Figure 1. Disease-associated mutations in CNGB3 alter the gating properties of heteromeric channels. A: Representative current traces are shown for CNGA3 plus CNGB3 channels after activation by saturating concentrations of CPT-cGMP
(4 μM) or CPT-cAMP (100 μM). Current traces were elicited by voltage steps from a holding potential of 0 mV to +80 mV, −80
mV, and then back to 0 mV. B: Representative dose–response relationships for CPT-cGMP activation of CNG channels, after expression of CNGA3 plus CNGB3-WT
(circles), T383fsX (squares), or F525N (triangles) subunits. Currents were normalized to the maximum cGMP current. Continuous
curves represent fits of the dose–response relationship with the Hill equation as described in the Methods section. The parameters
for each channel type were as follows: for WT, K1/2,CPT-cGMP=248 nM, h=1.5; for T383fsX, K1/2, cGMP=111 nM, h=1.9; and for F525N, K1/2,CPT-cGMP=79 nM, h=1.7.
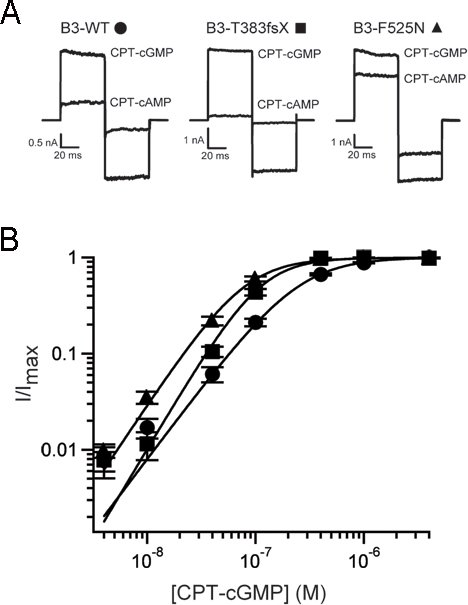
 Figure 1 of
Liu, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1268-1281.
Figure 1 of
Liu, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1268-1281.  Figure 1 of
Liu, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1268-1281.
Figure 1 of
Liu, Mol Vis 2013; 19:1268-1281. 