Figure 1. CERKL isoform structure. A:
The diagram shows the genomic exon-intron structure of the CERKL
gene with the initiation and stop codons. The position of the nonsense
mutation (R257X) identified in RP families as well as the splicing
junctions resulting in isoforms a, b, c, and d are indicated. Asterisks
indicate the position of the rare GC-splicing donor sites. B:
The mature CERKL mRNA isoforms, indicating the relative
position of the encoded DAG kinase and putative PH domains, are
depicted. Note that exon 4b (isoform b, in gray) is located well within
the DAG kinase domain, while isoforms c and d lack this domain. Grey
small double arrows indicate the position of the primers used for
specific isoform RT–PCR analyses (see Methods). The figure is drawn to
scale except for the introns depicted with a broken line.
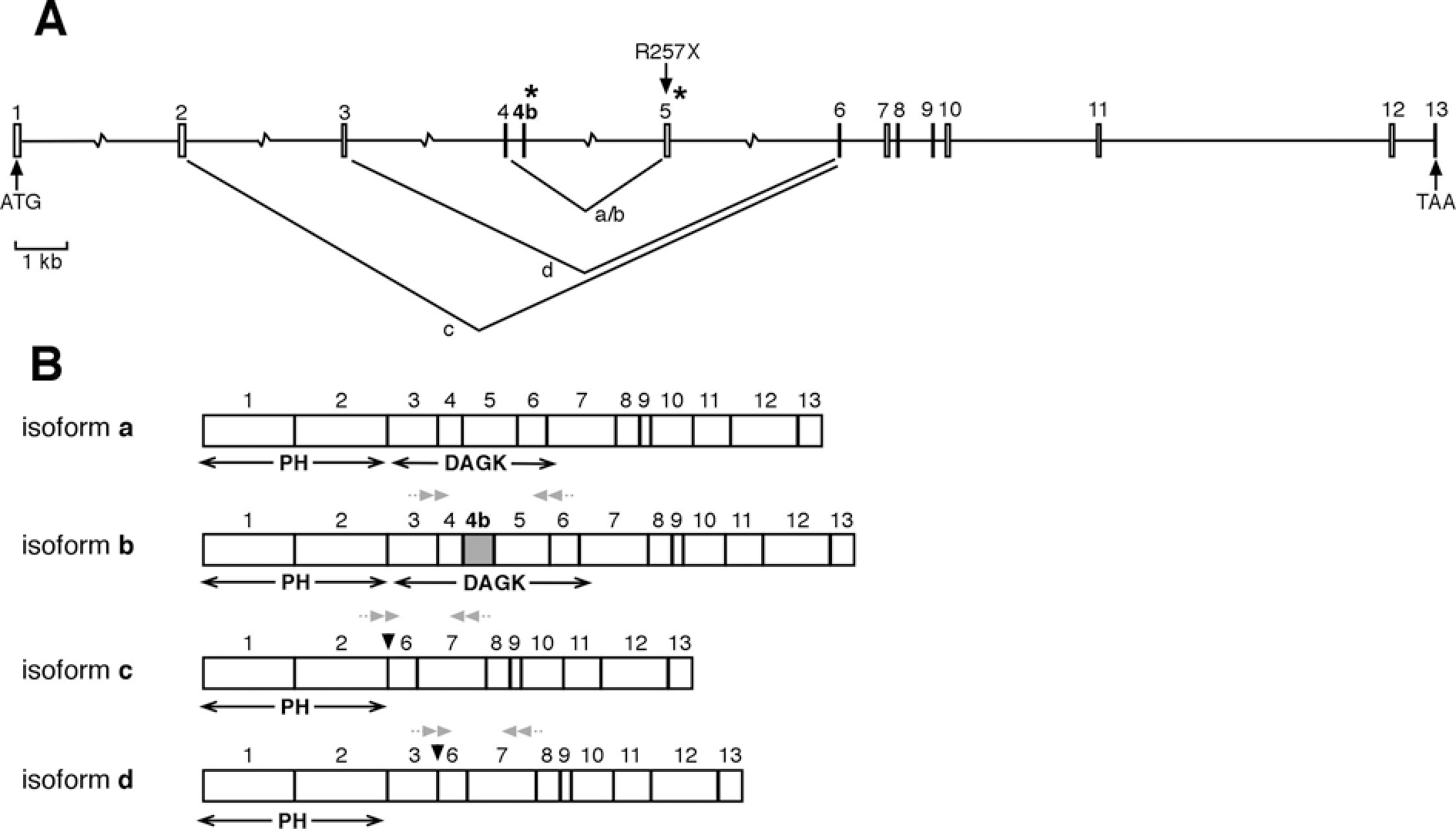
 Figure 1 of Tuson, Mol Vis 2009; 15:168-180.
Figure 1 of Tuson, Mol Vis 2009; 15:168-180.  Figure 1 of Tuson, Mol Vis 2009; 15:168-180.
Figure 1 of Tuson, Mol Vis 2009; 15:168-180. 