Figure 1. RPC treatment with different culture conditions resulted in morphological changes. RPC neurospheres were dissociated into
single cells and grown under five culture conditions. In each case, some cells attached to the surface of the flask and extended
processes (yellow arrows point to examples), while others formed clusters that often extended beyond the plane of focus (red
asterisks mark examples). For purposes of analysis, attention was directed to the former as opposed to the latter. A, B: Under standard proliferation conditions (EGF), RPCs continued to maintain the appearance of undifferentiated neuroectodermal
cells, singly or in clusters, and either adhered to the uncoated flask or floated in the culture medium. Some adherent cells
extended short processes. C, D, G, H: With FBS or EGF+FBS treatment, most cells were adherent and gave out short processes by the first day, some cells becoming
large with polygonal morphology (C, G); with time, most cells exhibited two or more long processes which formed a network between cells by day 7 (D, H), and these processes were of finer caliber with FBS treatment (D) than was observed with EGF+FBS (H). E, F: After CNTF treatment, most cells exhibited short processes on day 1 (E) and formed long neurite-like processes by day 7 (F). I, J: In EGF+CNTF treatment, some cells had short processes from day 1 to day 7, whereas long processes were not observed.
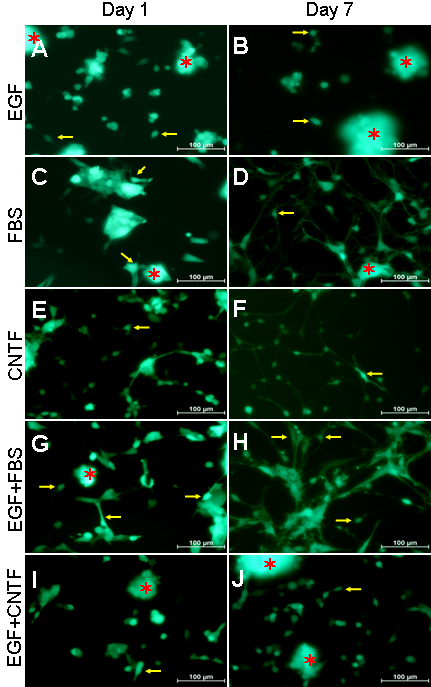
 Figure 1 of
Gu, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2111-2122.
Figure 1 of
Gu, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2111-2122.  Figure 1 of
Gu, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2111-2122.
Figure 1 of
Gu, Mol Vis 2009; 15:2111-2122. 