Figure 5. Quantum dots in the whole eye
after subretinal injection. The mouse was sacrificed 24 h after
injection of the quantum dots. This length of time allowed the three
blebs to resorb and the neural retina to return to contact with the RPE
sheet. Cryosections were collected and counterstained with DAPI (to
stain all nuclei blue). A: Shown is a composite of numerous
images originally collected with a 20X objective. Images were fused in
Photoshop with the Photomerge tool (Adobe Systems Inc., San Jose, CA).
The cornea was lanced at clock face position 11, and a small number of
quantum dots can be seen in the corneal stroma at the wound site. The
retina was punctured between clock face positions 4 and 5. The bright
yellow represents intense fluorescence of highly concentrated quantum
dots located in the subretinal space. There is a continuous gradient of
color from bright yellow to purple, indicating successively less
fluorescence of the quantum dots in proportion to their concentration.
The quantum dots were confined specifically to the subretinal bleb. The
scale bar represents 500 μm. B: A few dots were found in the
optic nerve head and interstitial spaces in the optic nerve, as
indicated by the red and purple colors. C: A distinctive
gradient of color from bright yellow to purple is illustrated from
right to left within the confines of the subretinal space. The
comparative absence of any color other than blue-stained nuclei in the
section suggests that there was no break in the RPE sheet or tear in
the neural retina during subretinal injection. D: Close-up
reveals quantum dots phagocytosed within the RPE cells. Quantum dots
(red) were detected at the level of the RPE cells, and the dots
surround the Yo-Pro-1 stained nuclei (green) of the RPE cells. This
location indicated that the quantum dots were internalized into the RPE
cells. The scale bar represents 50 μm.
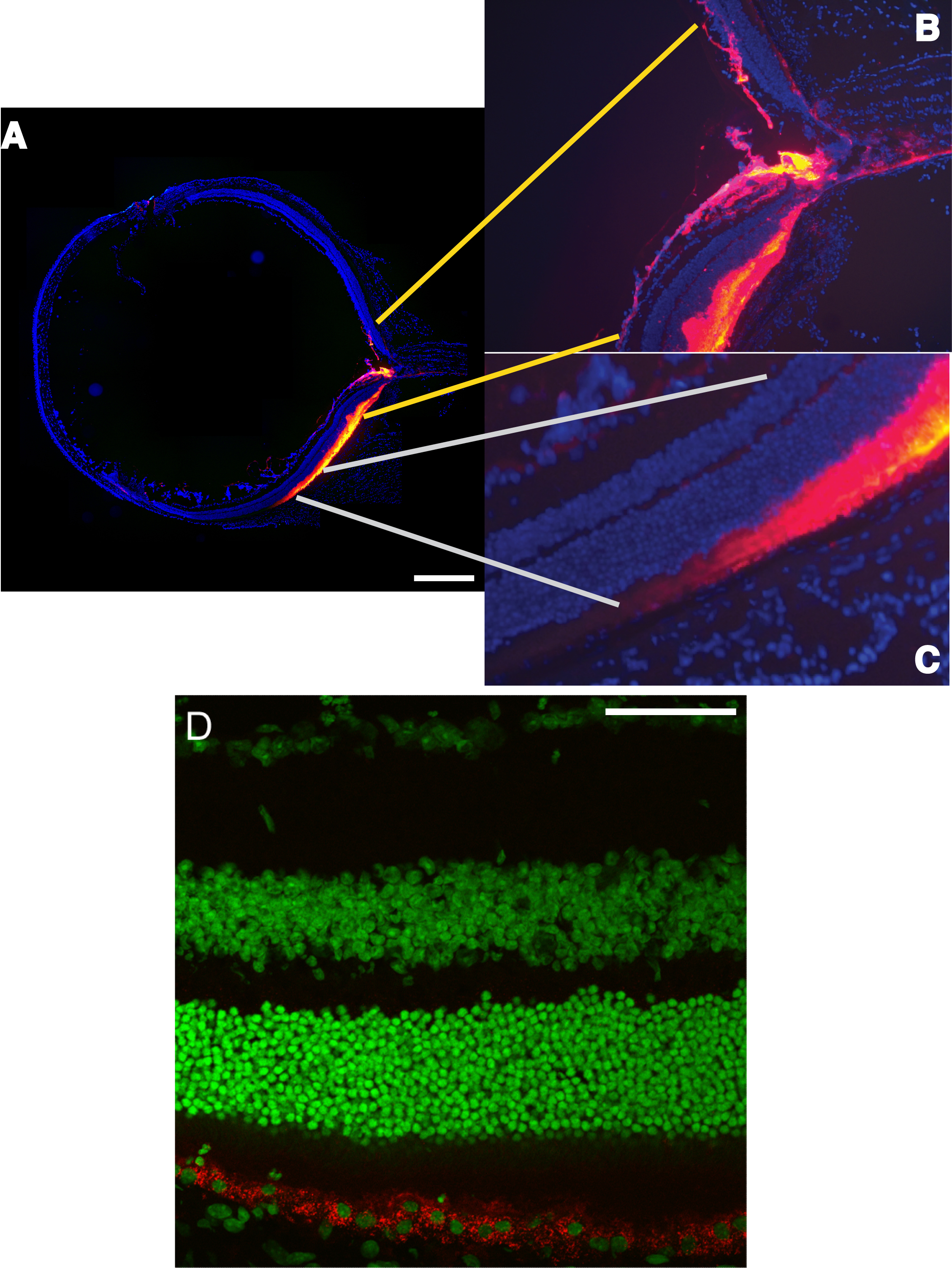
 Figure 5 of Johnson, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2211-2226.
Figure 5 of Johnson, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2211-2226.  Figure 5 of Johnson, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2211-2226.
Figure 5 of Johnson, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2211-2226. 