Figure 2. Optic nerve crush decreased AQP4
protein and mRNA levels. Following retinal injuries with optic nerve
crush, retinas were dissected and plasma membrane proteins were
isolated or total RNA was isolated and transcribed into cDNA. Thirty
microgram protein was loaded into each lane. Immunoreactive bands for
AQP4 and β-tubulin 2, 7, and 14 days after optic nerve crush showing a
significant reduction in AQP4 protein levels. Quantitative measurement
using western blot showed that optic nerve crush decreased AQP4 protein
levels by ~40% (60±10, 63±10, 38±10, at 2, 7, and 14 day, respectively,
n=7, A). Densitometric quantification is shown in B.
Data are expressed as a ratio of the treated to control or sham value
and each measurement represents mean±SEM *Denote statistical
significance of AQP4 protein levels in optic nerve crushed retinas
versus sham (p<0.005) as determined by one-way ANOVA and Tukey
multiple comparison test. Optic nerve crush also decreased AQP4
transcripts significantly (61±5%, 60±8%, 58±6, at 2, 7, and 14 day,
respectively, n=7), as determined by quantitative real-time PCR (B).
Gene
expression data of AQP4 is calculated after normalizing
with ACTB. **Denote significant differences compared with
sham-retinas at p<0.05. Abbreviations: sham eye (C), and crushed (R).
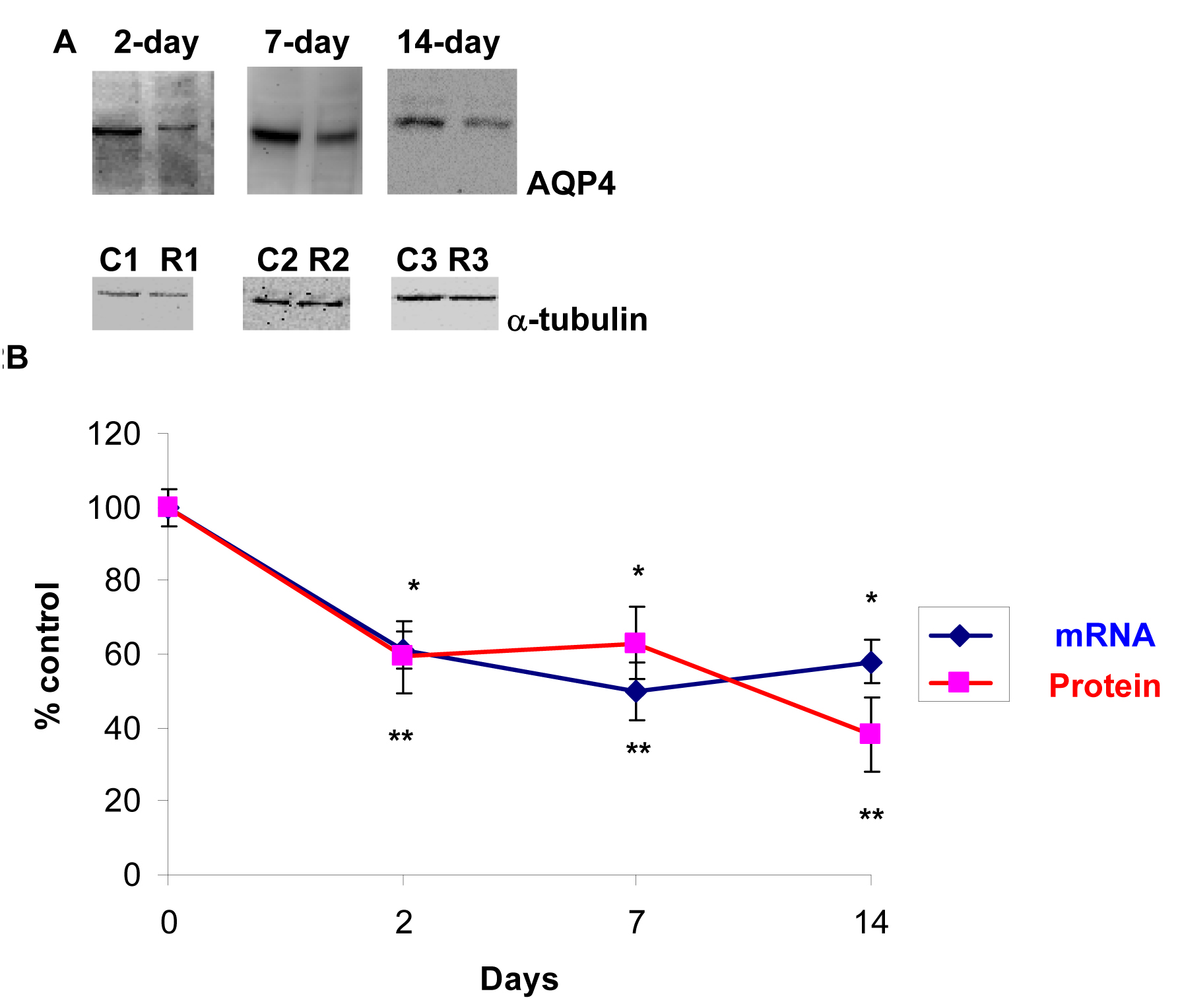
 Figure 2 of Dibas, Mol Vis 2010; 16:330-340.
Figure 2 of Dibas, Mol Vis 2010; 16:330-340.  Figure 2 of Dibas, Mol Vis 2010; 16:330-340.
Figure 2 of Dibas, Mol Vis 2010; 16:330-340. 