Figure 5. Light damage in Rdh13-/-
mice. Light damage was induced in Rdh13+/+
and Rdh13−/− mice by 48 h exposure to diffuse
white light (3,000 lx). Twenty-four h dark-adaption after
light exposure, and morphological and functional assays were
performed as described in Methods. A: Hematoxylin-eosin
(H&E) staining showed that the outer-plus-inner-segment and
outer nuclear layers of the retina from Rdh13−/−
mice that were exposed to light obviously disintegrated. B:
The thicknesses of the outer-plus-inner-segment and outer
nuclear layers of all genotypes exposed to the light and the
control group was valued. Values were mean±SD (n=5, each group).
There were statistically significant differences in the
thickness of the outer-plus-inner-segment and outer nuclear
layer between the light exposed Rdh13−/− mice
and the other three groups at any distance point. C: The
scotopic electroretinogram response of Rdh13+/+
and Rdh13−/− mice, which were recorded in all
groups. D: The amplitudes of a- and b-waves in all
genotypes was plotted as the mean±SD (n=5, each goup); *:
p<0.05. E: Mitochondria in photoreceptor inner
segments of Rdh13+/+ and Rdh13−/−
mice exposed to the light were detected by transmission electron
microscopy. Distinctly swollen mitochondria with disrupted
cristae were observed in Rdh13−/− mice
(arrows). F and G: Cytochrome c (CytC) and
apoptotic gene expression in all groups were analyzed by Western
Blot, which revealed that levels of CytC, apoptosis proteinase
activating factor-1 (Apaf-1), cleaved caspase 3, nuclear
factor-kappa B P65 (p65) and B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X
protein (Bax) were clearly increased in the cytoplasm of Rdh13−/−
mice; ONH, optic nerve head; RPE, retinal pigment epithelia; OS,
outer segment; IS, inner segment; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL,
outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner
plexiform layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; UV, ultraviolet.
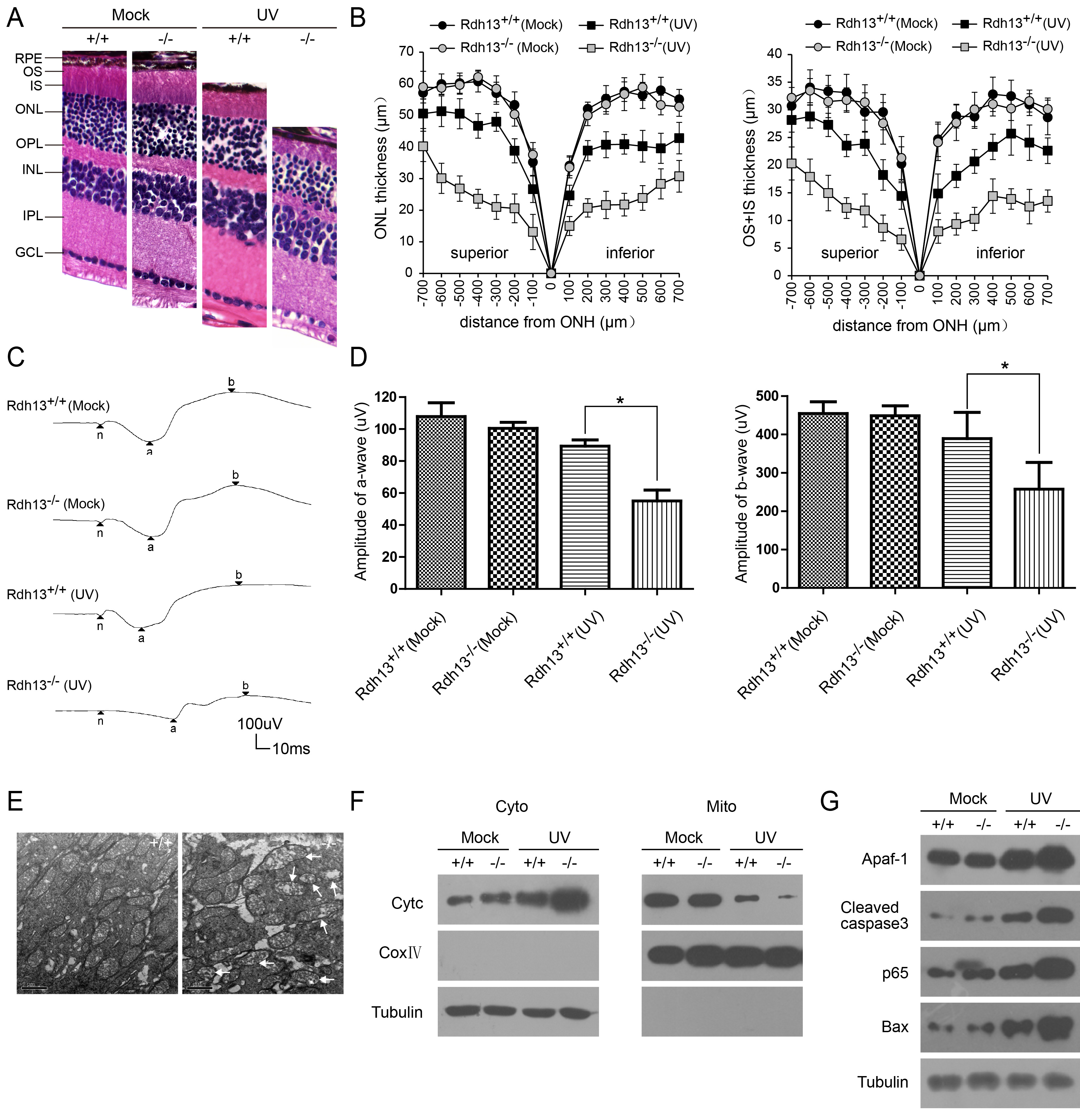
 Figure 5
of Wang, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1021-1030.
Figure 5
of Wang, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1021-1030.  Figure 5
of Wang, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1021-1030.
Figure 5
of Wang, Mol Vis 2012; 18:1021-1030. 