Figure 8. WFA and Cl-amidine have a compounding effect on soluble GFAP in the retina. Eyes were injured and left to recover for 7 days
in vivo. On day 7, mouse eyes were enucleated and posterior eyecups were placed into culture with no drug added (lane 1),
or containing either Cl-amidine alone (lane 2), WFA alone (lane 3), or both drugs combined (lane 4). A: Western blot analysis of GFAP in soluble fractions of untreated, Cl-amidine treated, WFA treated, or WFA/Cl-amidine treated
eyecups. The arrowhead points to a 55 kDa band. Densitometric quantification of high molecular weight GFAP (B, >75 kDa), low molecular weight GFAP (C, 37-50 kDa), or 50 kDa GFAP (D, asterisk). E: Western blot analysis of F95 in soluble fraction from untreated, Cl-amidine treated, WFA treated, or WFA/Cl-amidine treated
eyecups. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). P values less than 0.05 (asterisk) were considered significant
as determined by t test.
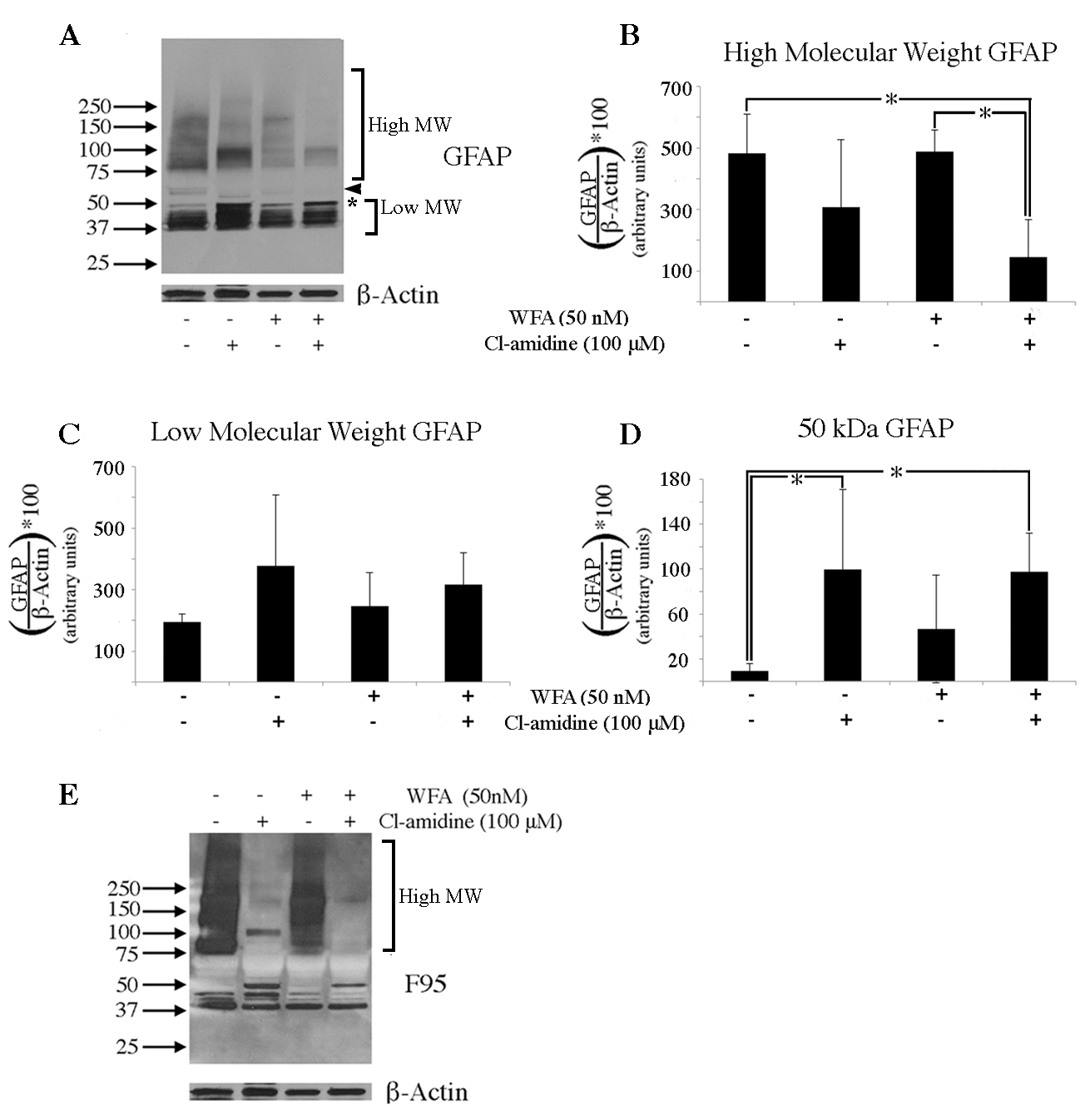
 Figure 8 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.
Figure 8 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.  Figure 8 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155.
Figure 8 of
Wizeman, Mol Vis 2016; 22:1137-1155. 