Figure 1. Structure of the eye and
cellular lens; organization of vertebrate lenses. Small cuboidal
epithelial cells cover the anterior surface. At the anterior/posterior
equator, these cells exit the cell cycle and begin to elongate as they
move into the interior. A few hundred microns into the lens, fiber
cells undergo a final stage of terminal differentiation where they lose
cell nuclei and organelles. At right is a histological section of an
adult mouse eye.
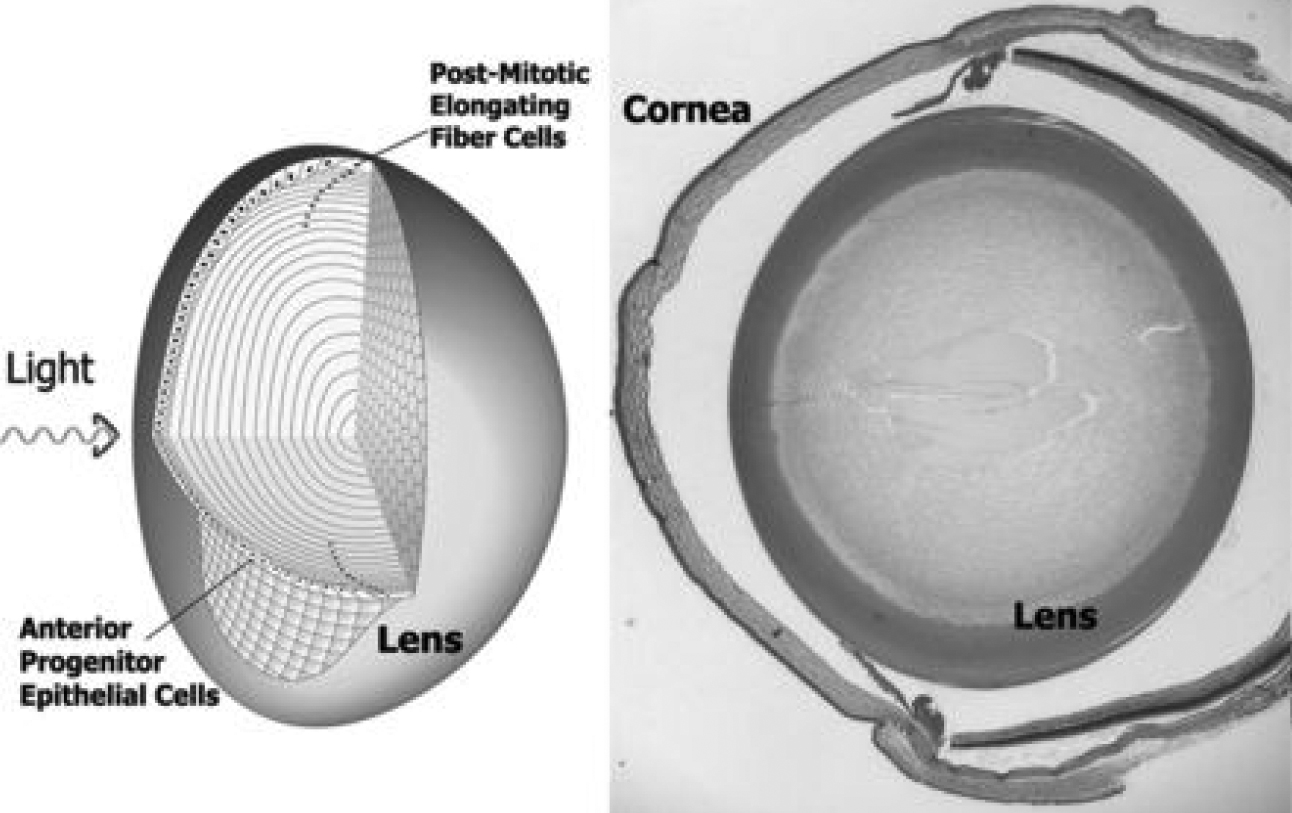
 Figure 1 of Bitel, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2301-2316.
Figure 1 of Bitel, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2301-2316.  Figure 1 of Bitel, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2301-2316.
Figure 1 of Bitel, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2301-2316. 