Figure 1. Representative retinal cross sections of C57BL/6J mice after subretinal delivery of AAV-9.RSV.AP. Panels A and B show global view of AAV-9 transduction in adult (3-month-old) C57BL/6J mouse eyes at 5 weeks after subretinal AAV-9.RSV.AP injection (A) and HEPES buffer injection (B). Yellow arrows indicate the injection sites. Panels C and D show the enlarged retinal sections of the boxed regions in A and B, respectively. Panels E and F are representative retinal sections obtained from young (3-week-old) mice at 3 weeks after subretinal injection. E shows the area close to the injection site while F shows an area distant from the injection site. Panels G and H are representative retinal sections obtained 5 weeks after subretinal injection in a 12-month-old mouse. G shows the area close to the injection site while H shows an area distant from the injection site. Similar AP expression pattern can be seen in all AAV-9.RSV.AP-injected eyes.
Dark blue AP staining is readily visible throughout the entire retina. The RPE, ONL, INL, and RGC layers show punctate staining.
AP-positive Müller cells display staining across majority of the retina thickness from the ONL to the RGC layers. AP expression
in the OPL and the IPL layers is prominent. Although staining in the region distant from the injection site is weaker, AP
expression is widespread in the two synaptic layers. Representative photomicrograph from a HEPES buffer mock-infected eye
shows no evidence of AP expression. Yellow arrows mark the injection site; red arrows indicate outer plexiform layer (OPL);
red arrowheads indicate inner plexiform layer (IPL); green arrows indicate Müller cells; yellow arrowheads indicate RPE. Abbreviations:
alkaline phosphatase (AP), inner nuclear layer (INL), outer nuclear layer (ONL), retinal ganglion cell (RGC), retinal pigment
epithelium (RPE).
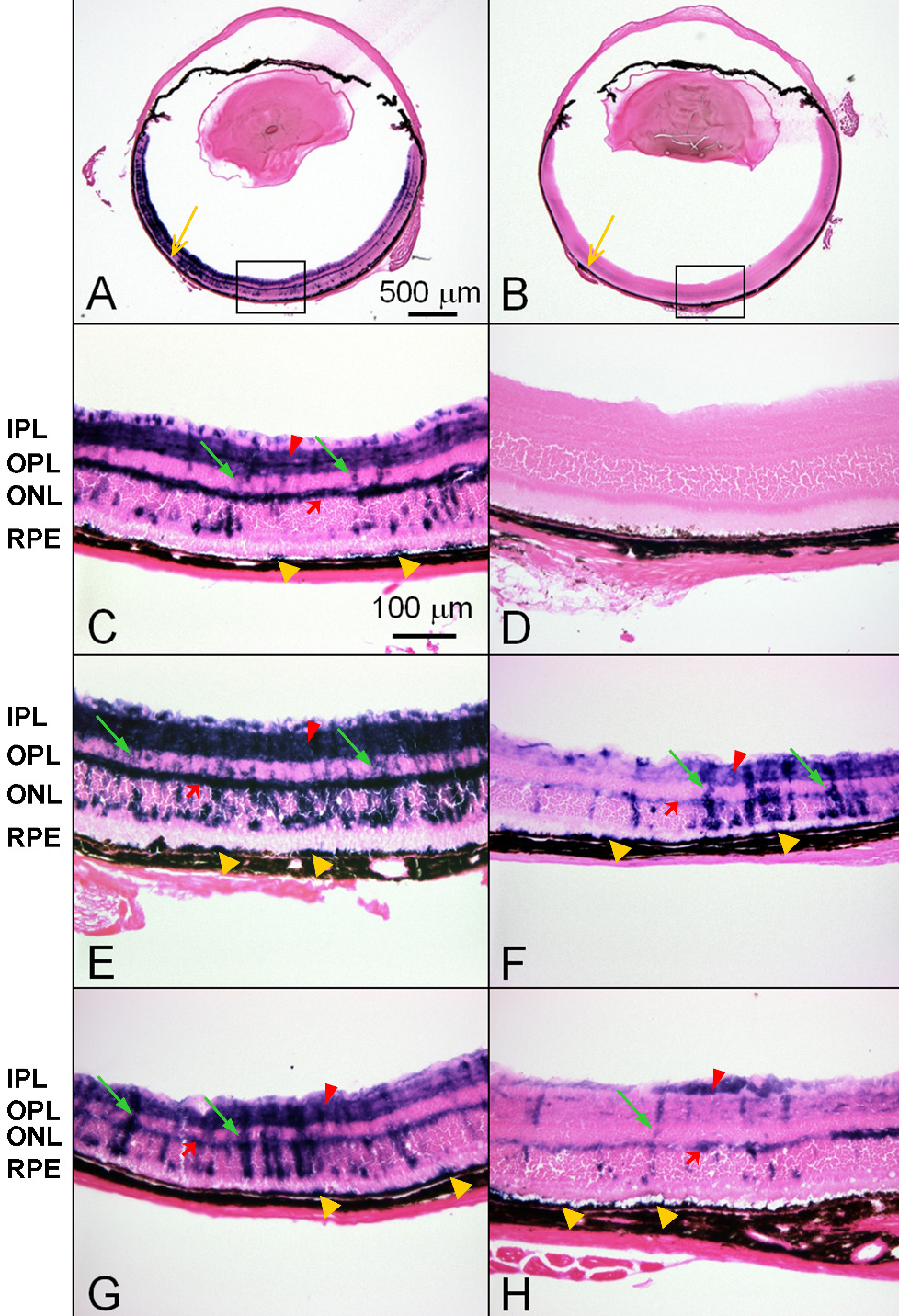
 Figure 1 of
Lei, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1374-1382.
Figure 1 of
Lei, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1374-1382.  Figure 1 of
Lei, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1374-1382.
Figure 1 of
Lei, Mol Vis 2009; 15:1374-1382. 