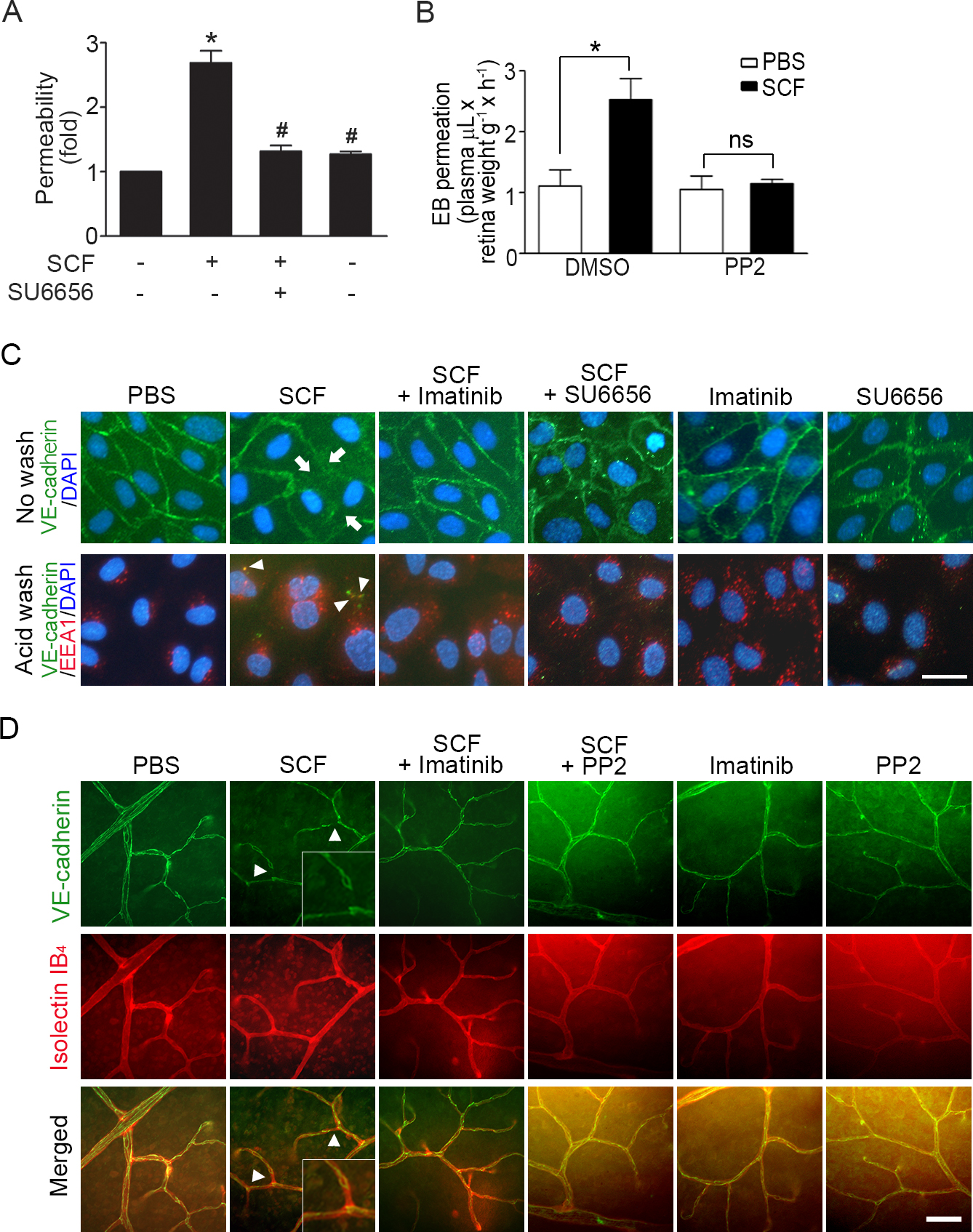
 Figure 3 of
Im, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1213-1220.
Figure 3 of
Im, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1213-1220.  Figure 3 of
Im, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1213-1220.
Figure 3 of
Im, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1213-1220. 