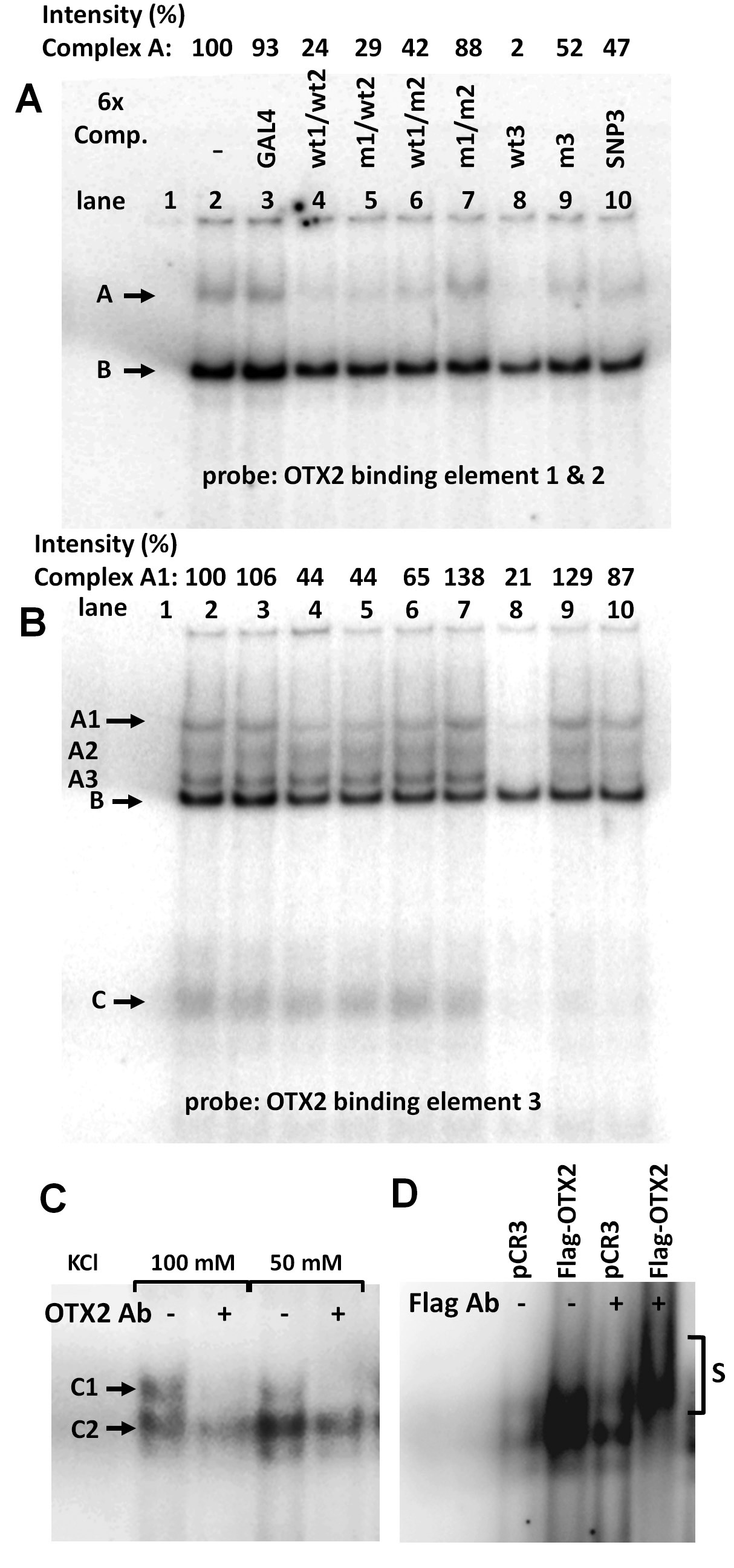
Figure 5. Specific nuclear protein
binds to OTX2 binding elements in the human tyrosinase promoter.
ARPE-19 cells were cultured for 14 days, and nuclear extracts
were prepared. Binding of nuclear proteins to labeled OTX2
probes 1 and 2 (
A) and 3 (
B) was competed with
only a sixfold excess of unlabeled probes for unrelated GAL4
(lanes 3), wild-type or mutated OTX2 sites 1 and 2 (lanes 4–7),
wild-type or mutated OTX2 site 3 (lanes 8–9), and SNP
rs4547091
at OTX2 site 3 (lanes 10). Complexes showing specific
DNA-nuclear protein interaction are indicated with the symbol A,
A1, A2, A3, or C. Non-specific DNA-nuclear protein complexes are
indicated with
B. Free probes in the absence of nuclear
extracts are on lanes 1, and full reactions without competitor
are on lanes 2. Above the gel images, intensities of the most
specific DNA nuclear protein complexes A (
A) and A1 (
B)
are shown relative to nuclear extracts without competitor (lanes
2=100).
C: Supershift assay of OTX2 binding site 3 was
performed by incubating nuclear extracts from ARPE-19 cells with
or without the OTX2 antibody. Strong and modest inhibition of
the specific complexes C1 and C2, respectively, was observed.
D:
D407 cells were transfected with the Flag-tagged OTX2 cDNA or
with empty control plasmid (pCR3), and nuclear extracts were
prepared and incubated with the Flag-specific antibody. The
supershifted DNA–protein complex is indicated with the symbol S.
Both supershift assays were controlled by using a non-specific
control antibody (data not shown).
 Figure 5
of Reinisalo, Mol Vis 2012; 18:38-54.
Figure 5
of Reinisalo, Mol Vis 2012; 18:38-54.  Figure 5
of Reinisalo, Mol Vis 2012; 18:38-54.
Figure 5
of Reinisalo, Mol Vis 2012; 18:38-54.