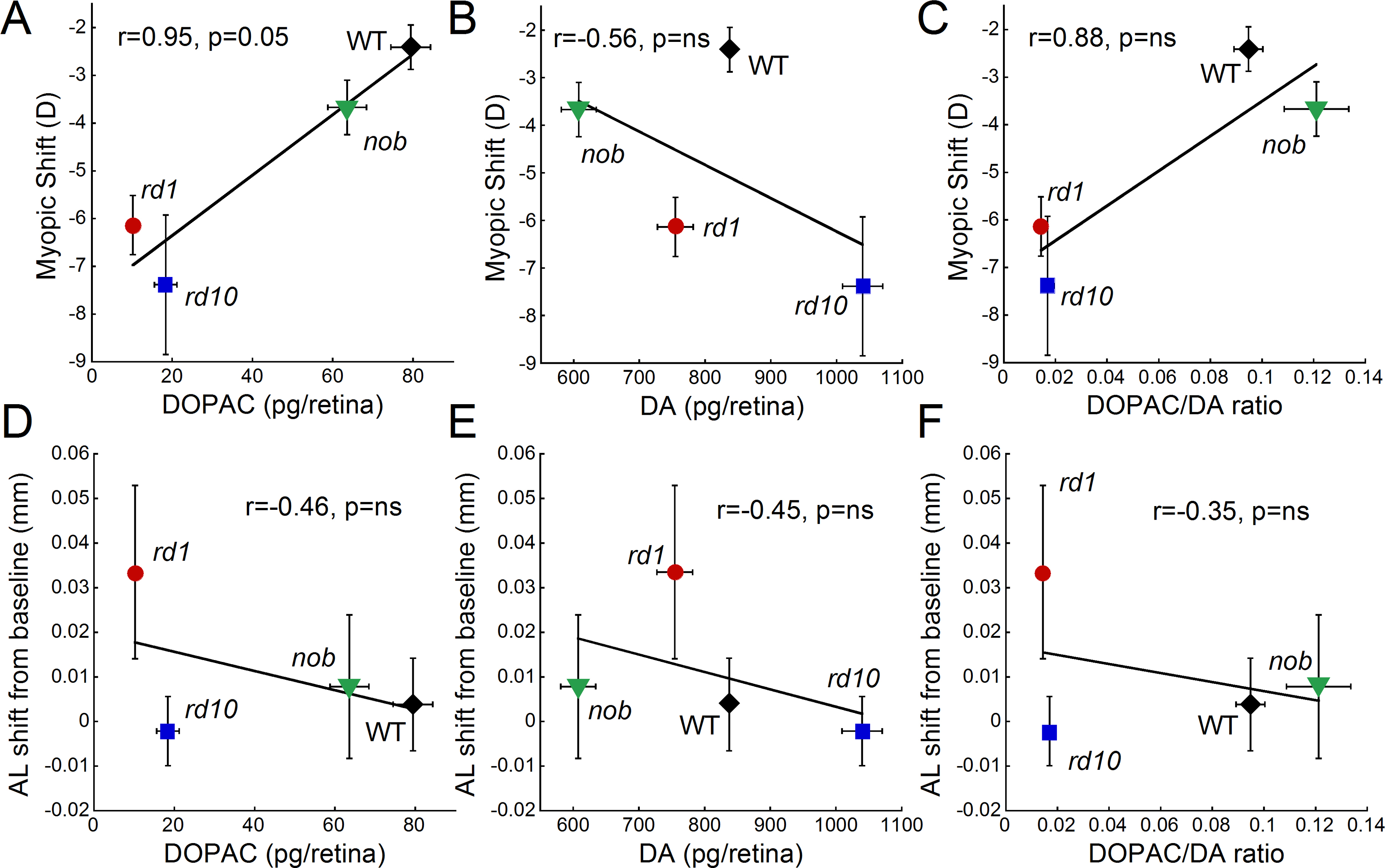
Figure 5. The influence of dopamine levels on form deprivation myopia susceptibility. The 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and
dopamine (DA) levels and the DOPAC/DA ratio are the average levels obtained from retinas under normal visual conditions for
each strain. These dopamine levels are plotted against the average myopic shift (
A–
C) or the axial shift from baseline (
D–
F) for each strain. Myopic shift was most strongly correlated with DOPAC levels across strains (Pearson’s correlation r=0.94,
p=0.05), while basal state DA levels did not predict susceptibility to myopia (Pearson’s correlation r=–0.56). DA and DA metabolism
(DOPAC levels) showed the strongest correlation with axial length shifts from baseline across strains (Pearson’s correlation
r=–0.45 and r=–0.46, respectively), although DA turnover (DOPAC/DA ratio) had similar trends (Pearson’s correlation r=–0.35).
Data for
rd1,
rd10, and wild-type (WT) retinas were obtained from this study, while the data from
nob retinas were a combination of data obtained from [
11] and recent additional measurements (n=33 for myopic shift, n=18 for axial length shift, and n=72 for dopamine data). Symbols
and bars represent average±standard error of the mean (SEM).
 Figure 5 of
Park, Mol Vis 2013; 19:2068-2079.
Figure 5 of
Park, Mol Vis 2013; 19:2068-2079.  Figure 5 of
Park, Mol Vis 2013; 19:2068-2079.
Figure 5 of
Park, Mol Vis 2013; 19:2068-2079.