Figure 1. Corneal NV induced by alkali
burn. A: slit-lamp photograph of corneal NV on the 10th and
14th days after chemical cauterization. The NV of the PBS-treated group
was dense, fine, and almost reached to the central cornea. The NV of
all KH906-treated groups and the Avastin-treated group was less dense
and shorter than that of the PBS group. The inhibitive effect on NV in
the dexamethasone-treated group was the best. B: The length of
the longest vessel in all groups on the 10th and 14th days. The mean
length of the longest new vessel in all medicine-treated groups was
shorter than that of the PBS control group on both the 10th and 14th
days after cauterization (p<0.05). The vessel length was shortest in
both the dexamethasone-treated group and the KH906 (20 mg/ml)-treated
group, and there was a statistically significant difference between the
two groups and the other groups on the 10th day (p<0.05). Meanwhile,
only the length of the longest vessel in the dexamethasone-treated
group differed significantly from those of the other medicine-treated
groups on the 14th day (p<0.05). C: Area of corneal NV in
all groups on the 10th and 14th days. The change in the area of corneal
NV showed the same trend as that of the length of the longest new
vessel. PBS: PBS, DEX: dexamethasone, AV: Avastin, K-5:KH906 (5 mg/ml),
K-10:KH906 (10 mg/ml), K-20:KH906 (20 mg/ml). *There is a statistically
significant difference between groups with a *symbol and groups without
a *symbol. #There is a statistically significant difference between
groups with a #symbol and groups without a #symbol.
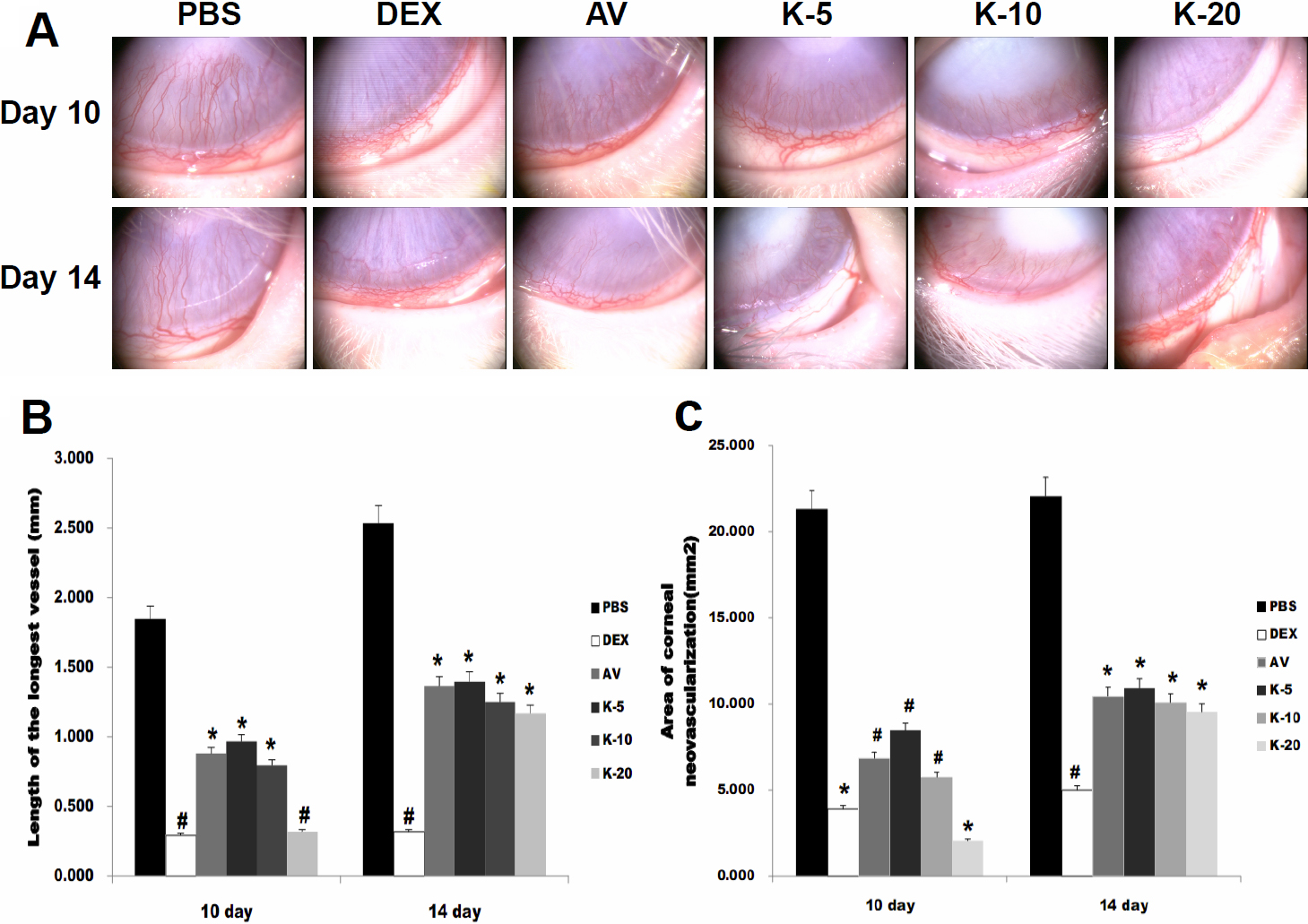
 Figure 1 of Li, Mol Vis 2011; 17:797-803.
Figure 1 of Li, Mol Vis 2011; 17:797-803.  Figure 1 of Li, Mol Vis 2011; 17:797-803.
Figure 1 of Li, Mol Vis 2011; 17:797-803. 