Figure 4. Positive feedback control
of JNK1 phosphorylation by NF-κB through DUSP1. A:
Time-dependent increases in p- IκBα. Scrambled shRNA subline was
exposed to CAP (20 µM) for up to 90 min. Western blots reveal
the time course of changes in p-IκBα formation, which serves as
a readout of NF-κB activation. B: Contribution by JNK1
to IκBα phosphorylation. Western blots compare CAP (20
µM)-induced IκBα phosphorylation in scrambled shRNA and JNK1
sublines at 60 min. Preincubation with either 5z-OX (0.1 µM),
CPZ (10 µM) or PDTC (50 µM) for 60 min suppressed CAP-induced
IκBα phosphorylation. C: Positive feedback control by
NF-κB of JNK1/2 activation. Loss of NF-κB activation reduces
transient JNK1/2, p38, and ERK1/2 MAPK activation induced by CAP
(20 µM) for up to 90 min. Summary plots contrast time-dependent
patterns of MAPK activation in the scrambled shRNA subline
(left) with those in NF-κB1 subline (right). D: Inverse
relationship between changes in PKCδ and DUSP1 expression.
Scrambled shRNA and NF-κB1 sublines were exposed to CAP (20 µM)
as described in B. Summary plot (left) indicates that in
the scrambled shRNA subline CAP-induced increases in PKCδ
expression whereas DUSP1 remained invariant (left). Summary plot
(right) reveals inverse responses by PKCδ and DUSP1 to CAP in
NF-κB1 subline.
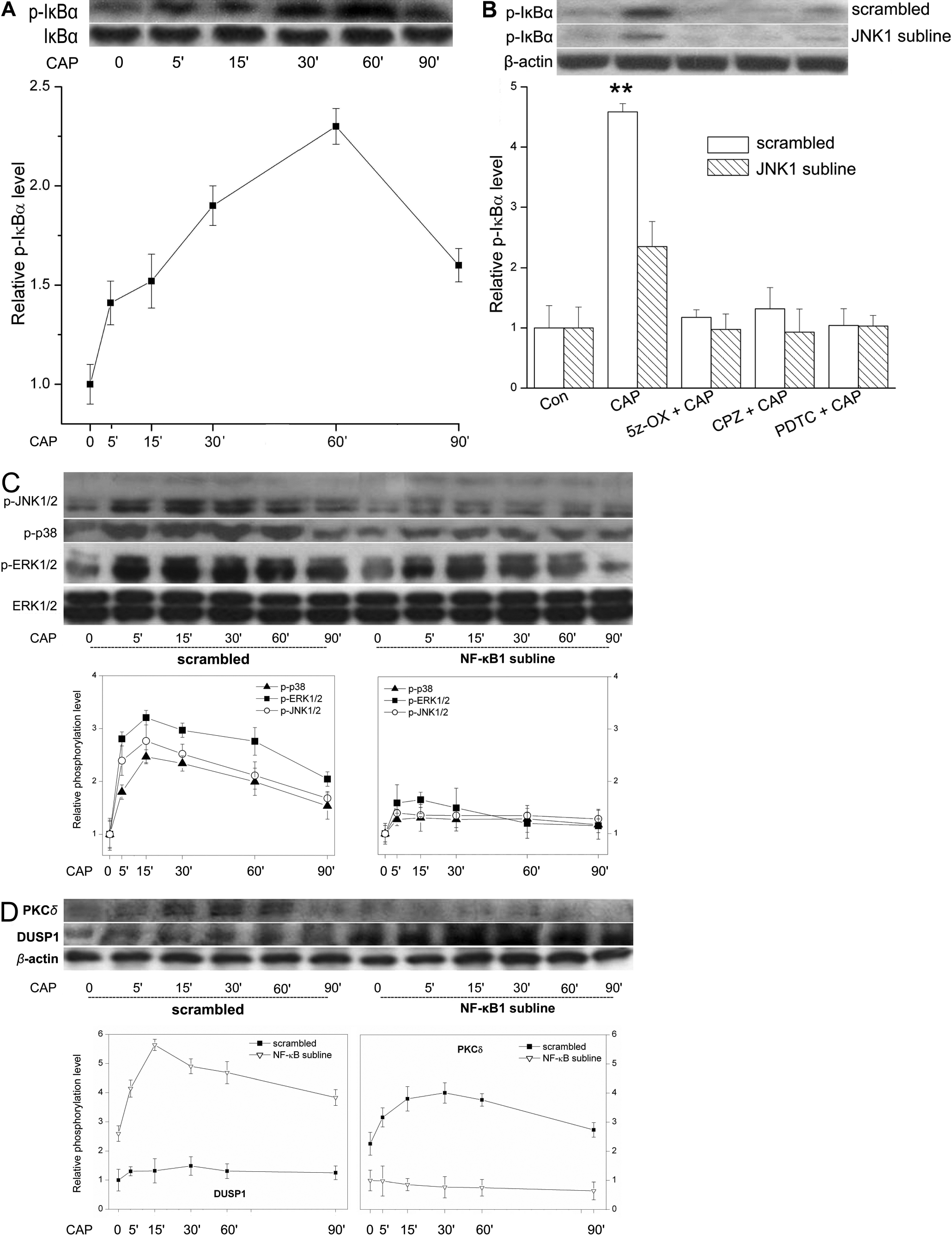
 Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3137-3146.
Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3137-3146.  Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3137-3146.
Figure 4
of Wang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3137-3146. 