Figure 3. The benefit of both CR-39™ spectacle lenses in visual performance against UV radiation. A: The UV-induced decline in visual acuity was significantly prevented by CR-39™ spectacle lens protection. B, C, and D: Scatterplots demonstrating the relationship between the changes in corneal smoothness, corneal opacity, and corneal lissamine
green staining scores and the reduced degrees of visual acuity after UVB exposure. E and F: Scatterplots demonstrating the relationship between the changes in total corneal pathological changes scores, and baseline
visual acuity and the reduced degrees of visual acuity after UVB exposure. G: HE staining showing the normal cornea and retina of the blank control mouse. H: HE staining showing severe damage in the corneal tissue of the unprotected mouse, in which no evidence of histological abnormality
was found in the retinal photoreceptor. I: The outer nuclear layer thickness for UVB-exposed and blank control mice was valued. Values were mean±SD (n=6, each group).
There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups at any distance point. ONL: outer nucleus layer.
ONH: optic nerve head. Scale bars: 35 mm.
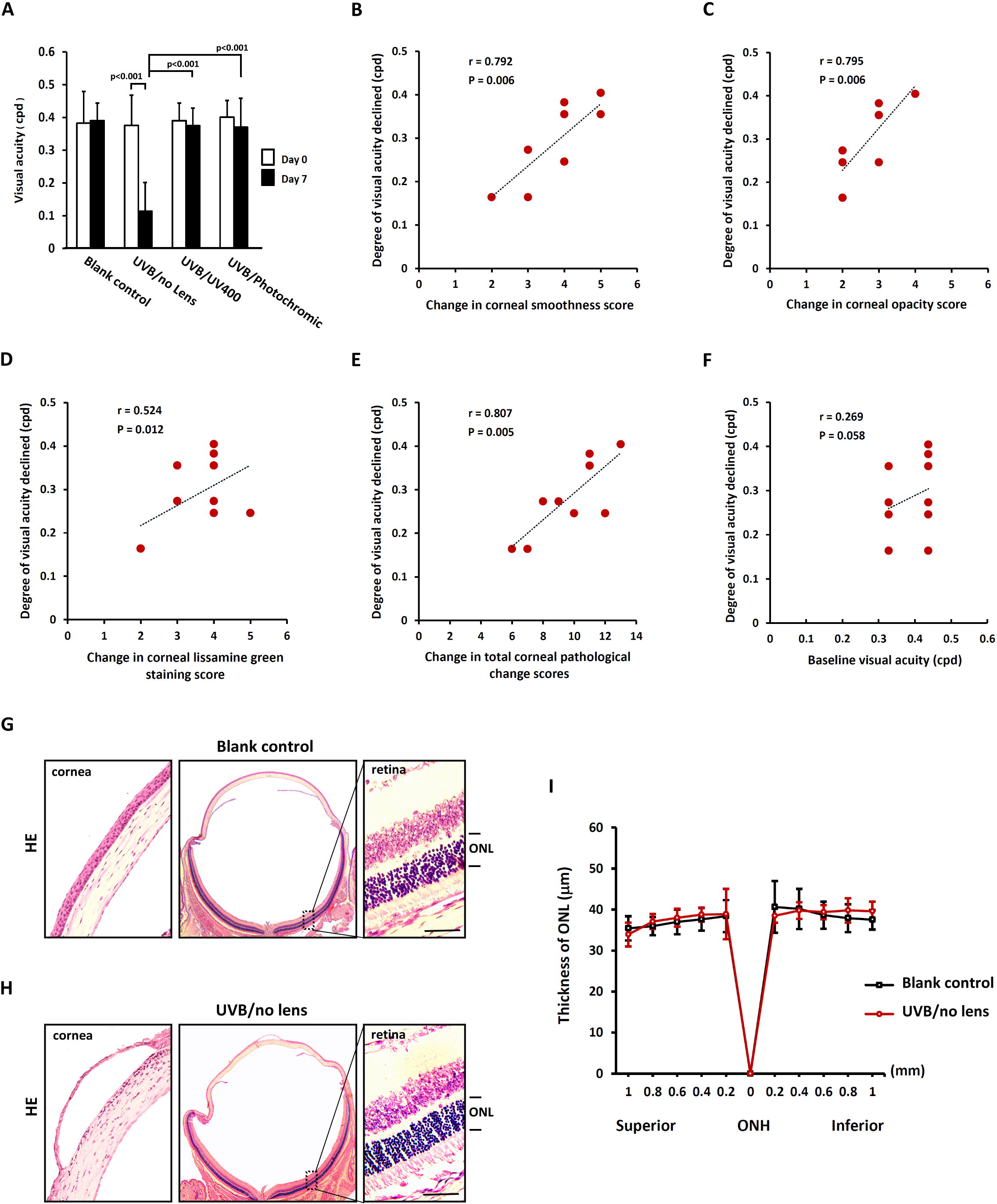
 Figure 3 of
Liou, Mol Vis 2015; 21:846-856.
Figure 3 of
Liou, Mol Vis 2015; 21:846-856.  Figure 3 of
Liou, Mol Vis 2015; 21:846-856.
Figure 3 of
Liou, Mol Vis 2015; 21:846-856. 