Figure 3. A schematic representation of the consensus secondary structure of a prototypical cbEGF-like domain. Calcium binding in the
NH2-terminal region of the wild-type domain is mediated by the highly conserved amino acids highlighted in blue. The highly conserved
cysteines of the cbEGF-like domain are marked with a C, and the lines between the cysteine residues represent disulfide bridges.
The mutation Cys790Ser affects the 4th cysteine residue, which is predicted to form a disulfide bridge with the 2nd cysteine
residue (Cys776). The mutation abolishes the disulfide bond formation and thus causes misfolding of the protein.
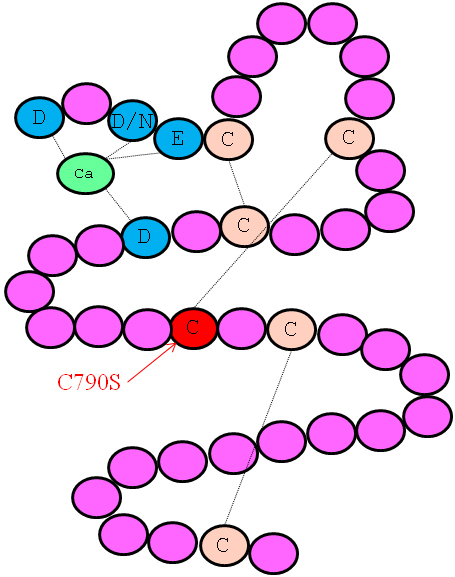
 Figure 3 of
Micheal, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1918-1926.
Figure 3 of
Micheal, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1918-1926.  Figure 3 of
Micheal, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1918-1926.
Figure 3 of
Micheal, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1918-1926. 