Figure 1. G98R αA-crystallin was TritonX-100-insoluble and formed aggregates inside cells. A: Triton X-100 (Tx) solubility assay of wild-type (WT) and cataract-causing mutant CRYAA in B3 cells by western blotting of
myc (detecting CRYAA), housekeeping GAPDH, and β-actin. The band densitometry analysis showed the drastic reduction of Tx
solubility of G98R CRYAA when compared to WT or other mutants. B: Direct sequencing of pHis/myc-CRYAAG98R to indicate the base change at c.292G>A. C–L: Confocal double immunofluorescence of WT and G98R CRYAA in B3 cells. C and D: A lower magnification to show the expression of WT (C) and G98R CRYAA (D) in cells. E–H: G98R CRYAA (myc staining in F) formed intracellular aggregates and was intensely co-distributed with PDI (G) in the overlay image (H). I–L: WT CRYAA (J, myc staining) was diffusely distributed in cytoplasm and had only mild co-distribution with PDI (K) in overlay image (L). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue, E and I). Scale bars: 10 μm (C–L). PDI: protein disulphide isomerase; DAPI: 4'-6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
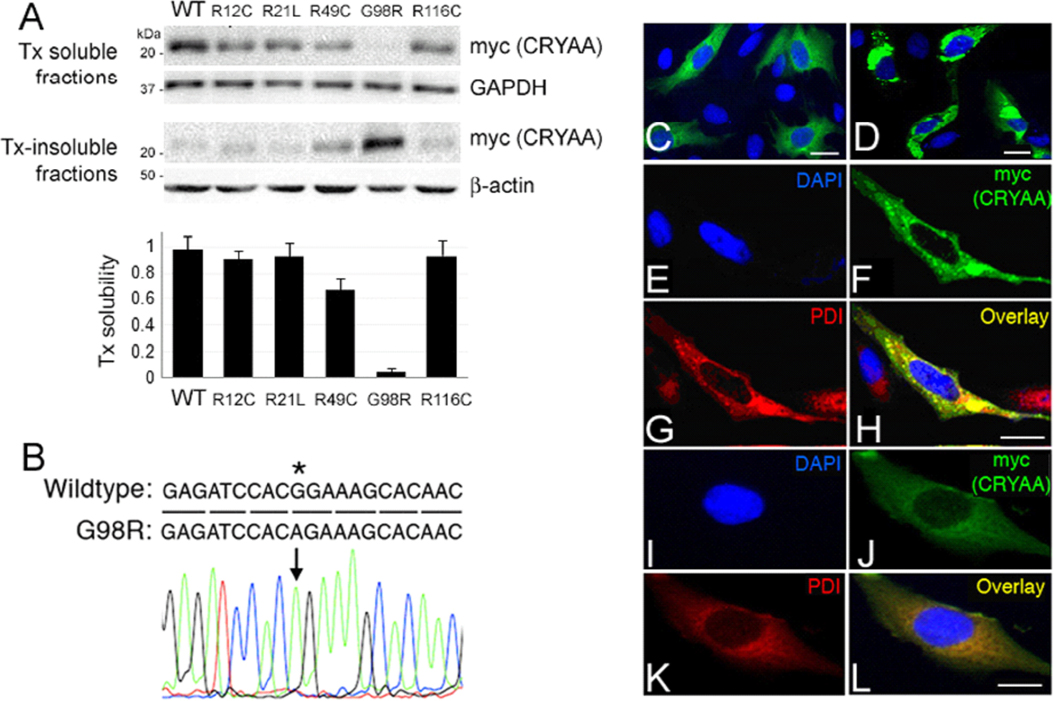
 Figure 1 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.
Figure 1 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.  Figure 1 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840.
Figure 1 of
Gong, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2829-2840. 