Figure 3. Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion regulation by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 and downstream kinases.
Organ cultures at day 2 of preparation were treated with the indicated inhibitors and supernatant was collected for 1 h after
6 h, 24 h, and 48 h. Untreated cultures served as controls. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) content was evaluated
with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) inhibitor SU1498 significantly
reduced VEGF secretion after 48 h (A), so did the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) inhibitor LY294002 (B). Inhibiting protein kinase C (PKC) with bisindolylmaleimide displayed no effect (C). The combination of either LY294002 or bisindolylmaleimide with SU1498 mimicked the effect of SU1498 alone (D, E). The results are depicted as % VEGF at 0 h (before treatment). The bars depict the mean and standard deviation of three
to five independent experiments. Absolute concentration of VEGF at 0 h was 301.46±136.17 pg/ml for SU1498, 475.46±208.25 pg/ml
for bisindolylmaleimide, and 473.690 ±262.03 pg/ml for LY294002. The absolute concentration of VEGF of the respective controls
at 0 h was 390.69±238.69 pg/ml for SU1498, 410.78 +/− 134.4 for bisindolylmaleimide, and 418.30±109.30 pg/ml for LY294002.
Absolute concentration of VEGF at 0 h was 307.95±145.19 for the combination of SU1498 and bisindolylmaleimide and 346.91±104.65
for the combination of SU1498 and LY294002. The absolute concentrations for the respective controls were 269.37±149.19 pg/ml
for SU1498 and bisindolylmaleimide and 240.3±60.94 for SU1498 and LY29002. Statistical significance was determined with the
Student t test. Significant is depicted as follows: +p<0.05; ++ p<0.01. +++ p<0.001.
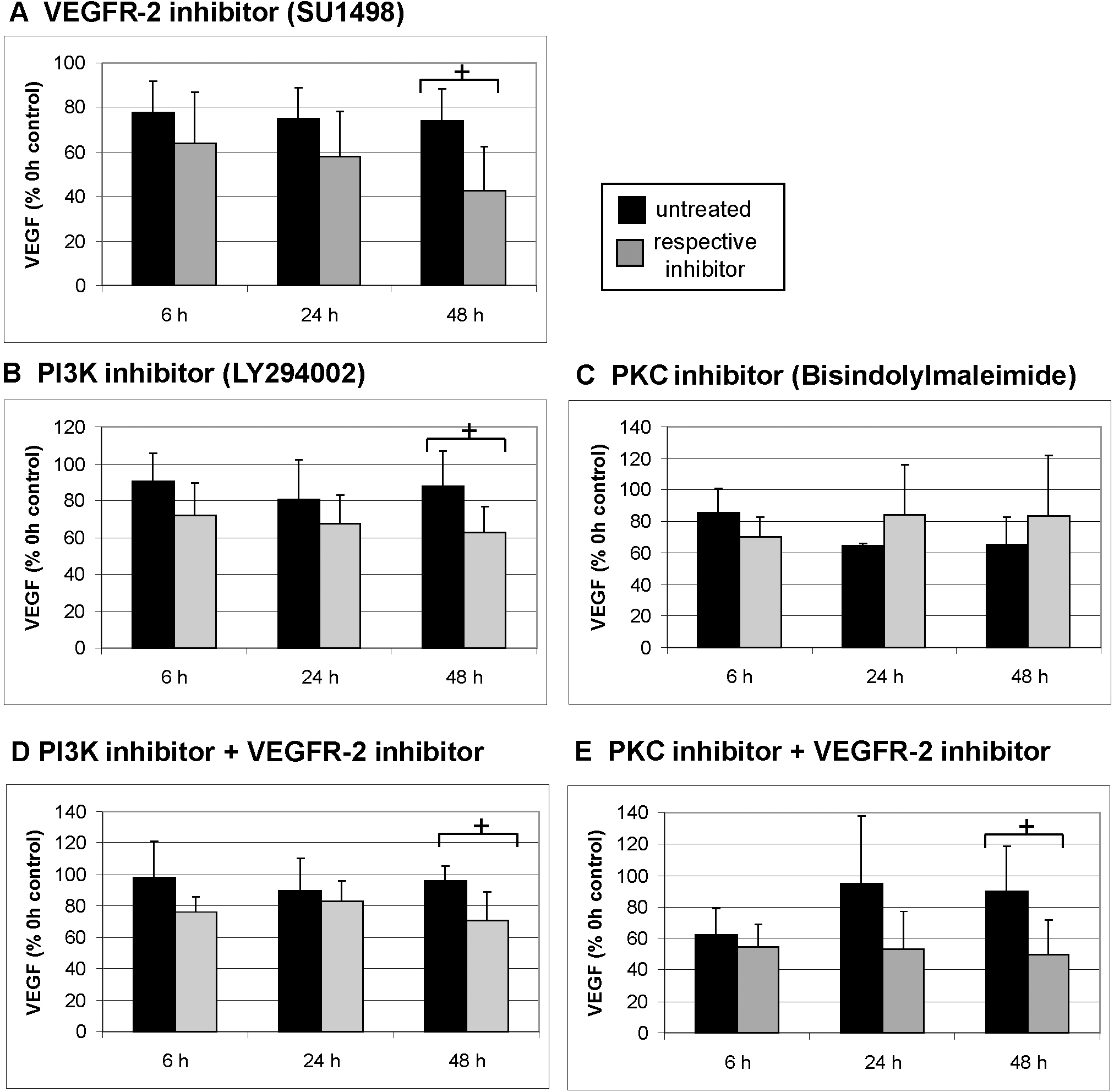
 Figure 3 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.
Figure 3 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.  Figure 3 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291.
Figure 3 of
Klettner, Mol Vis 2013; 19:281-291. 