Figure 4. Melatonin dose-dependently protected retinal pigment epithelial cells against H2O2 damage as tested by microculture tetrazoline test. Retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells were pretreated with melatonin
(M) at concentrations of 10−10 M (M-10), 10−8 M (M-8), 10−6 M (M-6), and 10−4 M (M-4). After 24 h, 0.5 mM H2O2 (H) was added and cultured for 24 h. Cells treated with H2O2 alone were used as the controls (H). Cell viability was evaluated by the microculture tetrazoline test and expressed as percentages
of the controls (mean±standard deviation [SD] in triplicate tests). Error bars represent SD. Pretreatment with melatonin showed
dose-dependent protective effects on ARPE-19 cells (an immortal RPE cell line from a 19-year-old donor) against H2O2 damage (A). Studies in primary culture of human RPE cells isolated from the donor eye showed similar results (B). *p<0.05, compared with the controls (cells treated with H2O2 alone).
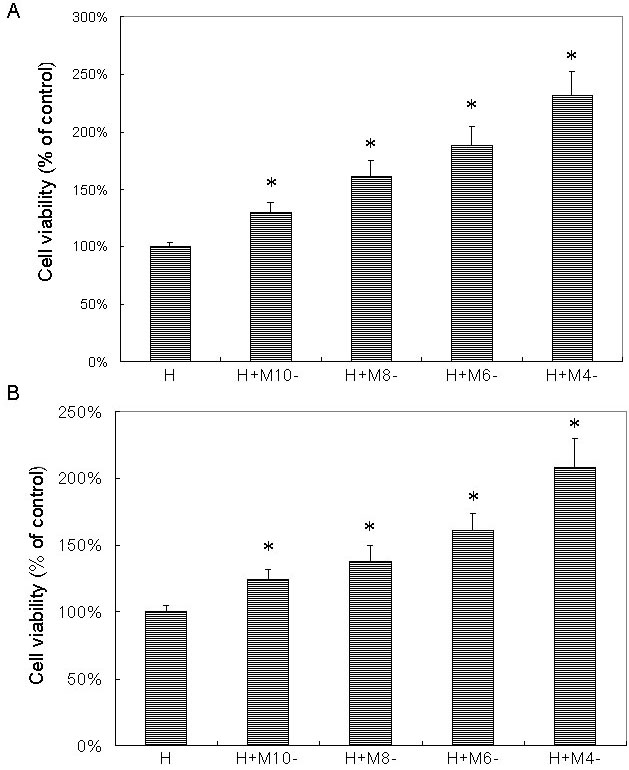
 Figure 4 of
Rosen, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1640-1648.
Figure 4 of
Rosen, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1640-1648.  Figure 4 of
Rosen, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1640-1648.
Figure 4 of
Rosen, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1640-1648. 