Figure 5. Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion and combinations of nuclear factor kappaB, VEGFR-2, and p38. Organ cultures at
day 2 of preparation were treated with a combination of indicated inhibitors and supernatant was collected for 1 h after 6
h, 24 h, and 48 h. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) content was evaluated with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
A combination of SU1498 with either nuclear factor kappaB (NFkB) inhibitor (A) or SB203580 (B) displayed similar results as the inhibition of NFkB or SB203580 alone. However, a combination of NFkB inhibitor and SB203580
abolishes VEGF secretion, indicating an additive effect of these two inhibitors (C). The results are depicted as % VEGF at 0 h (before treatment). The bars depict the mean and standard deviation of three
to five independent experiments. Absolute concentration of VEGF at 0 h was 67.08 ±24.08 pg/ml for SB203580 + the NFkB inhibitor,
119.97±50.98 pg/ml for SB203580 + SU1498, and 99.15±41.66 pg/ml for SU1498 and NFkB inhibitor. The absolute concentration
of VEGF of the respective controls at 0 h was 82.89±26.90 for SB203580 + NFkB inhibitor, 115.02 ±76.57 pg/ml for SB203580
+ SU1498, and 177.23±85.04 pg/ml for SU1498 + NFkB inhibitor. Statistical significance was determined with the Student t test. + p<0.05; ++ p<0.01. +++ p<0.001.
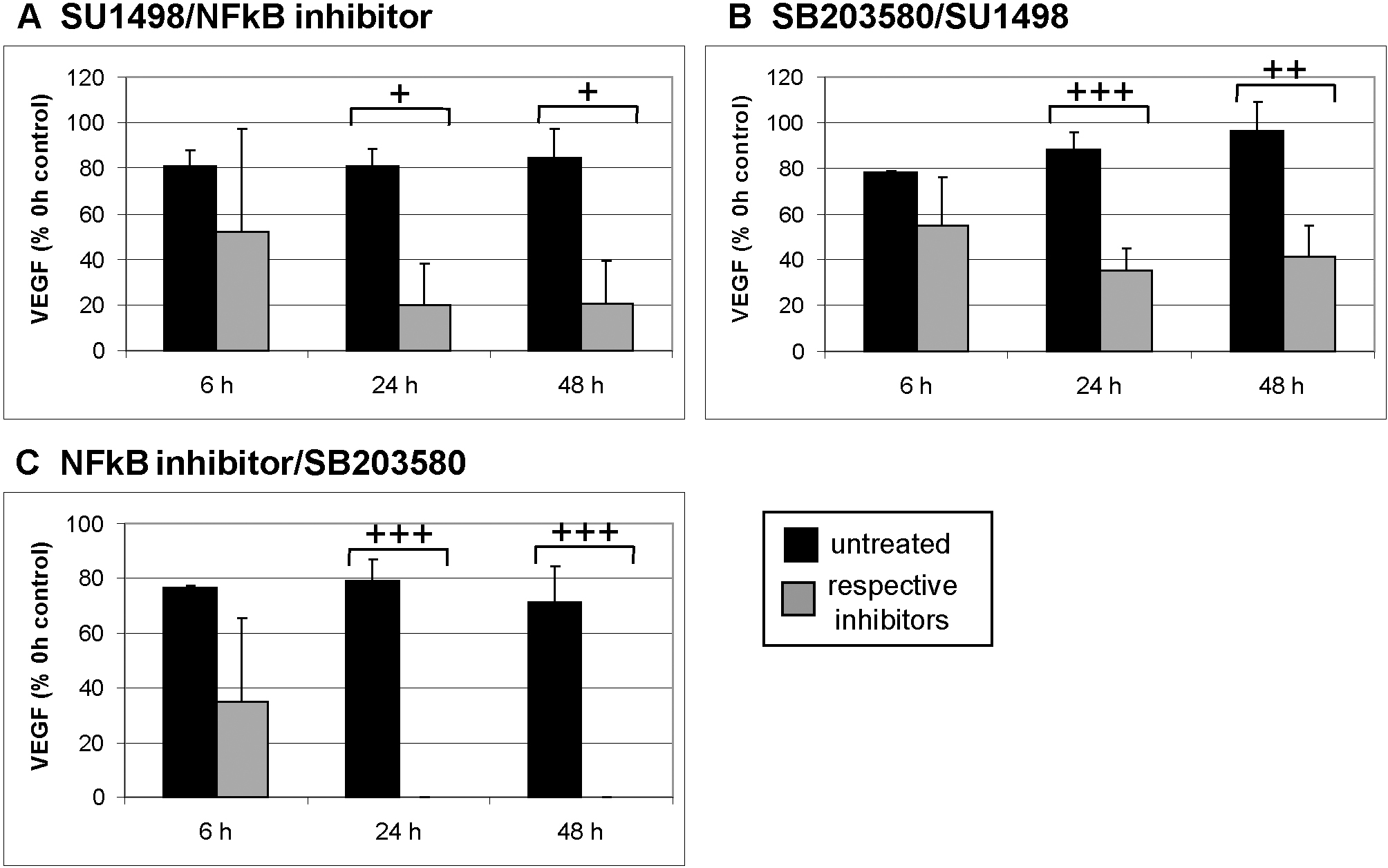
 Figure 5 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.
Figure 5 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.  Figure 5 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.
Figure 5 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291. 