Figure 4. Trimethylamine N-oxide treatment degraded reduced G98R αA-crystallin (CRYAA) via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. A: Reduced level of Tx-insoluble G98R CRYAA after TMAO (100 mM, 2 days) was reversed by MG132 (10 μM, 8 h). MG132 alone further
increased Tx-insoluble mutant protein. B–E: Cytoplasmic G98R CRYAA aggregates were reduced after TMAO treatment (C). Intense aggregation was observed in cells treated with TMAO and MG132 (E), MG132 only (D), and untreated cells (B). F: Percentages of cells with CRYAA aggregates after treatments. G: Null changes of Tx-insoluble G98R CRYAA after treatment with 3-MA, unlike that of MG132 treatment. The asterisk indicates
a p<0.05 by independent Student t test. Tx: Triton X-100; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; UPR: unfolded protein response; PERK: phosphorylated protein kinase-like
ER-kinase; BiP: binding immunoglobulin protein; CHOP/GADD153: C/EBP homologous protein/growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible
gene 153; WT: wild-type.
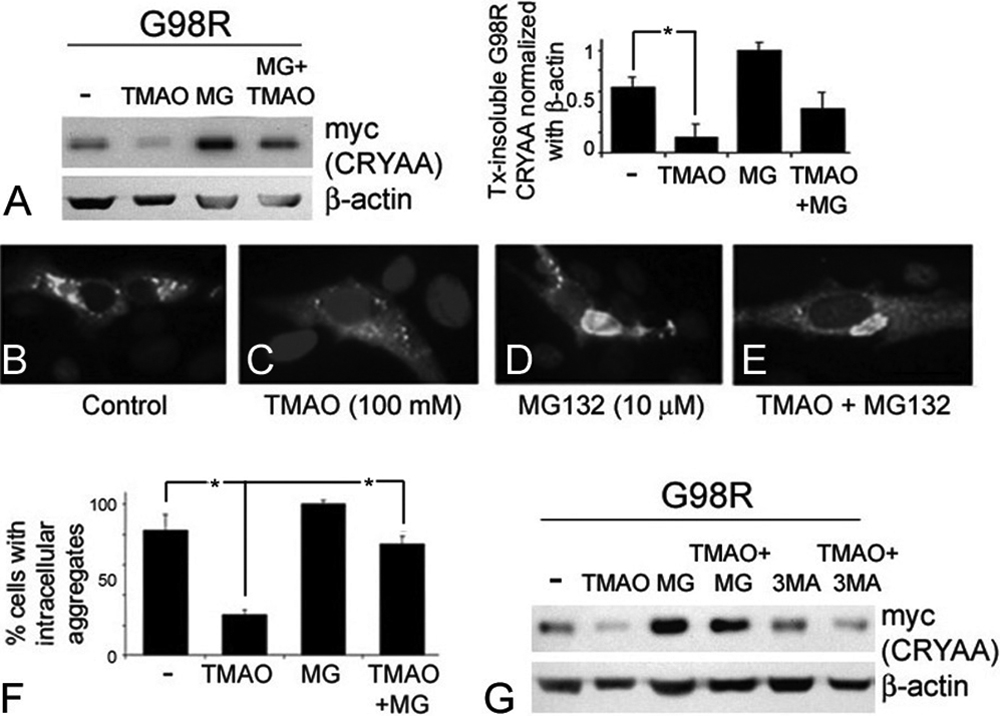
 Figure 4 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.
Figure 4 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.  Figure 4 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.
Figure 4 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840. 