Figure 3. As a tyrosine kinase inhibitor,
genistein mitigates tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) release in
stimulated retinal microglia cells. A: Genistein’s
dose-dependent inhibition of TNF-α release from activated microglia.
Cells were treated with (500 μg/ml) glycated albumin for 4 h in the
presence of indicated concentrations of genistein. TNF-α released was
analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Values represent
the means percentage±SD of TNF-α release compared with that of glycated
albumin-treated in presence of vehicle for three experiments. B:
Genistein
also
had
no effect on cell viability, as determined by trypan
blue exclusion test. C: Time-dependent, glycated
albumin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation in microglial cells. Cells
were treated with (500 μg/ml) glycated albumin in the presence or
absence of 100 µM genistein for the indicated time. Phosphorylated
tyrosine was determined by Western analysis. Intensities of
phosphorylated tyrosine for each time points were compared with the
control (time 0). Data shown is the mean±SD of three experiments. *
p<0.001 compared with 0 time; $ p<0.001 compared with
non-genistein treated, 1 h; # p<0.001 compared with non-genistein
treated, 4 h.
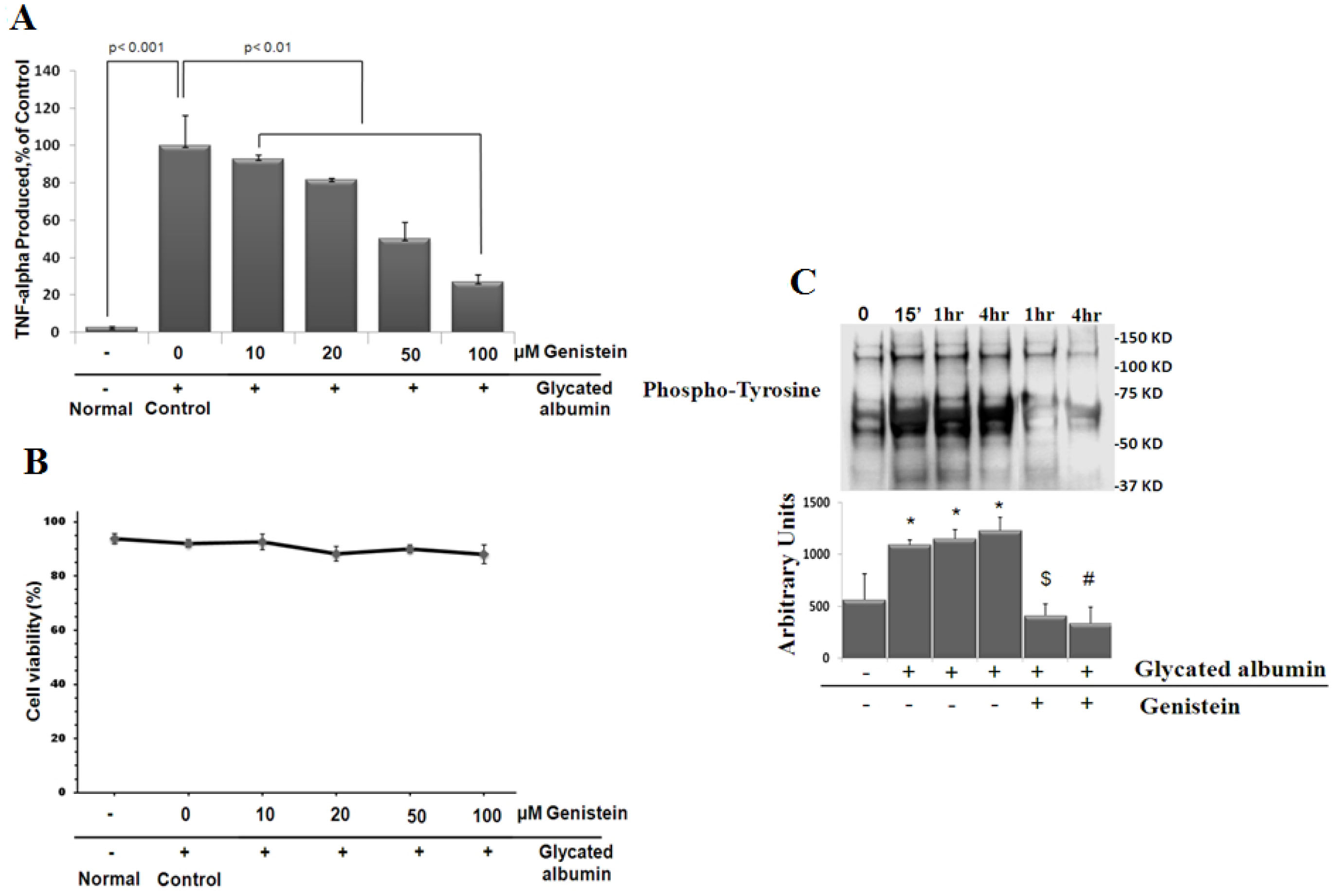
 Figure 3 of Ibrahim, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2033-2042.
Figure 3 of Ibrahim, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2033-2042.  Figure 3 of Ibrahim, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2033-2042.
Figure 3 of Ibrahim, Mol Vis 2010; 16:2033-2042. 