Figure 3. RP1 gene and
identified mutations. Schematic representation of the location
of mutations in the RP1 gene. Below are mutations
responsible for dominant retinitis pigmentosa (adRP) whereas
mutations above the gene cause autosomal recessive RP (arRP).
The mutation identified in this study is indicated with a black
rectangle. The portion of the gene that encodes the doublecortin
(DCX) domains (amino acids 36–118 and 154–233) is indicated with
green, and the Drosophila melanogaster bifocal (BIF)
domain (amino acids 486−635) is depicted in red. Missense
changes, for which the pathogenicity is uncertain, are not
included in this scheme. Four groups of arRP-causing mutations
are marked with numbers. GR.1=protein-truncating mutations that
reside in exon 2 or exon 3 (nonsense-mediated mRNA decay);
GR.2=missense mutations; GR.3=protein-truncating mutations near
the 3′ end of the gene, preserving residual activity;
GR.4=truncating mutations located in the proximal part of exon
4.
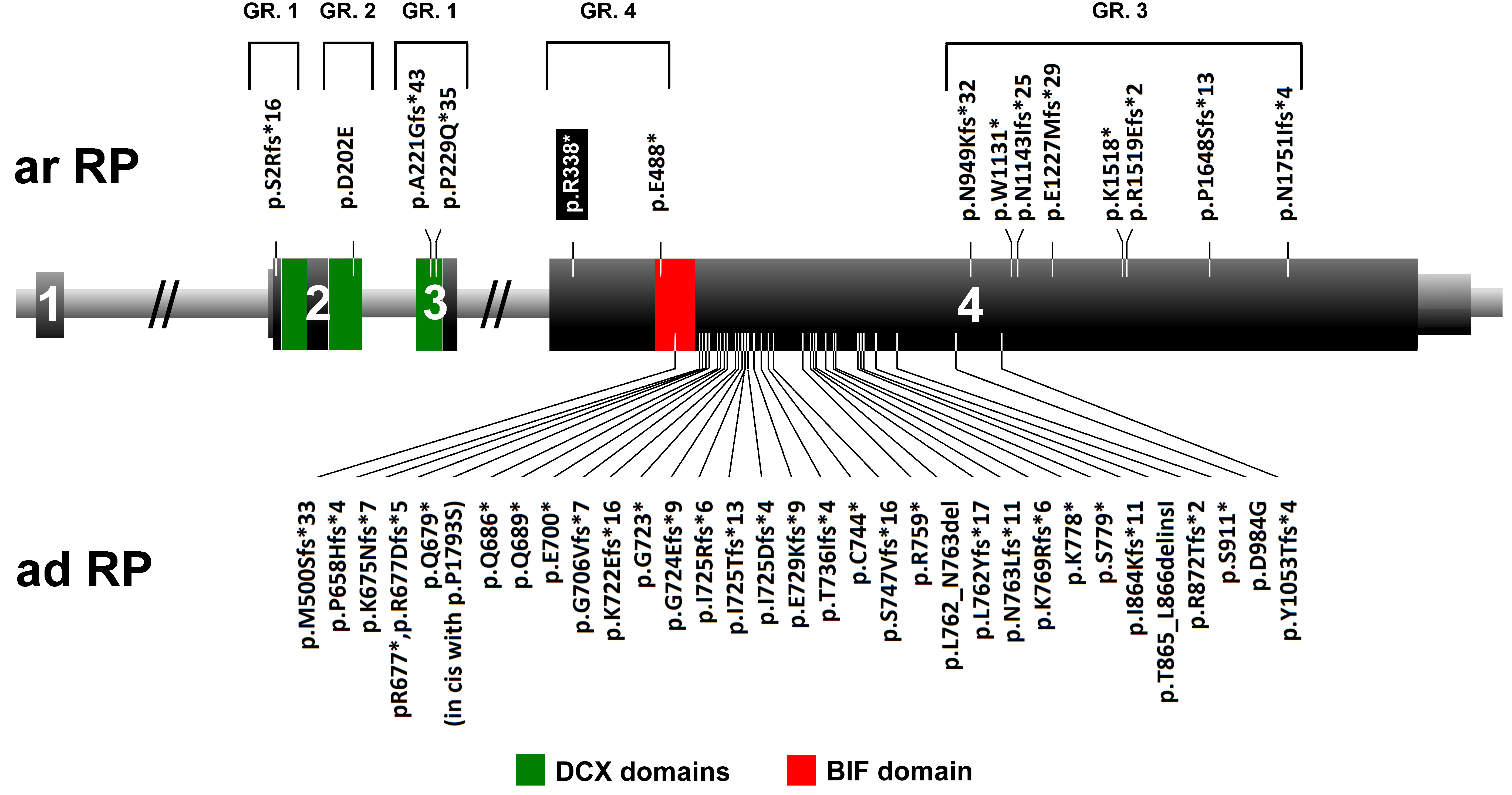
 Figure 3
of Siemiatkowska, Mol Vis 2012;
18:2411-2419.
Figure 3
of Siemiatkowska, Mol Vis 2012;
18:2411-2419.  Figure 3
of Siemiatkowska, Mol Vis 2012;
18:2411-2419.
Figure 3
of Siemiatkowska, Mol Vis 2012;
18:2411-2419. 