Figure 4. Co-localization of
Nε-(3-formyl-3,4-dehydropiperidino)lysine (FDP-lysine) and glial
fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the diabetic retina. Retinal
sections from nondiabetic (NonDb) and diabetic (Db) rats were labeled
with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) nuclear stain (A and E),
GFAP
(B and F), and FDP-lysine (C and G).
In the nondiabetic retina, GFAP immunoreactivity was selectively
localized to astrocytes at the inner retinal surface. In diabetes,
Müller cells acquired prominent GFAP immunoreactivity within their end
feet at the vitreoretinal border and throughout their radial processes
spanning from the inner to the outer limiting membranes. D and H:
In
merged images, FDP-lysine was found to co-localize strongly with
GFAP in the retina of diabetic but not nondiabetic rats. The scale bars
indicate 50 μm.
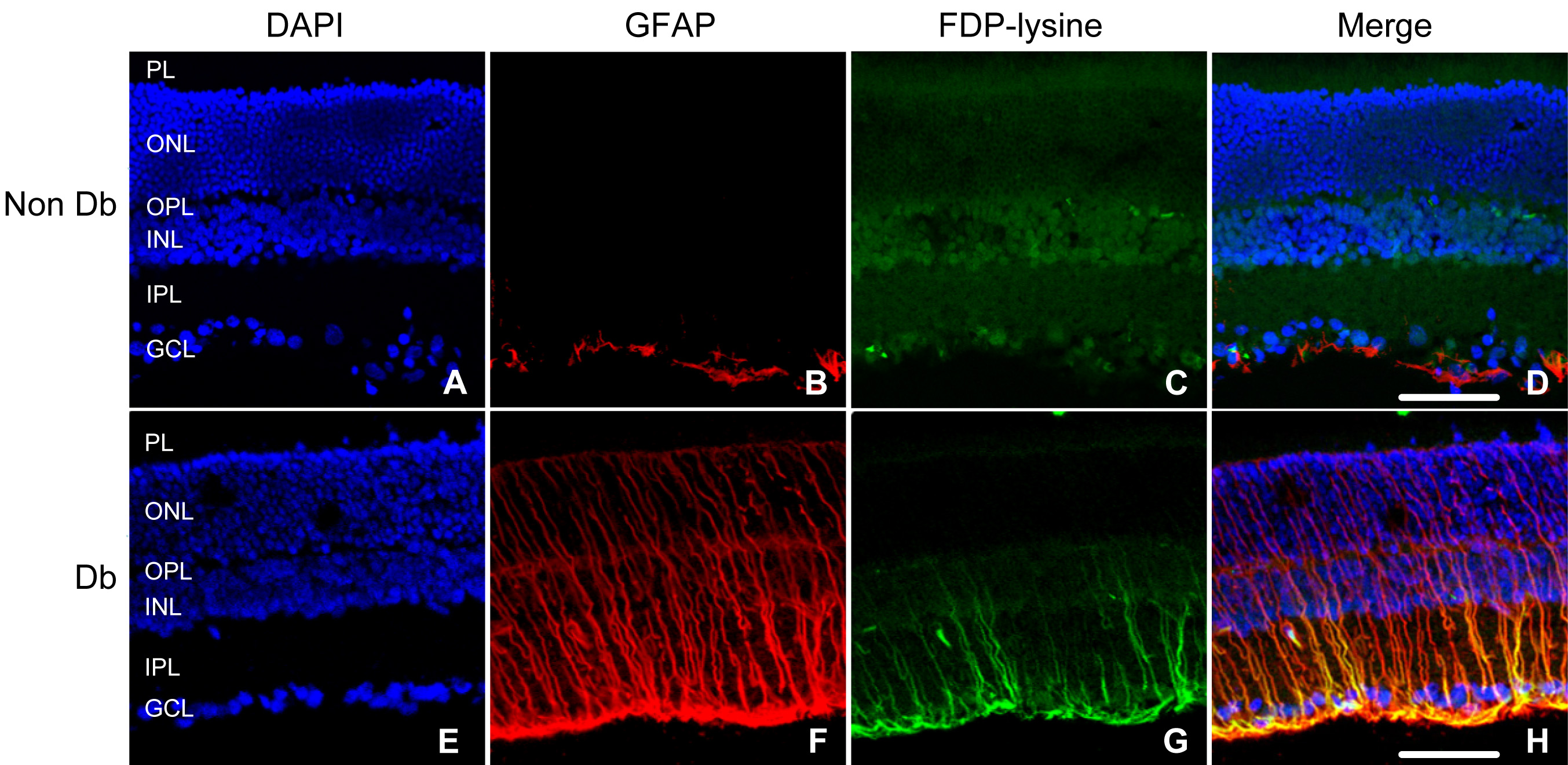
 Figure 4 of Yong, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2524-2538.
Figure 4 of Yong, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2524-2538.  Figure 4 of Yong, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2524-2538.
Figure 4 of Yong, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2524-2538. 