Figure 1. Representative images of
slit-lamp photographs, 1310 nm time-domain and 1310 nm swept
source spectral domain optical coherence tomography scans of
patients with granular corneal dystrophy type I (family F4),
granular corneal dystrophy type II (family F9), and Thiel-Behnke
corneal dystrophy (family F8). A: Female patient (F4; 53
years). Slit-lamp photograph showing gray-white granular
deposits located centrally, with clear intervening stroma. GCDI/
R555W mutation. B: Female patient (F4; 53 years).
High-resolution corneal scan – 1310 nm time. domain OCT. Focal
granular hyperreflective changes located at different depths
within the corneal stroma. GCDI/ R555W mutation. C:
Female patient (F4; 53 years). Radial scan-swept source 1310 nm
spectral OCT. Focal granular hyperreflective changes located at
different depths within the corneal stroma. The Bowman’s layer
area shows a distinct irregularity. GCDI/ R555W mutation. D:
Female patient (F9; 44 years). Slit-lamp photograph. Centrally
located, multiform: star- and disc-shaped opacities. No lattice
lines are visible, either on direct light nor on
retroillumination. GCDII/ R124H mutation. E: Female
patient (F9; 44 years). High-resolution corneal scan – 1310 nm
time domain OCT. Highly reflective opacities with distinct
borders located in the anterior corneal part. GCDII/ R124H
mutation. F: Female patient (F9; 44 years). Radial
scan-swept source 1310 nm spectral OCT. Highly reflective
disc-shaped changes located in the anterior stroma, under the
epithelium, involving Bowman’s layer. One hyperreflective
granular opacity located deeper in the mid stroma. GCDII/ R124H
mutation. G: Female patient (F8; 38 years). Slit-lamp
photograph. Diffuse corneal changes showing reticular,
“honeycomb” pattern located in the anterior corneal part. TBCD/
R555Q mutation. H: Female patient (F8; 38 years).
High-resolution corneal scan – 1310 nm time domain OCT. The
diffuse boarder of increased reflectivity in the anterior part
of the cornea (arrowheads). In the Bowman’s layer area, there is
a distinct irregularity due to corneal opacities (arrows). TBCD/
R555Q mutation. I: Female patient (F8; 38 years). Radial
scan-swept source 1310 nm spectral OCT. Bowman’s layer is
replaced by an irregular pattern of opacities. TBCD/R555Q
mutation.
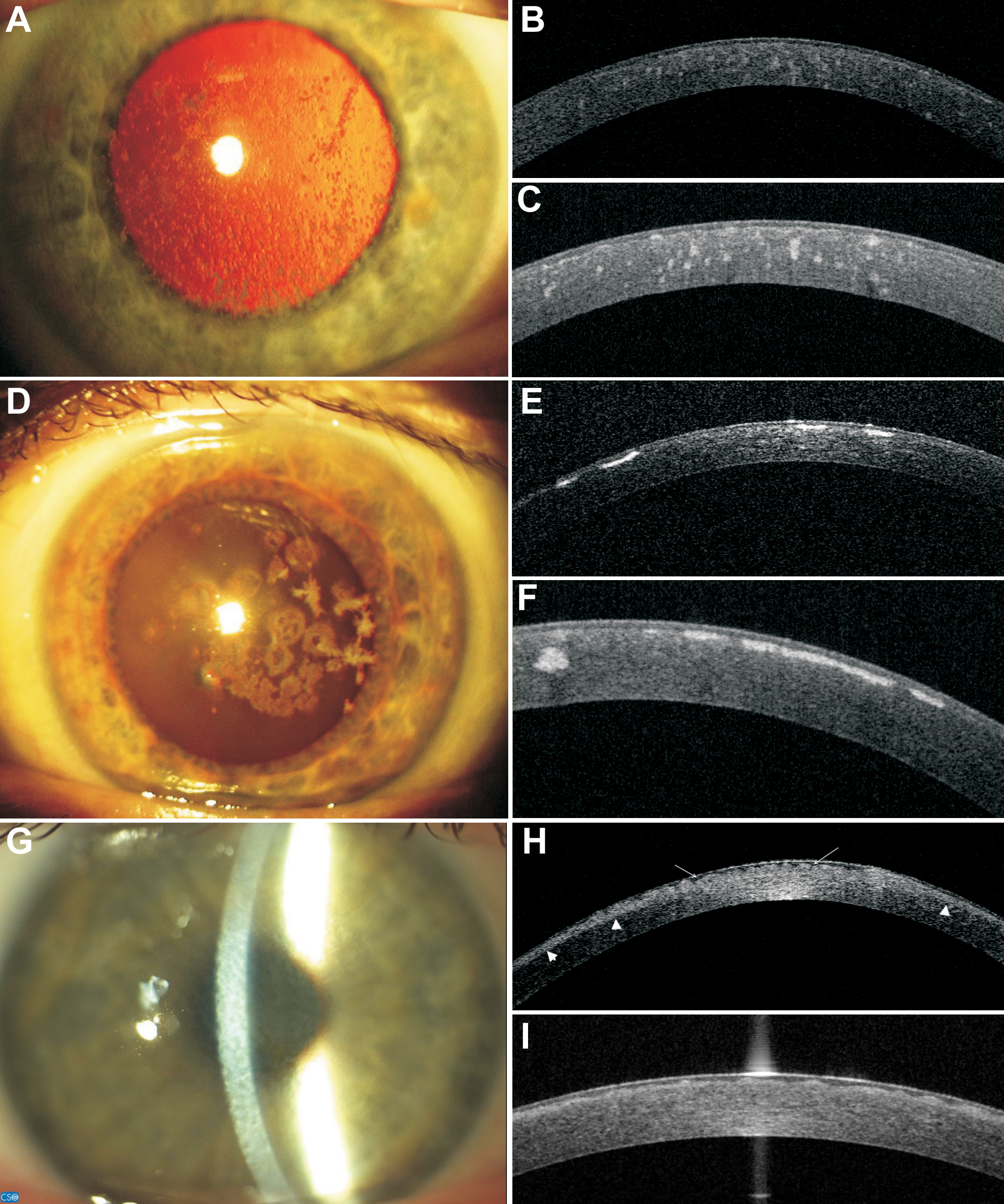
 Figure 1
of Nowińska, Mol Vis 2011; 17:2333-2342.
Figure 1
of Nowińska, Mol Vis 2011; 17:2333-2342.  Figure 1
of Nowińska, Mol Vis 2011; 17:2333-2342.
Figure 1
of Nowińska, Mol Vis 2011; 17:2333-2342. 