Figure 2. The hyperosmotic upregulation of VEGF is induced by the stimulation of gene transcription. mRNA expression was measured with
real-time RT–PCR analysis. A. Inhibition of the gene transcription by actinomycin D (ActD; 5 µg/ml) abrogated the increase in VEGF mRNA induced by hyperosmotic
(+ 100 mM NaCl) medium. The data were obtained after 6 (n=4) and 12 h (n=5) of stimulation, respectively, and are expressed
as folds of isoosmotic unstimulated control. Actinomycin D was preincubated for 30 min. B. The stability of VEGF mRNA did not differ between isoosmotic (control; n=6) and hyperosmotic (+ 100 mM NaCl; n=4) conditions.
The cells were first treated with isoosmotic (control) and hyperosmotic (+ 100 mM NaCl) media for 12 h, followed by the addition
of actinomycin D (5 µg/ml). Total RNA was isolated at different time periods after the addition of actinomycin D. Data are
means ± SEM obtained in independent experiments performed in triplicate, and expressed in percent of 0-h control. Significant
differences versus isoosmotic unstimulated control (A) and 0 h (B): *p<0.05. Significant difference versus NaCl control: ●p<0.05.
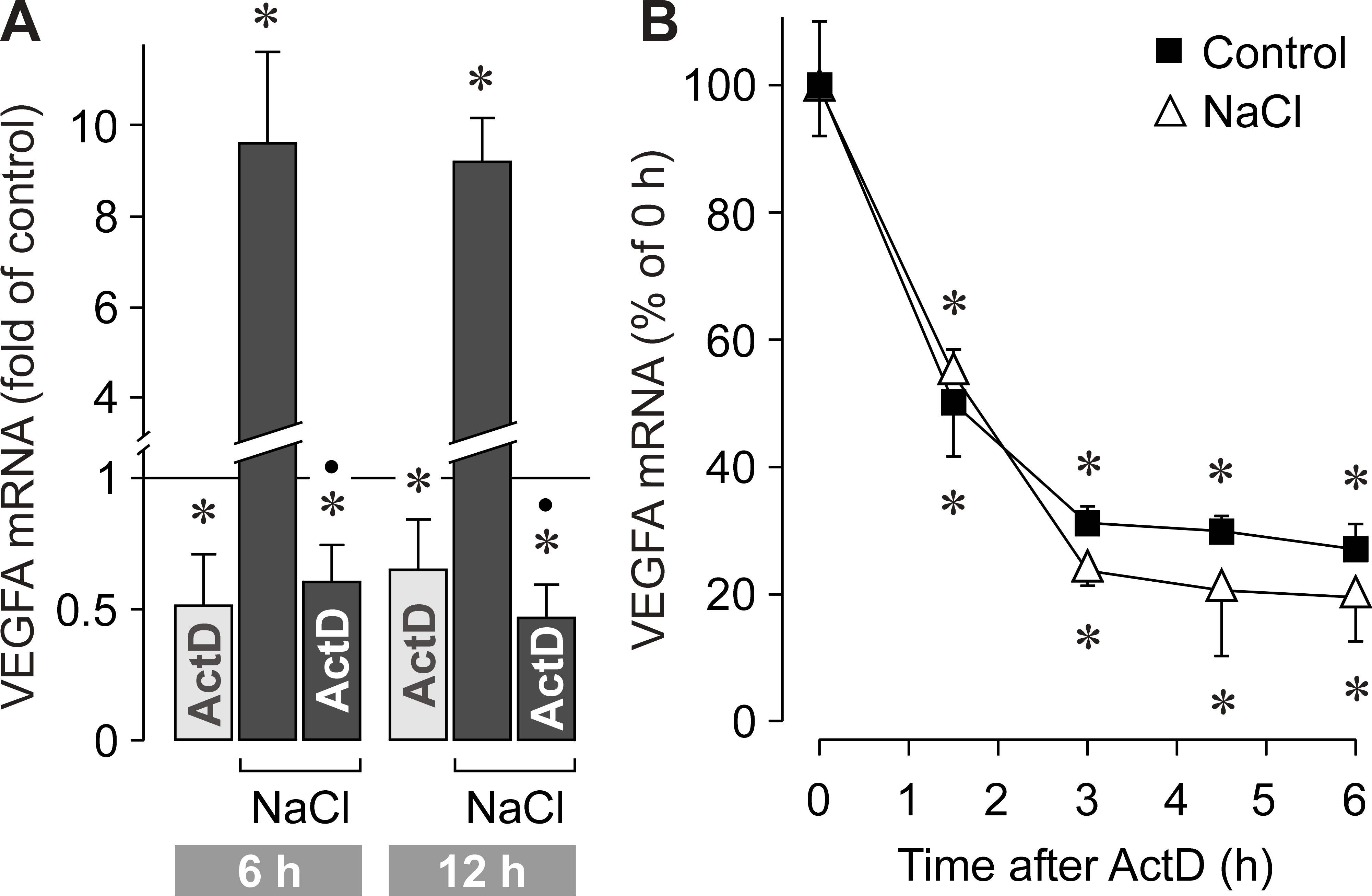
 Figure 2 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.
Figure 2 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.  Figure 2 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377.
Figure 2 of
Hollborn, Mol Vis 2015; 21:360-377. 