Figure 7. Dependence of the hyperosmotic induction of AQP5 in RPE cells on the activation of signal transduction pathways. The mRNA
level was measured with real-time RT–PCR analysis. The cells were cultured for 24 h in isoosmotic (control) and hyperosmotic
(+ 100 mM NaCl) media. The hyperosmotic elevation of AQP5 expression was decreased by the inhibitor of p38 MAPK activation,
SB203580 (10 µM; n=8), and the inhibitor of ERK1/2 activation, PD98059 (20 µM; n=10), respectively. Inhibitors of JNK activation
(SP600125; 10 µM; n=10), of the catalytic subunits of PI3K-related kinases (LY294002; 5 µM; n=8), of the PDGF receptor tyrosine
kinase (AG1296; 10 µM; n=8), of the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase (AG1478; 600 nM; n=8), and of the VEGF receptor-2 (SU1498;
10 µM; n=8) did not decrease the hyperosmotic induction of AQP5. The vehicle control was made with DMSO (1%; n=6). Data are
means ± SEM obtained in independent experiments performed in triplicate. Significant difference versus isoosmotic unstimulated
control: *p<0.05. Significant difference versus NaCl control: ●p<0.05.
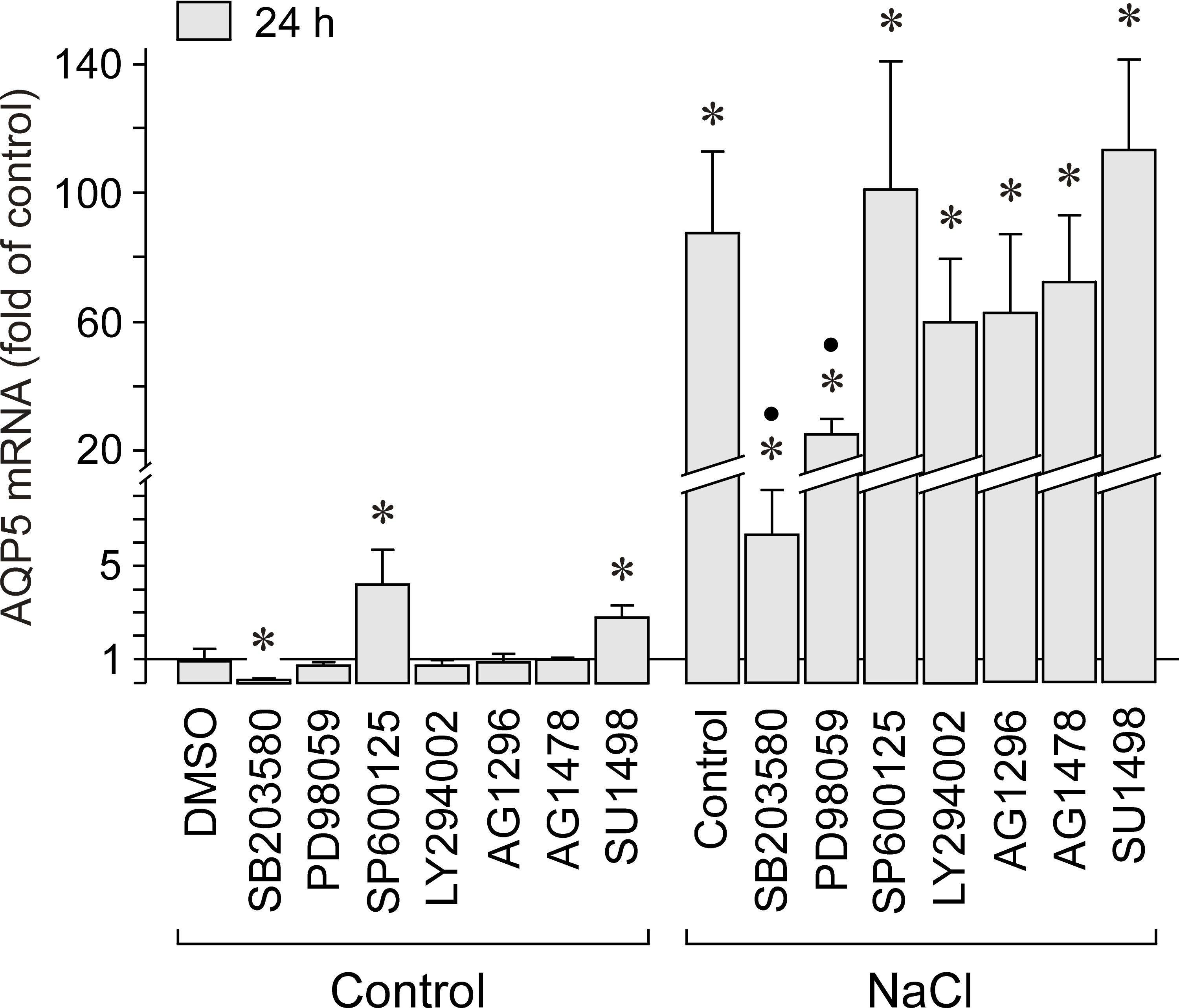
 Figure 7 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.
Figure 7 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.  Figure 7 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.
Figure 7 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377. 