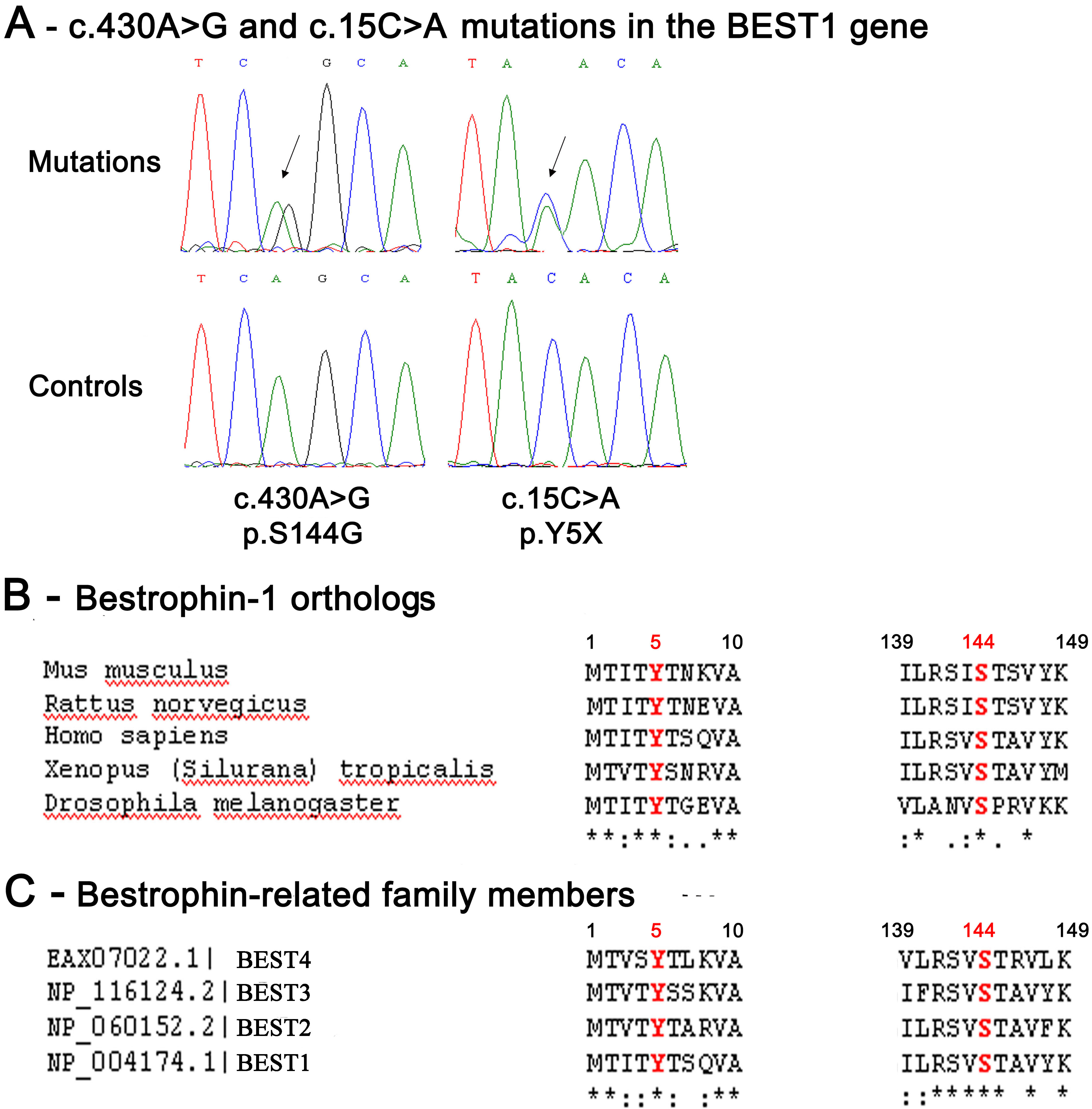
Figure 2. Two novel nucleotidic mutations
in the
BEST1 gene. Electrophoregrams of the
BEST1 gene
mutations found in the affected members of the French family studied
and phylogenetic conservation throughout evolution of the normal BEST-1
amino-acid residues affected by these mutations.
A: These
electrophoregrams show heterozygous mutated nucleotides in the
BEST1
gene: An adenine (A) is replaced by a guanine (G) at the 430th
nucleotidic position of the
BEST1 cDNA sequence (c.430A>G)
and and a cytosine (C) is replaced by an adenine (A) at the 15th
nucleotidic position of the
BEST1 cDNA sequence (c.15C>A)
(top panel), and normal sequences (low panel). The peaks in red
indicate thymidine (T), green indicate A, black indicate G, and blue
indicate C.
B: This panel shows the multiple sequence alignment
of human bestrophin-1 protein (BEST-1 protein;
NP_004174) with
the BEST-1 protein sequences from
Mus musculus (
NP_036043.2),
Rattus norvegicus (
NP_001011940.1),
Xenopus tropicalis (
BAH70274.1),
and
Drosophila melanogaster (
AAF54503.1).
This multiple sequence alignment highlights the strong conservation
throughout evolution of the amino-acid residues of the normal BEST-1
protein which were found affected by mutations in this study.
C:
This
panel shows the multiple sequence alignment of the human BEST1
protein with the bestrophin paralogs: BEST2, BEST3, and BEST4.
Alignments are zoomed into the relevant region. The amino- acids
affected by a mutation are shown in red. The stars indicate 100%
conservation.
 Figure 2 of Lacassagne, Mol Vis 2011; 17:309-322.
Figure 2 of Lacassagne, Mol Vis 2011; 17:309-322.  Figure 2 of Lacassagne, Mol Vis 2011; 17:309-322.
Figure 2 of Lacassagne, Mol Vis 2011; 17:309-322.