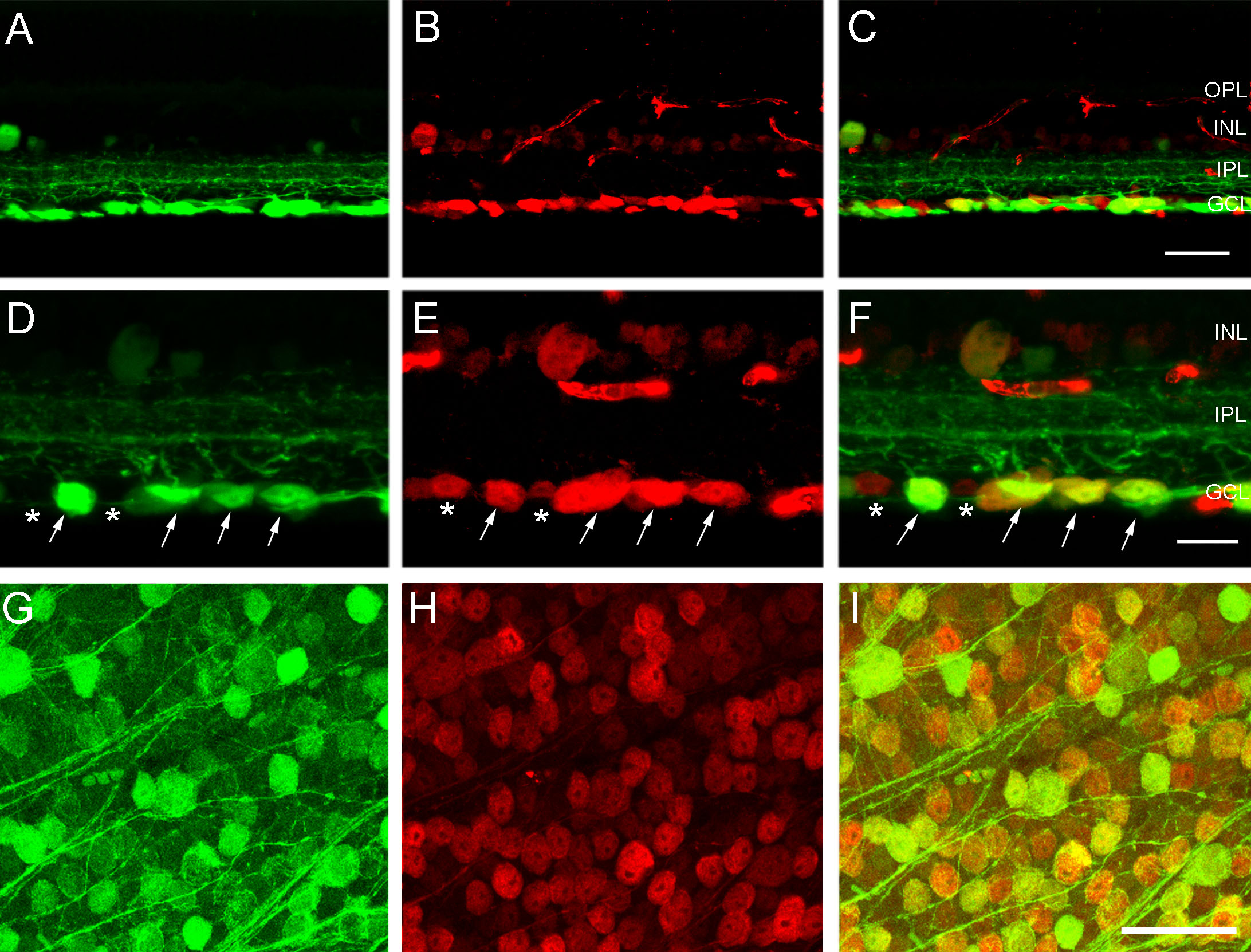
Figure 5. CFP-containing ganglion cells
express NeuN immunoreactivity, a marker commonly used to identify
retinal ganglion cells. A: Transverse section of peripheral
retina shows cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) expression in numerous cell
bodies in the ganglion cell layer (GCL). B: Neuronal nuclei
(NeuN) immunoreactivity is localized in ganglion cell somata in the GCL
(and weak immunoreactivity is in cell bodies in the inner nuclear
layer; INL). C: A merged image of A and B shows
colocalization of CFP expression and NeuN immunoreactivity in most cell
bodies in the GCL. The scale bar for A–C is 45 μm. D: A
higher magnification image shows CFP fluorescence in large ganglion
cells (arrows) in the GCL. E: The same section as in D
shows NeuN immunoreactivity in numerous ganglion cell somata in the GCL
(arrows). The small, weakly NeuN-immunoreactive cells are displaced
amacrine cells (stars). F: A merged image of D and E
shows colocalization of CFP and NeuN immunoreactivity in ganglion cells
(arrows) and a lack of colocalization of CFP and NeuN immunoreactivity
in displaced amacrine cells (stars). The scale bar for D-F
is 25 μm. G: CFP is localized to brightly and weakly
fluorescent cell bodies of various sizes in the GCL. The image is from
a retinal wholemount located 1.5 mm from the optic nerve head in
midperipheral nasal retina. H: The same region as in G
shows NeuN immunoreactivity in numerous cell somata in the GCL,
including ganglion cells and displaced amacrine cells. I: The
merged image of G and H shows colocalization of CFP and
NeuN immunoreactivity in numerous ganglion cell somata in the GCL. The
scale bar for G-I is 45 μm. In C and F
inner plexiform layer is abbreviated IPL, and outer plexiform layer is
abbreviated outer plexiform layer (OPL).
![]() Figure 5 of Raymond,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1559-1574.
Figure 5 of Raymond,
Mol Vis 2008; 14:1559-1574. 