Figure 2. Dose-dependent effects of lutein supplementation on protein and lipid oxidations. Subconfluent human lens epithelial cells
were incubated with 0, 1, or 5 µM lutein for 48 h to allow the cells to accumulate lutein. The cells were then treated with
or without 100 µM H2O2 for 1 h. Levels of protein carbonyl and MDA in the cells were determined as described in the “Methods.” A: The effects of lutein supplementation on protein carbonyl in HLEC that were not exposed to H2O2. B: The effects of lutein supplementation on protein carbonyl in HLEC that were exposed to 100 µM H2O2 for 1 h. C: Densitometry quantification of western-blotting results in B (n=3). D: The effects of lutein supplementation on MDA levels (n=6), *Indicates a p<0.05 when comparing H2O2-exposed groups to the control group that were not treated with H2O2 and **indicates a p<0.05 when comparing lutein supplemented groups to the unsupplemented group upon exposure to 100 µM H2O2 for 1h.
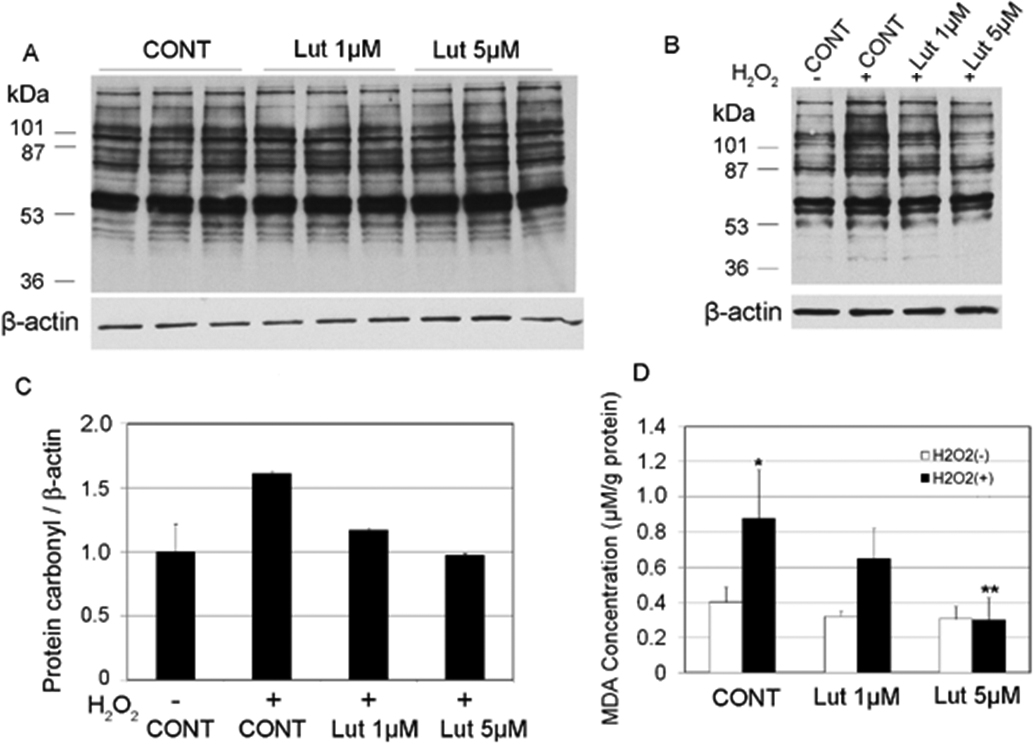
 Figure 2 of
Gao, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3180-3190.
Figure 2 of
Gao, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3180-3190.  Figure 2 of
Gao, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3180-3190.
Figure 2 of
Gao, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3180-3190. 