Figure 3. Mutation analysis of CRYBB1.
A: The sequence chromatogram of a wild type allele shows
glutamine (CAG) at codon 223. B: The sequence chromatogram of a
mutant allele shows a heterozygous C→T transition that changed
glutamine 223 to a stop codon (TAG). C: RFLP analysis
illustrates that the mutation, Q223X, introduces a new BfaI site. This
mutation-specific BfaI digestion pattern co-segregated with the disease
phenotype. Squares and circles symbolize males and females,
respectively. The clear and shaded symbols denote unaffected and
affected individuals, respectively. D: Multiple sequence
alignment of the fourth Greek key motif of CRYBB1 is shown from Homo
sapiens (codons 191–233), Mus musculus, Rattus
norvegicus, Bos Taurus, Cavia porcellus, Gallus
gallus, Danio rerio, and Xenopus tropicalis. The
Gln223 residue is highly conserved. “X” indicates premature
chain-termination mutations in human CRYBB1 (Q223X).
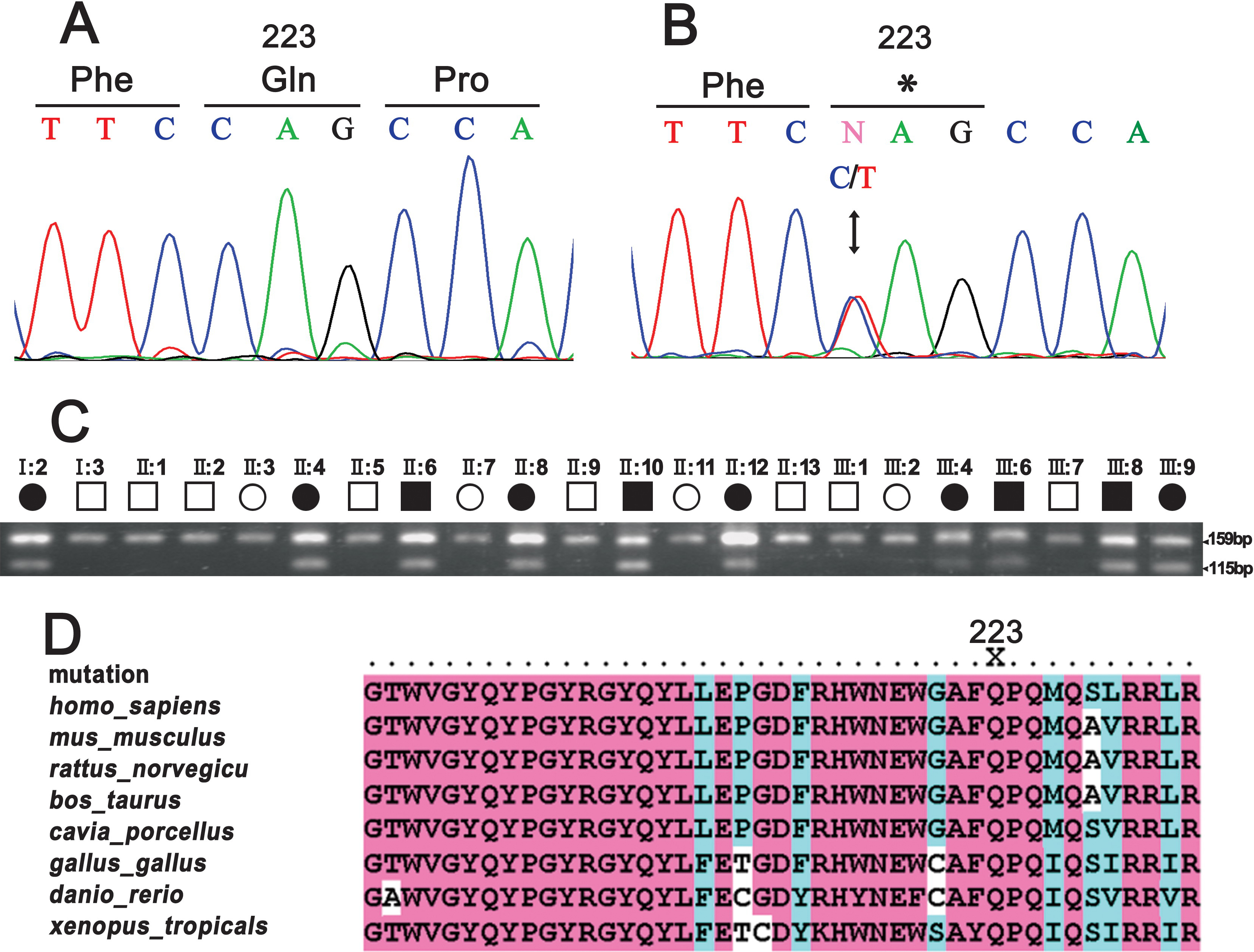
 Figure 3 of Yang, Mol Vis 2008; 14:727-731.
Figure 3 of Yang, Mol Vis 2008; 14:727-731.  Figure 3 of Yang, Mol Vis 2008; 14:727-731.
Figure 3 of Yang, Mol Vis 2008; 14:727-731. 