Figure 1. Clinical phenotype and whole exome sequence analysis. A: Pedigree diagram of family A. B: Microspherophakic lens in the right eye. C: Brachydactyly of the toes. D: Dorsal and ventral sides of hands from the patient and her unaffected sister to show brachydactyly only in the patient.
E: X-ray images of the hands of the patient and her unaffected sibling to show brachydactyly in the patient. Both images are
at the same magnification. F: Short stature. G: The absence of stiffness of joints in the patient and her unaffected sister is shown by the ability to make fists. H: Whole exome sequencing (WES) data. I: Sequencing chromatograms of individuals from family A. Arrows mark the nucleotide change G>T. + and m represent the wild-type
and mutant alleles, respectively. The age of individuals in years is given below the symbols.
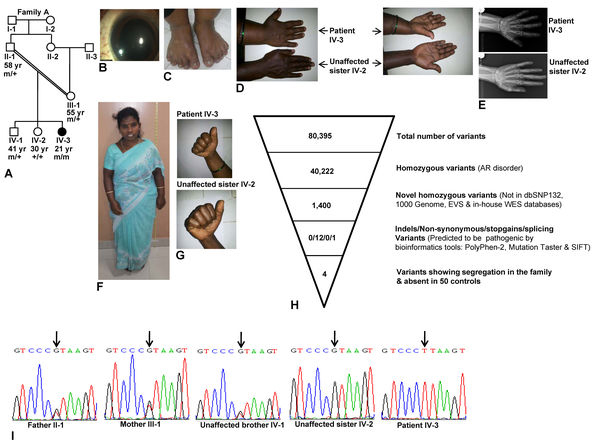
 Figure 1 of
Shah, Mol Vis 2014; 20:790-796.
Figure 1 of
Shah, Mol Vis 2014; 20:790-796.  Figure 1 of
Shah, Mol Vis 2014; 20:790-796.
Figure 1 of
Shah, Mol Vis 2014; 20:790-796. 