Figure 9. Schematic showing imatinib
dysregulation of PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling in RGCs. PI 3-kinase is a
heterodimer consisting of p85 regulatory and p110 catalytic subunits.
Imatinib inhibition of PDGFR tyrosine kinase abrogates PDGF-induced
PDGFR tyrosine phosphorylation, p85 regulatory subunit recruitment, PI
3-kinase activity, and the phosphorylation of downstream effectors such
as Akt, GSK-3β, and p70S6kinase. In contrast, imatinib exposure
maintains insulin receptor-mediated IRS-associated PI 3-kinase activity
and the downstream phosphorylation of Akt, GSK-3β, and p70S6kinase.
Thus, an imbalance between receptor- and IRS-associated PI 3-kinase
activity attenuates coordinated increases in phosphatidylinositol
3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) lipids. The resultant diminutions in the
overall phosphorylation of Akt, GSK-3β, and p70S6kinase increase the
propensity toward apoptotic cell death.
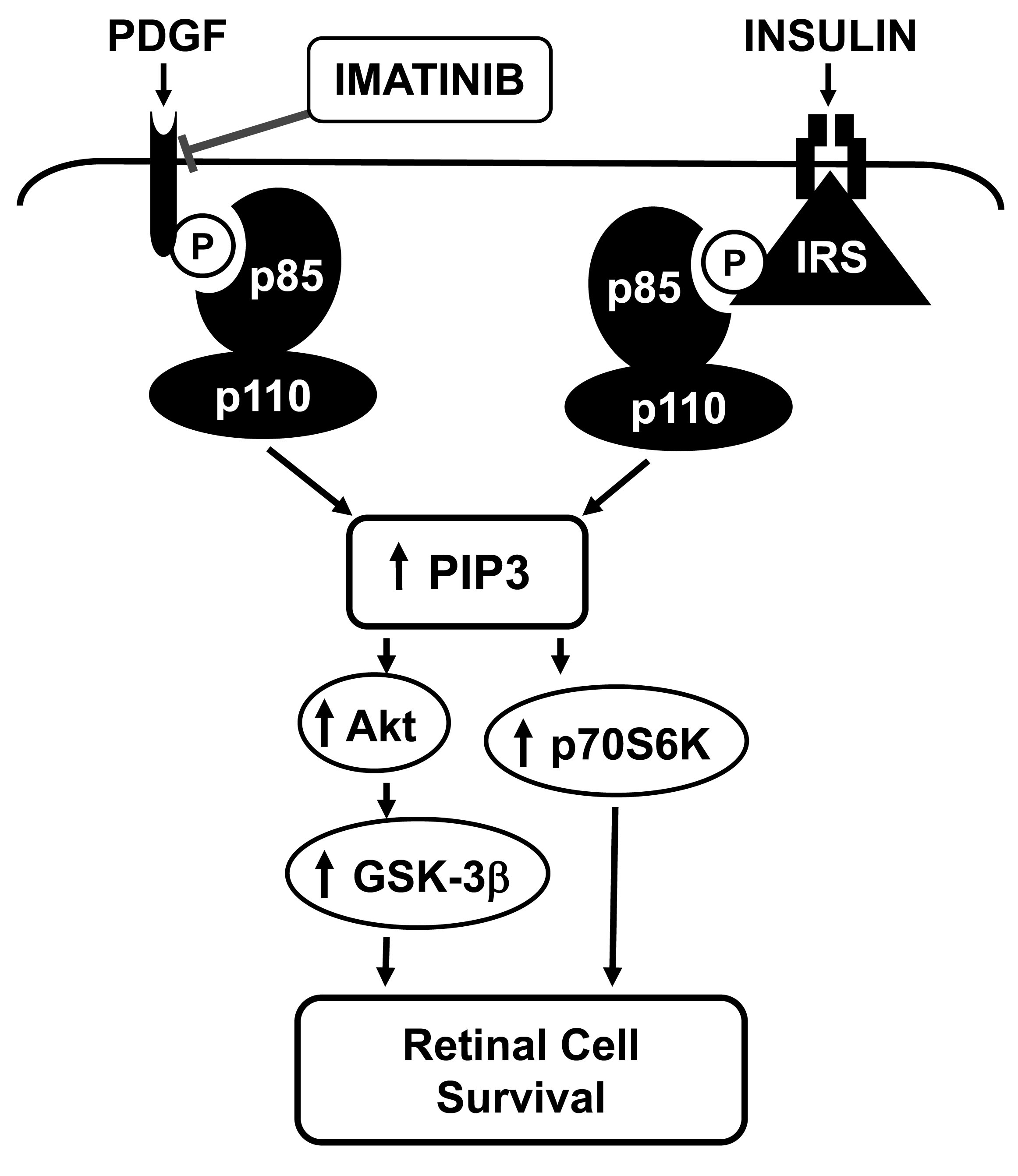
 Figure 9 of Biswas, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1599-1610.
Figure 9 of Biswas, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1599-1610.  Figure 9 of Biswas, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1599-1610.
Figure 9 of Biswas, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1599-1610. 