Figure 4. Subcellular localization of cellular junctions associated and cytoskeletal proteins in human SRA 01/04 and mouse αTN4 lens
epithelial cells. Endogenous occludin, zona occludin-1 (ZO-1) and E-cadherin proteins were respectively immunolabeled with
the anti-occludin, anti-ZO-1, and anti-E-cadherin antibodies. The cytoskeletal actin was stained with phalloidin-TRITC. The
labeled protein is indicated on the left. Occludin (green) localized to the cellular periphery as punctate strands perpendicular
to the cell boundary (arrow) in both SRA 01/04 and αTN4 cells. In the αTN4 cell panel inset shows magnified view of the cell
pointed with an arrow. In some cells, cytoplasmic localization of the protein was also observed. ZO-1 (green) also localized
to the cellular periphery in a strand-like pattern perpendicular to the cell boundary in both cell types. In the αTN4 cell
panel, arrow points to a cell with strand-like localization; inset shows magnified view of the same cell. Cytoplasmic localization
of ZO-1 was also observed in some cells. E-cadherin (green) localized as punctate dots in the cytoplasm in both the cell lines;
nuclei (red) stained with propidium iodide. The absence of a signal in each cell type upon hybridization with the secondary
antibody alone as a negative control (not shown) proved specificity of localization of each labeled protein. Actin (red) staining
showed its localization as radial filaments in the cytoplasm in both the cell types; nuclei (blue) labeled with DAPI. Occludin,
ZO-1 and E-cadherin labeling was detected by epifluorescence microscopy using a 40× objective. Actin staining was detected
by confocal microscopy using a 60× objective and further digital magnification. Representative images from two independent
experiments are shown.
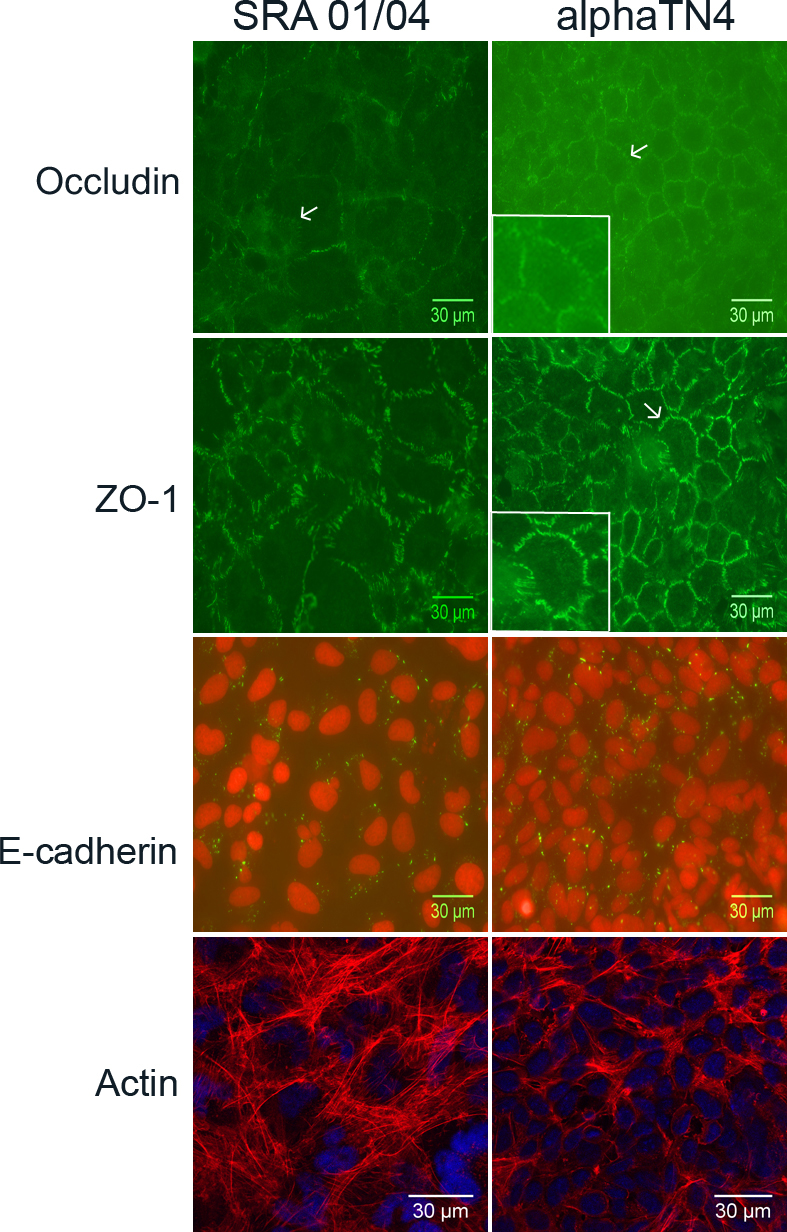
 Figure 4 of
Dave, Mol Vis 2012; 18:2937-2946.
Figure 4 of
Dave, Mol Vis 2012; 18:2937-2946.  Figure 4 of
Dave, Mol Vis 2012; 18:2937-2946.
Figure 4 of
Dave, Mol Vis 2012; 18:2937-2946. 