Figure 2. Cellular activities of cluster
differentiation (CD)44, vimentin (VIM), and glial fibrillary acidic
protein (GFAP) promoters in chicken retina. Lentiviral vectors were
injected into the ventricles of chicken embryos (embryonic day 2–E2) in
ovo. The retinas of the injected embryos were harvested on E19–20 and
the cells expressing the fluorescent reporter proteins were identified
using native fluorescent and immunofluorescent microscopy. The viruses
injected were as follows: A-I pFIN-CD44-GFP-WPRE; J-Q
pFM-VIM-GW; R-V pFM-GFAP-GW. All sections were counterstained
with DAPI, and all scale bars shown equal 50 µm. Abbreviations are as
follows: ONL represents outer nuclear layer; INL represents inner
nuclear layer; IPL represents inner plexiform layer; GCL represents
ganglion cell layer. CD44: A: Photograph of whole mount of
retina that had been treated with pFIN-CD44-GFP-WPRE. Clusters of
GFP-positive photoreceptors (arrows) were detected across the surface
of the whole mount. B: This image was produced by
re-photographing the boxed region shown in A using a focal plane just
below that used to obtain the image shown in A. Horizontal cells
(asterisks) were the predominant GFP-positive cell type observed in
this focal plane. C-I These images represent sections of
retinas showing the cell types (arrows) in which the CD44-GFP transgene
was active (C photoreceptors, D horizontal cells, E
amacrine cells, F-H Müller cells, I ganglion cells).
Section shown in F was counterstained with an antibody against
chicken carbonic anhydrase II (CAII), a marker for Müller cells (G).
The
merged image (H) shows that the GFP-positive cells also
expressed carbonic anhydrase II. VIM: J, K Photographs
of a whole mount of a retina treated with pFM-VIM-GW and viewed from
the photoreceptor side of the whole mount. J Numerous
GFP-positive horizontal cells were detected in the transduced retina
(arrow). K Enlargement of the region in image J (box) that
contains GFP-positive horizontal cells (arrow). L This image
was produced by re-photographing the boxed region shown in K using a
focal plane just below that shown in K. Müller cell bodies are
the predominant cell type observed in this image plane (asterisk). The
horizontal cell indicated in J, K, and L by the
arrow is the same cell. M,N Images of sections of the retinal
whole mount shown in J and K. GFP-positive horizontal (M,
arrow),
Müller (M, asterisk), and photoreceptor (N, ONL)
cells were detected in several sections. O-Q A section
containing GFP-positive cells located in the INL (O, arrow) was
counterstained with an antibody against chicken carbonic anhydrase II (P).
The
merged image (Q) shows that the GFP-positive cells also
expressed carbonic anhydrase II. GFAP: R, S Images of a
whole mount of a 5-week old GUCY1*B chicken retina that had been
treated with pFM-GFAP-GW on E2 and photographed from either the
photoreceptor (R) or the vitread (S) side of the whole
mount. The pattern of GFP localization observed in these whole mounts
suggested that the cells expressing the GFAP-GFP transgene were Müller
cells. T-V Sections of the transduced retinas showed that the
cell bodies of the GFP-positive cells observed in R and S were located
in the INL (T). Immunostaining of these sections with an
antibody against chicken carbonic anhydrase II (U) revealed that
the GFP-positive cells also expressed carbonic anhydrase II (V).
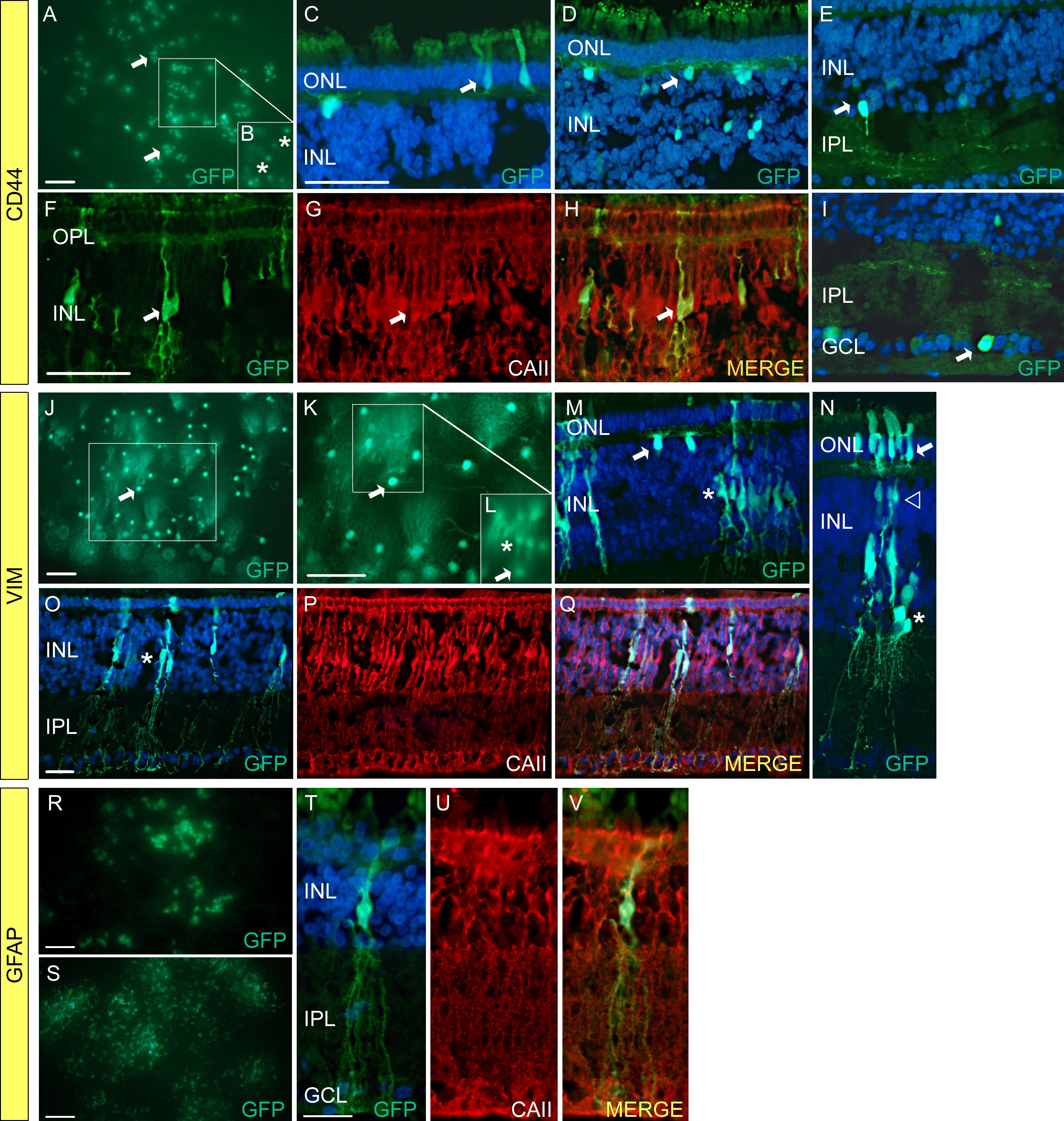
 Figure 2 of Semple-Rowland, Mol Vis 2010; 16:916-934.
Figure 2 of Semple-Rowland, Mol Vis 2010; 16:916-934.  Figure 2 of Semple-Rowland, Mol Vis 2010; 16:916-934.
Figure 2 of Semple-Rowland, Mol Vis 2010; 16:916-934. 