Figure 4. Causal variants in PDE6A identified in families PKRP133 and PKRP140. A: Sequence chromatogram of unaffected individual 15 homozygous for the wild-type. B: Sequence chromatogram of unaffected individual 28 heterozygous carriers. C: Sequence chromatogram of affected individual 29 of PKRP133 homozygous for the G to A variation in intron 16; c.2028–1G>A.
D: Pedigree of family PKRP140 with the haplotypes of four adjacent chromosome 5q33 microsatellite markers are shown with the
alleles forming the risk haplotype shaded black and the wild-type allele shown in white. Squares are males, circles are females,
filled symbols are affected individuals, the double line between individuals indicates consanguinity, and the diagonal line
through a symbol is a deceased family member. E: Sequence chromatogram of unaffected control homozygous for the wild-type. F: Sequence chromatogram of individual 13 heterozygous carrier. G: Sequence chromatogram of affected individual 14 of PKRP140 homozygous for the A to G transition in intron 10: c.1408–2A>G.
The arrows point to the splice site variation identified in families PKRP133 (c.2028–1G) and PRKP140 (c.1408–2A) whereas green,
red, and brown represent the exon, splice acceptor site, and intron, respectively. SA=splice acceptor.
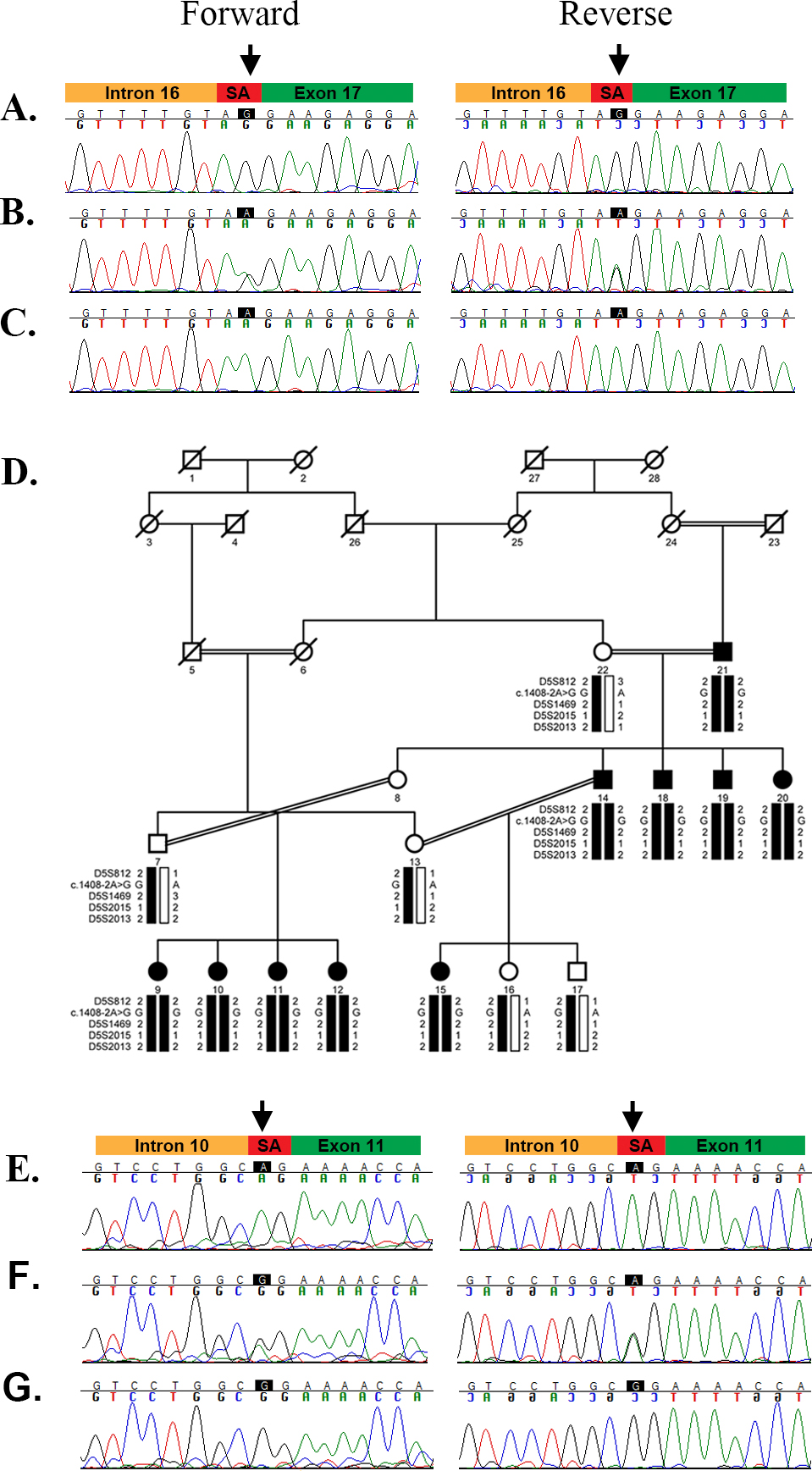
 Figure 4 of
Khan, Mol Vis 2015; 21:871-882.
Figure 4 of
Khan, Mol Vis 2015; 21:871-882.  Figure 4 of
Khan, Mol Vis 2015; 21:871-882.
Figure 4 of
Khan, Mol Vis 2015; 21:871-882. 