Figure 2. IVCM images of rabbit ocular
surface (cornea, limbus, and conjunctiva). IVCM images of rabbit ocular
surface at H4 after BAC+latanoprost (A), BAC+travoprost
(B), BAC+bimatoprost (C), PBS (D), and
LCEm (E) instillations, of the superficial epithelium (line 1),
the basal epithelium (line 2: 10–15 μm from the superficial epithelium
layer), the limbus (line 3: about 20–30 μm from the superficial
epithelium layer), and the conjunctival substantia propria (line 4:
50–80 μm from the superficial epithelium layer). BAC+Latanoprost
and BAC+travoprost-treated eyes showed the greatest damage
in the epithelium and the greatest inflammatory cell infiltration in
the basal epithelium and limbus. BAC+Bimatoprost induced
slight inflammation in the basal epithelium. These three BAC-containing
eye drops induced inflammatory cells rolling in conjunctival blood
vessels. PBS and LECm did not induce any obvious ocular surface
microstructure damage. The scale bar indicates 100 μm. IVCM scores (F)
for the five tested groups. BAC+Latanoprost and BAC+travoprost
presented the highest IVCM toxic score at H4 and D1, with intermediate
results for BAC+bimatoprost. The toxicity of LECm was less
than that of the three BAC-containing commercial prostaglandins with no
significant difference with the PBS group at all time points. The
asterisk indicates a p<0.002 compared with BAC+latanoprost.
The sharp indicates a p<0.002 compared with BAC+travoprost
and the filled diamond indicates a p<0.05 compared with BAC+bimatoprost.
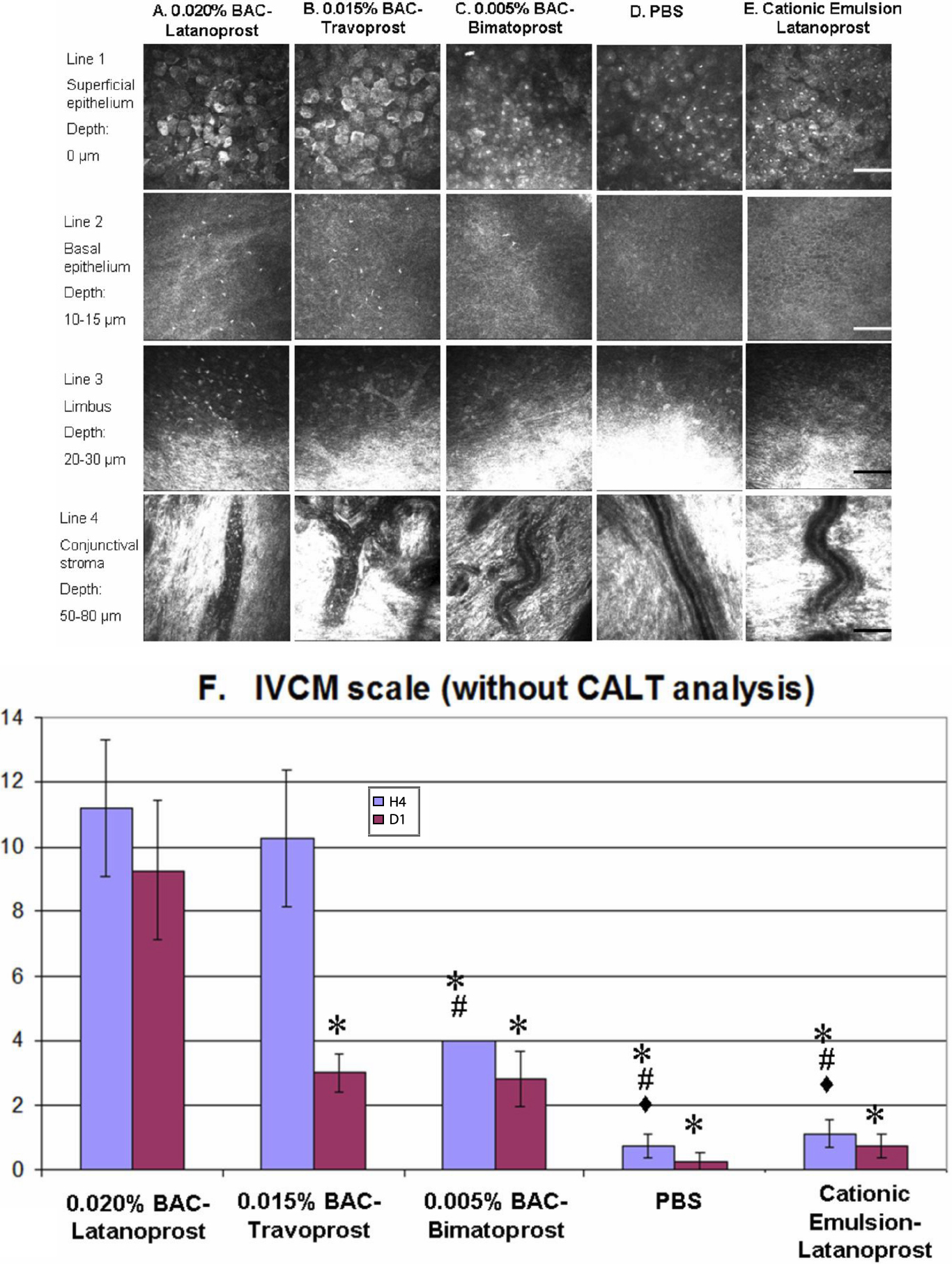
 Figure 2 of Liang, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1690-1699.
Figure 2 of Liang, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1690-1699.  Figure 2 of Liang, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1690-1699.
Figure 2 of Liang, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1690-1699. 