Figure 5. Schematic description of proposed nuclear events associated with the transductions performed in this study. Erk1/2 phosphorylation
causes nuclear translocation and activation of transcription factors that facilitate the G1 to S transition. JNK phosphorylation causes nuclear translocation and activation of antiproliferative events at some stage
of the cell cycle (indicated by gray lines). The proliferation-enhancing event is blocked by pErk/2 dephosphorylation, by
DUSP6 in the cytosol and DUSP5 and DUSP1 in the nuclei. The latter DUSP though, blocks JNK1/2 phosphorylation with high efficiency
nullifying its pro-proliferative action.
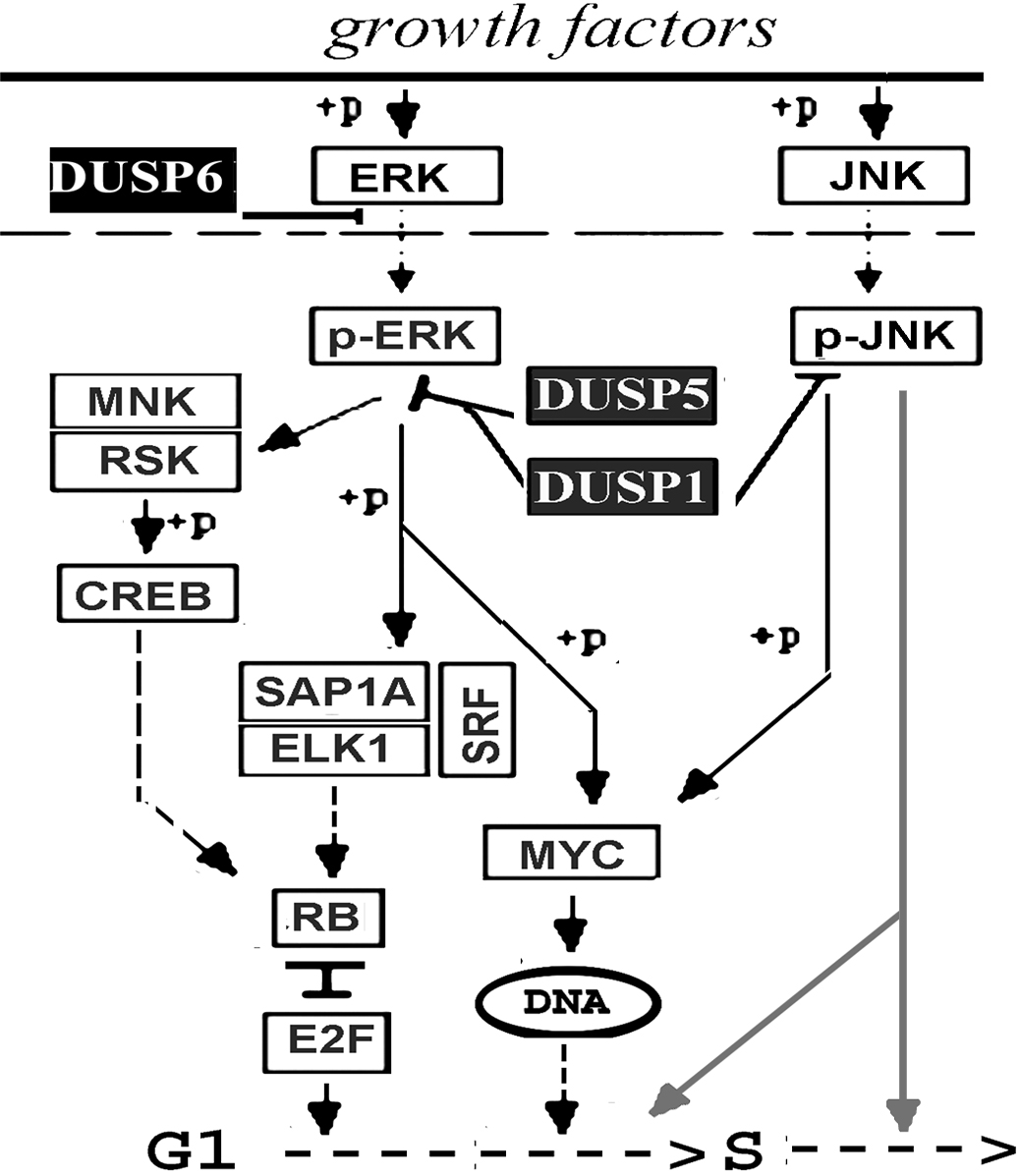
 Figure 5 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:1696-1704.
Figure 5 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:1696-1704.  Figure 5 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:1696-1704.
Figure 5 of
Wang, Mol Vis 2010; 16:1696-1704. 