Figure 1. Clinical features and genetic analysis. A: Ashkenazi Jewish family pedigree affected by Hereditary Hyperferritinemia Cataract Syndrome. B: Slit-lamp retroilluminative view of the lens discloses nuclear cataract with prominent Y sutures. C: DNA sequence analysis of the IRE (iron responsive element) part of FTL (ferritin light chain). A heterozygous G→C change in the 5`-untranslated region (5`-UTR) at position +32 from transcription
start site (c. −168G→C), is indicated by black arrow. D: Persian Jewish family pedigree affected by congenital cataract (no photograph available) and phenotype ii. E: DNA sequence analysis showing a homozygous G → A transition (indicated by black arrow) at cDNA position 935, resulting in
a change of Glycine to Aspartic acid (p.G312D) of all three isoforms of GCNT2.
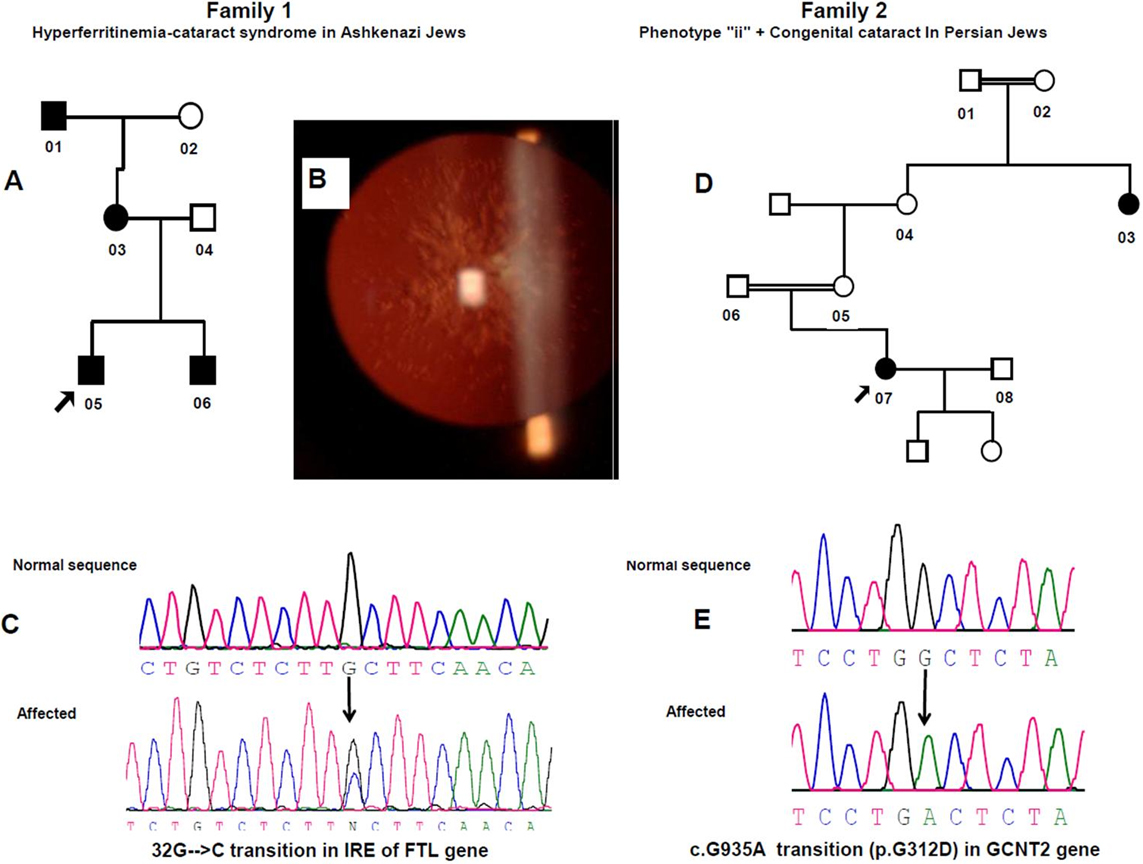
 Figure 1 of
Wussuki-Lior, Mol Vis 2011; 17:1011-1015.
Figure 1 of
Wussuki-Lior, Mol Vis 2011; 17:1011-1015.  Figure 1 of
Wussuki-Lior, Mol Vis 2011; 17:1011-1015.
Figure 1 of
Wussuki-Lior, Mol Vis 2011; 17:1011-1015. 