Figure 2. Analysis of wild type HSF4b
and mutant HSF4blop11 proteins. A: western
blot of nuclear extracts transfected with wild type Hsf4b
or Hsf4blop11 clones. B: EMSA showed
absence of HSE-DNA binding of HSF4blop11 when
compared to wild type HSF4b. A negative control was a binding
reaction with nuclear extracts following transfection with an
empty vector (pcDNA3.1; lanes 1 and 6). Labeled HSE and
wild-type HSF4b (lane 2) form a complex (arrow). Specificity of
HSF4b binding to HSE was determined by a specific competition
with cold HSE (lane 3), nonspecific competition by addition of
unlabeled SP1 (lane 4) and supershift (asterisk) by addition of
His-antibody (lane 5). Nuclear extracts from cells transfected
with Hsf4blop11 did not result in HSE-DNA
binding in the presence of labeled HSE (lane 7), presence of
labeled and unlabeled HSE (lane 8), presence of labeled HSE and
unlabeled SP1 (lane 9) and labeled HSE and His-antibody (lane
10). C: Transactivation of HSE-reporter in HEK293 cells
by wild type HSF4b and HSF4blop11 proteins.
Luciferase values were normalized to β-galactosidase activity,
averaged for three separate transfections and expressed relative
to the ration for wild-type Hsf4b. Error bars represent
SEM. Asterisk indicates samples with a significant difference
(p<0.05; t-test) calculated from comparison with
wild-type. D: western blot analysis of lens protein
extracts from P7 wild type (wt) and lop11 lenses
immunobloted with CRYAB-antibody (top panel) showing severely
reduced CRYAB levels in lop11 lenses. The molecular mass
is indicated to the right of each blot. Even loading was
confirmed by immunobloting with β-actin (bottom panel).
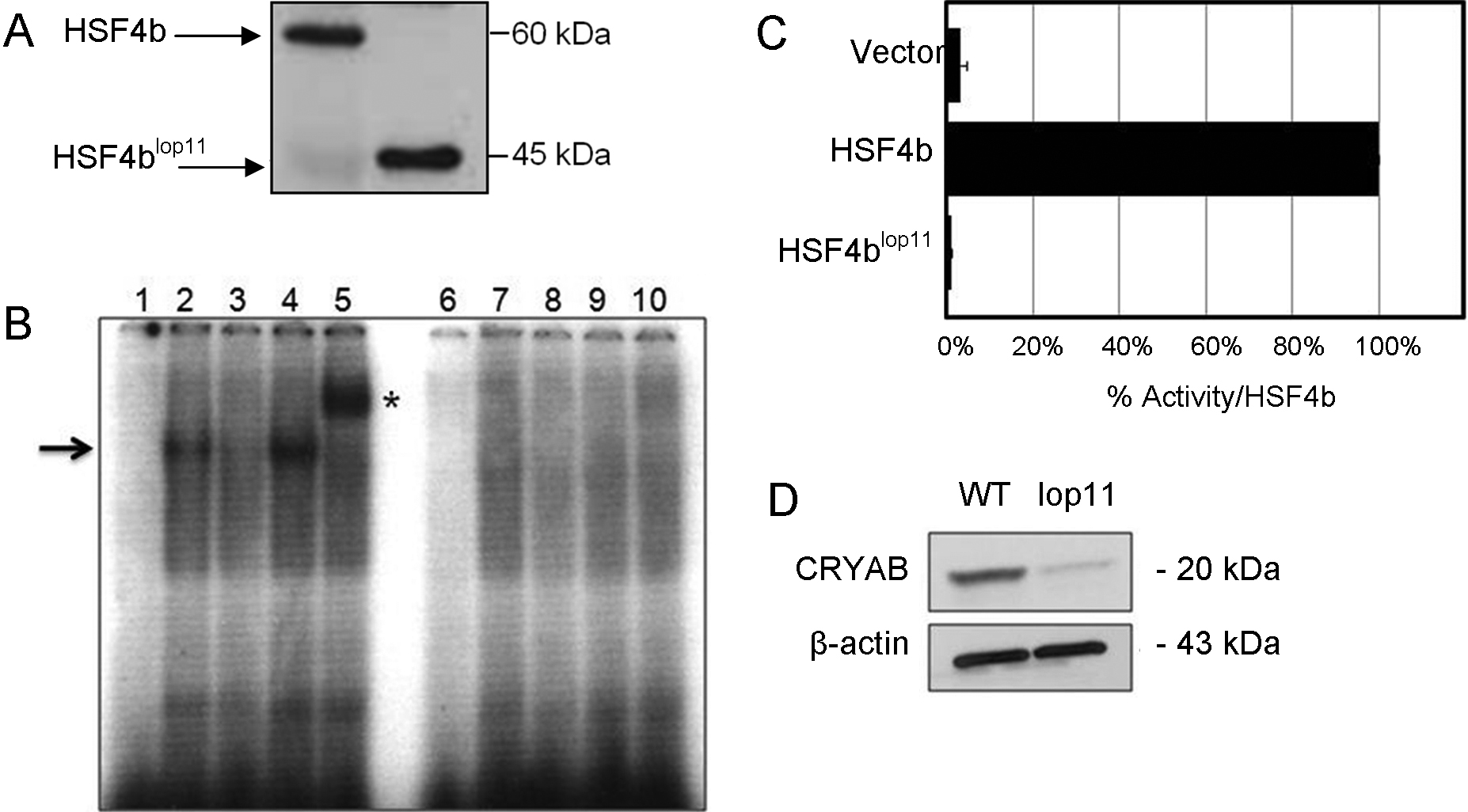
 Figure 2
of Liang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3062-3071.
Figure 2
of Liang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3062-3071.  Figure 2
of Liang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3062-3071.
Figure 2
of Liang, Mol Vis 2011; 17:3062-3071. 