Figure 2. Localization of NKCC1 and NCC
expression in the rat lens. Equatorial cryosections doubled-labeled
with either NKCC1 or NCC specific antibodies (green), and the membrane
marker TRITC-WGA (red). A: Image montage of the NKCC1 labeling
pattern from the periphery to the core of the lens. B-D:
High-powered images of areas indicated in A. B: In the
lens periphery labeling for NKCC1 in the epithelial and peripheral
fiber cells is predominately cytoplasmic in nature although some
membrane labeling is evident (insert). C: NKCC1 antibody
labeling is lost 350–400 μm in from the capsule. D: No NKCC1
labeling was found in the lens core. E: Image montage of the
NCC labeling pattern from the periphery to the core of the lens. F-H:
High-powered
images of areas indicated in E. F: In the
lens periphery labeling for NKCC1 in the epithelial and peripheral
fiber cells is predominately cytoplasmic in nature although some
membrane labeling is evident (insert). G: Image of the
transition zone showing a shift of NCC labeling from the cytoplasm to
the membrane. H: NCC in the core is strongly associated with
fiber cell membranes. I-J: High-powered images of the
outer cortex (OC), inner cortex (IC) and core (C), respectively, in
which sections were labeled with the NCC antibody preabsorbed with its
antigenic peptide.
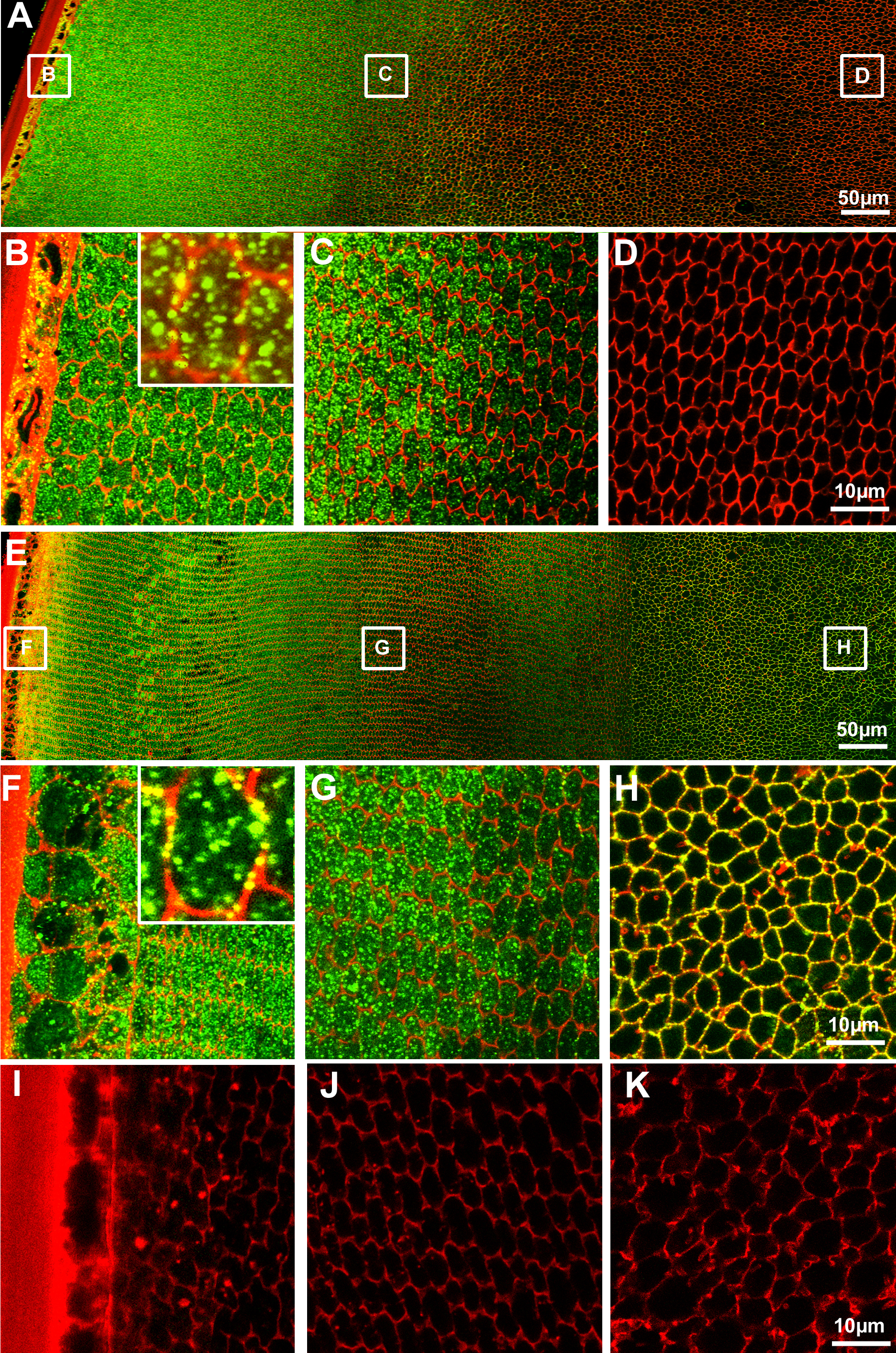
 Figure 2 of Chee, Mol Vis 2010; 16:800-812.
Figure 2 of Chee, Mol Vis 2010; 16:800-812.  Figure 2 of Chee, Mol Vis 2010; 16:800-812.
Figure 2 of Chee, Mol Vis 2010; 16:800-812. 