Figure 2. IL-8 promoter binding activity
of NFκB subunits is reduced by specific inhibitors. A: EMSA was
done using 10 μg nuclear extracts after 1 h of viral (V) or mock (M)
treatment in cells pretreated with signaling inhibitors SB203580 (SB:
p38), SP600125 (SP: JNK), PD98059 (PD: ERK), or PP2 (Src). Binding of
p65 to the IL-8 promoter appeared greater in viral-infected cells (lane
1) as compared to mock-treated cells (lane 5), and was reduced in cells
pretreated with SB (lane 9) and PP2 (lane 21), but not with SP (lane
13) or PD (lane 17). Supershift assays with NFκB p65, p50 and cREL
revealed more shift in viral-infected and SP-treated cells (lanes 2–4
and 14–16), but reduced shift or no shift in mock-treated (lanes 6–8)
or other inhibitor-treated cells: SB (lanes 10–12), PD (lanes 18–20),
and PP2 (lanes 22–24). B: Graphic representation of five
independent EMSA experiments. Overall binding was significantly greater
in viral-infected cells as compared to mock-treated cells (p<0.0001,
ANOVA). IL-8 promoter binding of NFκB subunits was significantly
reduced by all four inhibitors (p<0.05). Antibody binding/shift on
the IL-8 promoter was not observed in mock-treated cells or in cells
treated with any inhibitor prior to infection (p>0.05). C:
EMSA done for MCP-1 at both 1 and 4 h post infection. Viral infection
induced binding/shift relative to mock infection only at 4 h post
infection (lanes 1 and 5). Binding at 4 h post infection was reduced in
mock-treated and inhibitor-pretreated groups (lanes 5–24). At 4 h post
infection, antibody to p50 and cREL reduced binding (lanes 3 and 4),
but antibody to p65 (lane 2) did not. D: Graphical
representation of five independent EMSA experiments for MCP-1 at 4 h
post infection. Overall binding was significantly greater in
viral-infected cells as compared to mock-treated cells at 4 h post
infection (p<0.0001, ANOVA). Binding was reduced in viral-infected
cells only by SP (p<0.05). No shift was seen in mock-infected cells
due to addition of antibody. In viral-infected cells, a statistically
significant shift was seen with p50 and cREL (p<0.05), but not with
p65. In viral-infected inhibitor-treated cells only SP reduced binding
(p<0.05).
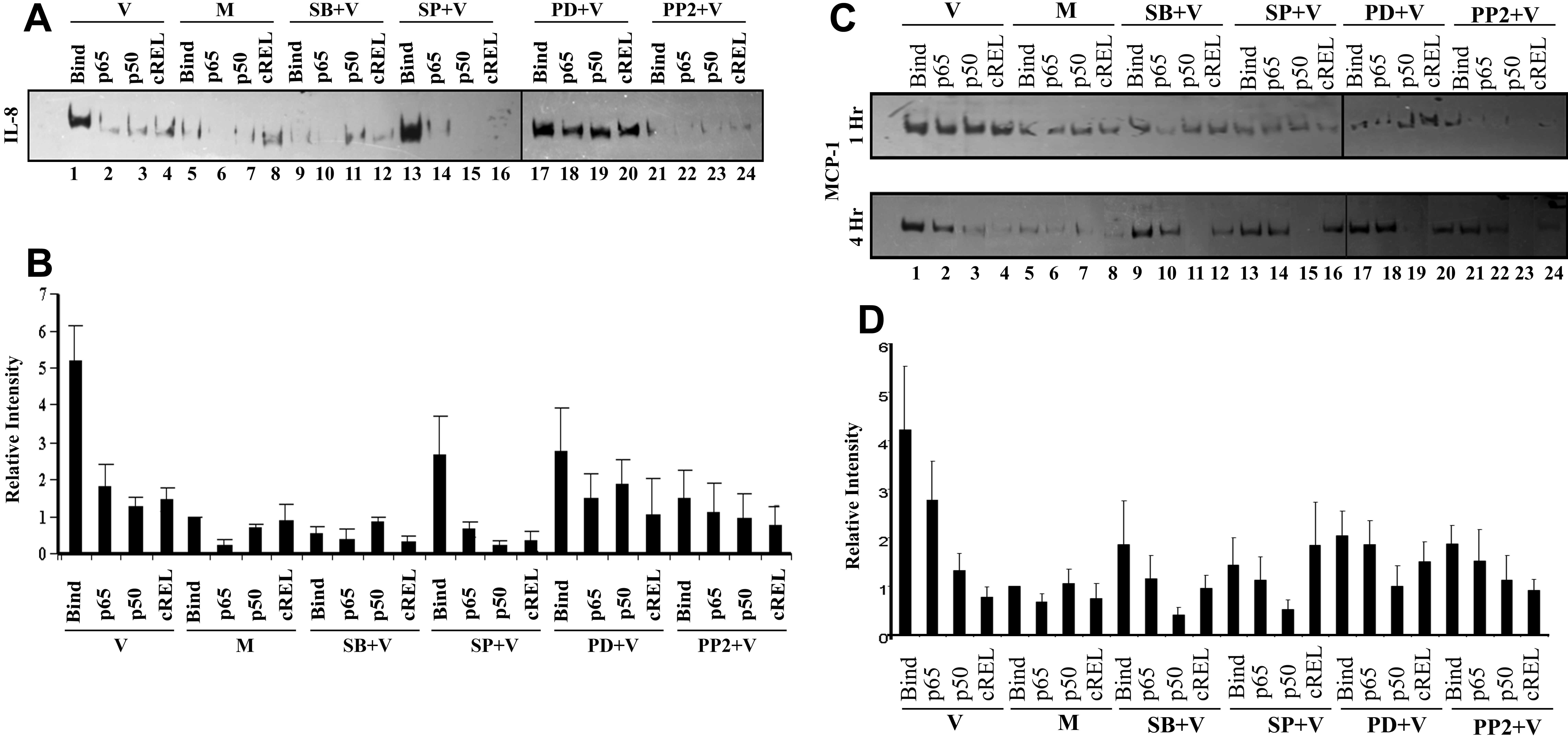
 Figure 2 of Rajaiya, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2879-2889.
Figure 2 of Rajaiya, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2879-2889.  Figure 2 of Rajaiya, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2879-2889.
Figure 2 of Rajaiya, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2879-2889. 