Figure 4. BBS4 is required for
normal zebrafish development and rhodopsin localization. A:
Representative examples of whole-mounted wild-type (WT) embryos,
morpholino-injected (MO) embryos, embryos injected with
wild-type (wt) or mutant (mut) human BBS4 mRNA, or
embryos coinjected with morpholino and mRNA. Dorsal view (top
row) and lateral view (bottom row) are shown of embryos at the
12–14 somite stage following in situ hybridization with pax2a
and myoD riboprobes. Embryos were categorized
phenotypically based on shortened body axis (anterior and
posterior ends marked by red triangles) and notochord defects
(red arrow). B: Quantification of the efficiency of
rescue from gastrulation defects following coinjection of BBS4
morpholino (MO) and mRNA. The number of animals analyzed for
each group is noted above each bar. C: Retinal
cryosections of 5 dpf zebrafish retinas stained for rhodopsin
(red). White arrows indicate rhodopsin mislocalization (Scale
bar=10 μm).
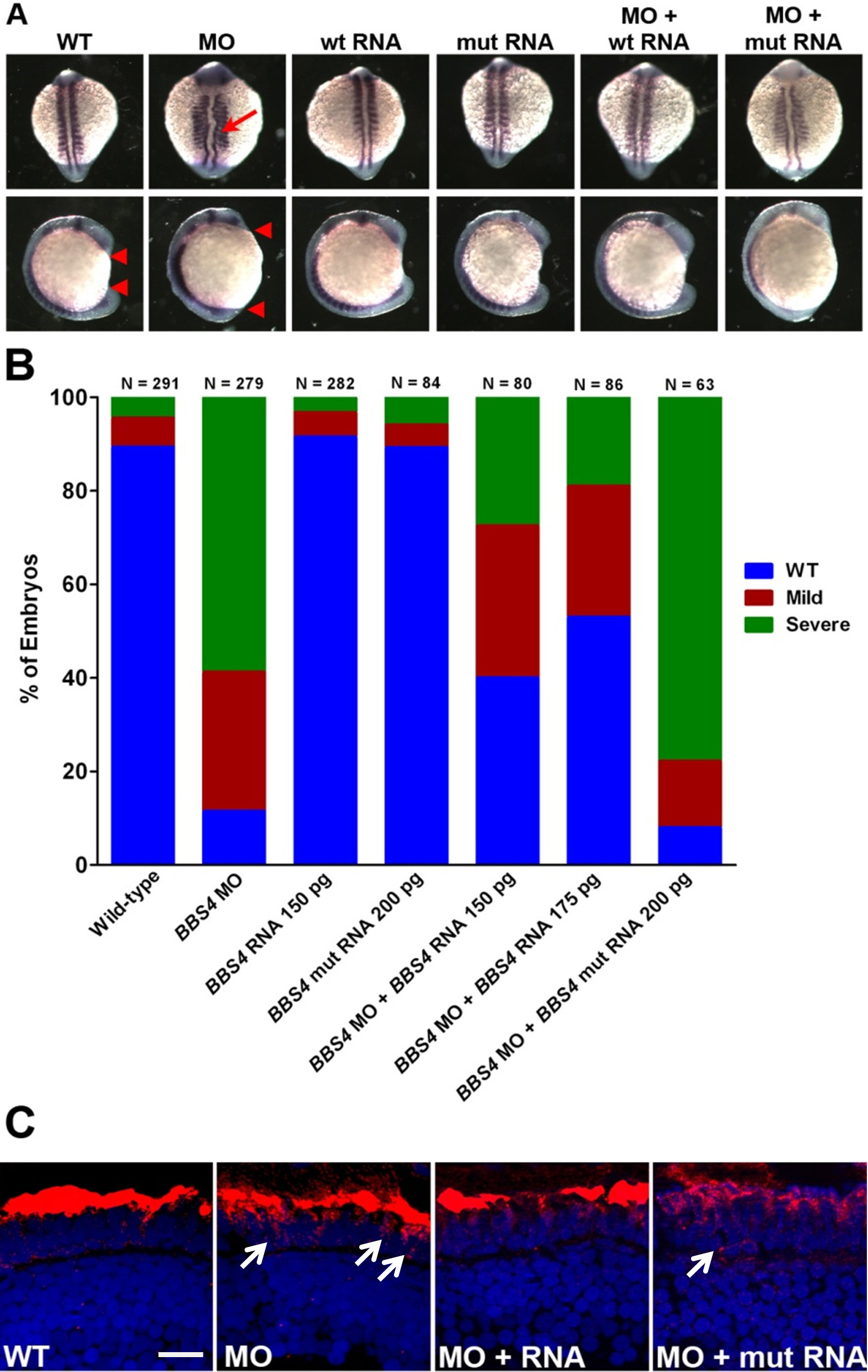
 Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3529-3540.
Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3529-3540.  Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3529-3540.
Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3529-3540. 