Figure 3. Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF- α) was released from the activated microglia induced by retinal neuronal monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 (MCP-1) via the phosphorylation of p38. A: Real-time PCR was used to measure TNF-α mRNA expression. Dose-dependent inhibition of the expression of TNF-α mRNA was induced
by retinal neuronal MCP-1 in the retinal neuron–microglia Transwell culture system by p38 inhibitors. B: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to measure the soluble TNF-α concentration. Dose-dependent inhibition
of the expression of soluble TNF-α was induced by p38 inhibitors. C: Phospho-p38 levels were detected with western blotting. Phosphorylated p38 MAPK levels from the microglial cells increased
due to retinal neuronal MCP-1; however, anti-MCP-1 preincubated with primary cultured retinal neurons led to downregulation
of the levels of phosphorylated p38 (**p<0.01). D: Purified microglia were stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-CD11b (green) and the expression of TNF-α labeled
with PE (red). The number of CD11b and TNF-α double-stained cells (activated microglia) decreased markedly after advanced
glycation end product (AGE) treatment with p38 inhibitors (control: 12.21±5.32 cells/microscopic visual field; AGE: 28.23±3.62
cells/microscopic visual field; p38 inhibitors: 18.36±6.17 cells/microscopic visual field; p=0.013).
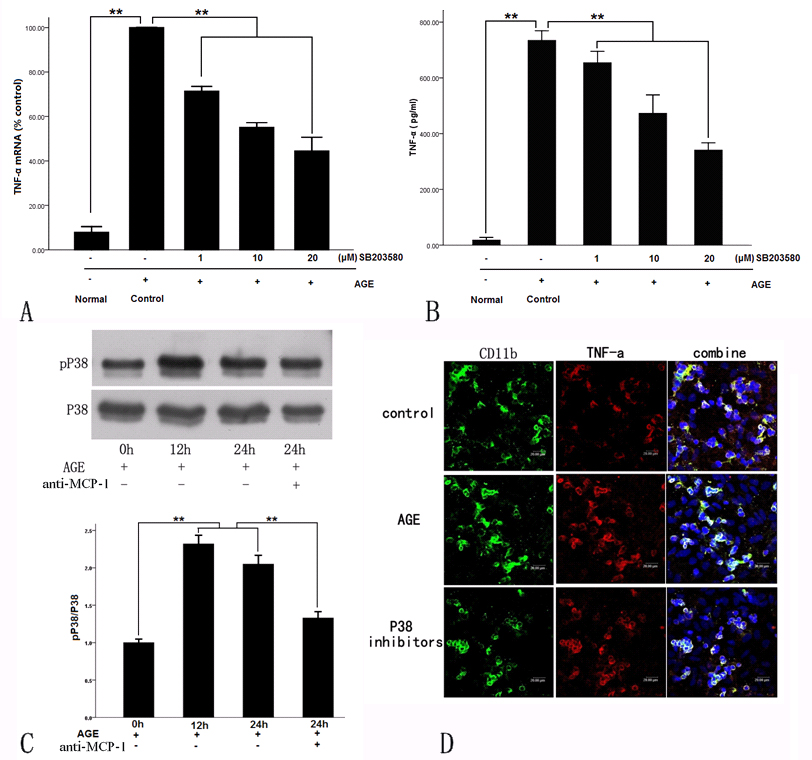
 Figure 3 of
Dong, Mol Vis 2014; 20:616-628.
Figure 3 of
Dong, Mol Vis 2014; 20:616-628.  Figure 3 of
Dong, Mol Vis 2014; 20:616-628.
Figure 3 of
Dong, Mol Vis 2014; 20:616-628. 