Figure 1. Morphology of the canine retina.
Morphology of the peripheral retina in a healthy dog (A) and dog
with advanced glaucoma (B). Glaucomatous changes include
dramatic loss of cells in the retinal nerve fiber layer, ganglion cell
layer and inner nuclear layer compared to healthy eyes. In the
glaucomatous retina GFAP can readily be detected in retinal glial cells
(arrows) and indicates extensive gliosis in the nerve fiber layer. GFAP
can also be detected in the NFL of normal eyes when extended periods of
color development are used. (NFL-nerve fiber layer, RGC-retinal
ganglion cell layer, IPL-inner plexiform layer, INL-inner nuclear
layer, OPL-outer plexiform layer, ONL-outer nuclear layer,
OS-Photoreceptor cell outer segments).
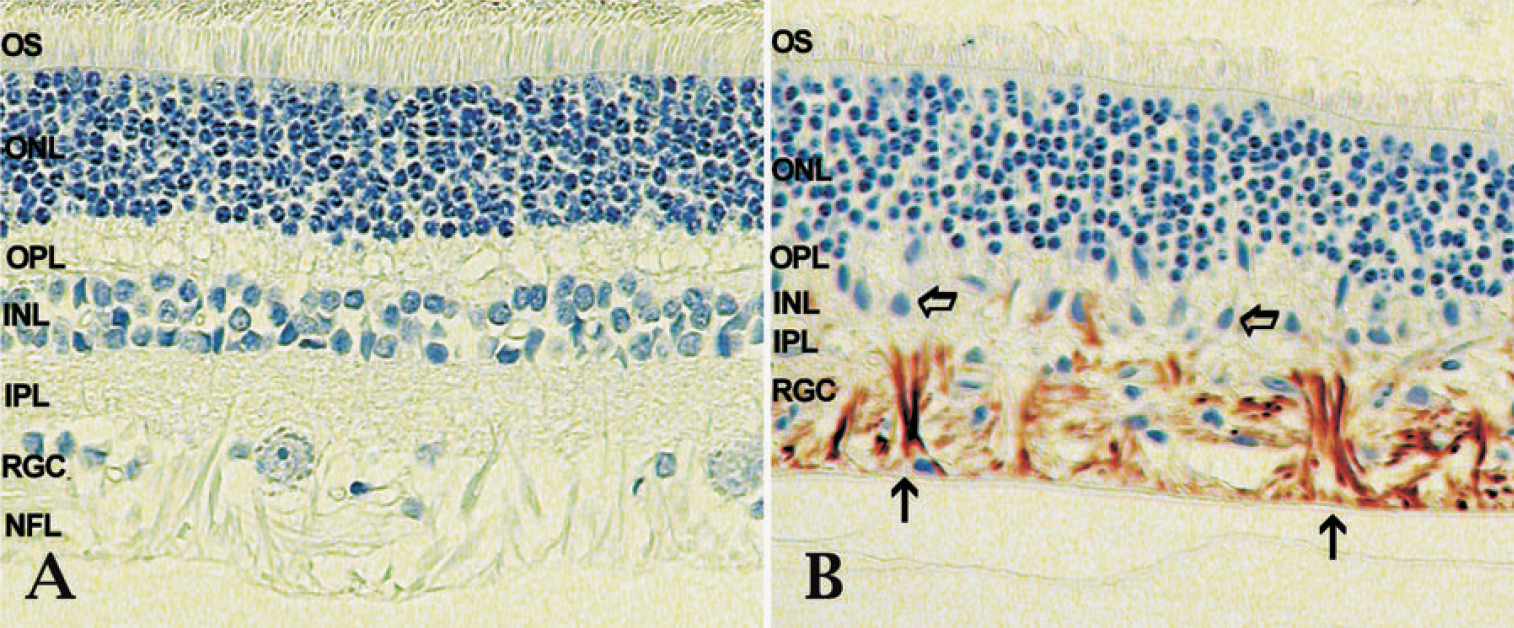
 Figure 1 of Jiang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2092-2108.
Figure 1 of Jiang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2092-2108.  Figure 1 of Jiang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2092-2108.
Figure 1 of Jiang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2092-2108. 