Figure 3. Prox1 interacted with PCNA
through the PIP box. A: Sequence alignment of the PIP box-like
sequence (red) in vertebrate Prox1 and its invertebrate homologs. B:
The sequence of the PIP box found in Prox1 aligned with a series of
mutants created in the HD/PD of Prox1 to test its role in PCNA-Prox1
interactions. C: The resulting PIP mutants were transformed
into AH109 and mated with Y187 containing the original PCNA clone
(amino acids 167-261). The work plates were made by restreaking the
colonies obtained on the original DO plates on both DO (testing for the
presence of the plasmids) and QDO plates (to test for protein-protein
interactions). The wildtype HDPD interacted with PCNA (2) and the
mutants LF (3) and ELF (4) still had the ability to bind. In contrast,
mutants LFF (5) and QLFF (6) could not survive on QDO plates suggesting
that they did not interact with the carboxyl-terminus of PCNA. The P53-
SV40-T antigen interaction (1) was used as a positive control. D:
The PIP mutants were transformed into AH109 and mated with Y187
containing the C+ PCNA clone which includes the IDCL (amino acids
115-261). The work plates were made by restreaking the colonies
obtained on the original DO plates on both DO (to test for the presence
of the plasmids) and QDO plates (to test for protein-protein
interactions). The wildtype HDPD interacted with PCNA (2) and the
mutants LF (3) and ELF (4) still had the ability to bind. In contrast,
mutants LFF (5) and QLFF (6) could not survive on QDO plates suggesting
that they did not interact with the carboxyl-terminus plus the IDCL of
PCNA. The P53- SV40-T antigen interaction (1) was used as a positive
control.
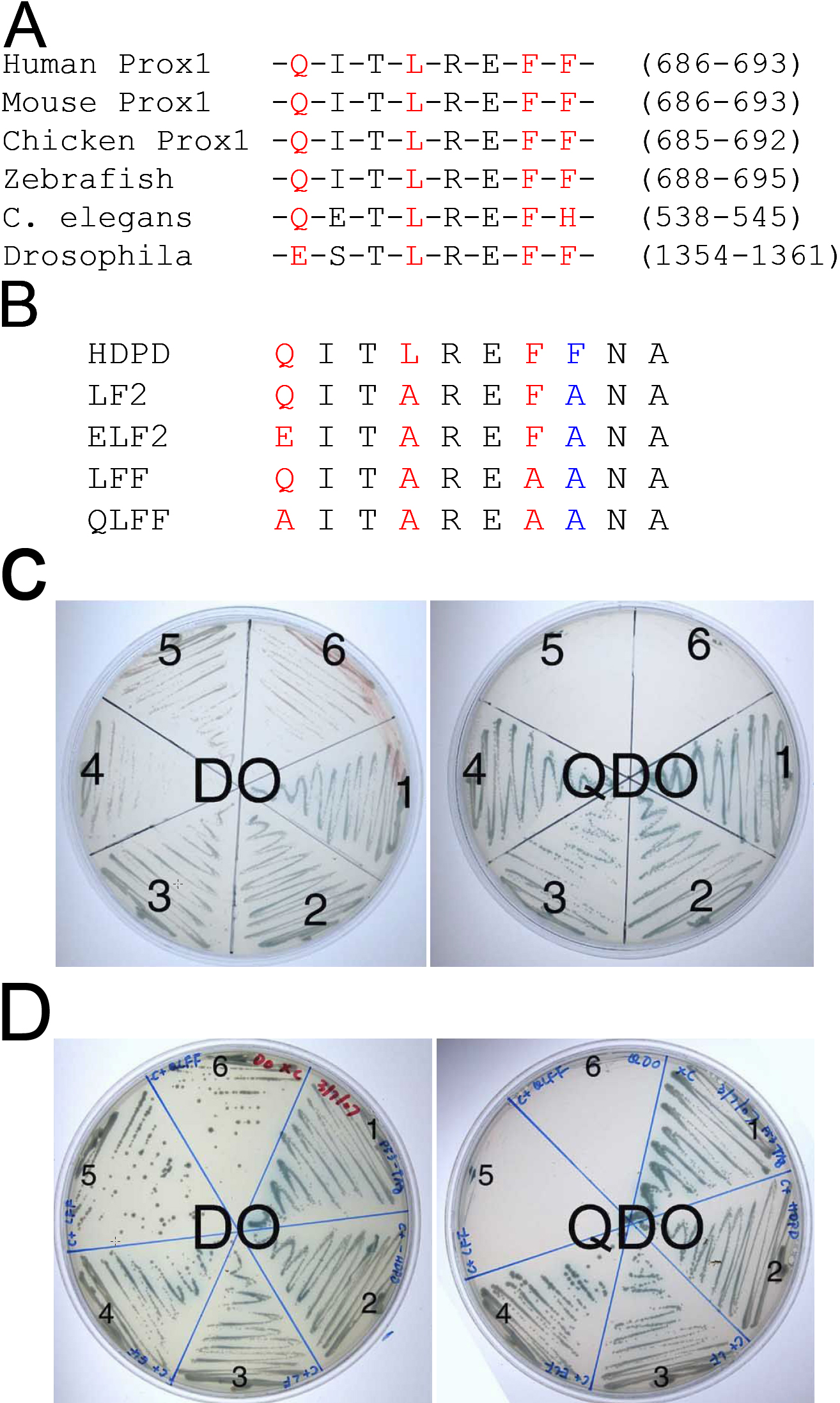
 Figure 3 of Chen, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2076-2086.
Figure 3 of Chen, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2076-2086.  Figure 3 of Chen, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2076-2086.
Figure 3 of Chen, Mol Vis 2008; 14:2076-2086. 